中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (36): 5811-5815.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0616
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
胫骨横向骨搬移后巨噬细胞促进重度糖尿病足创面的愈合
高 伟,林震迅,镇普祥,陈 炎,邝晓聪,花奇凯
- (广西医科大学第一附属医院骨关节外科,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530021)
Macrophages promote the healing of severe diabetic foot wounds after tibial transverse transport
Gao Wei, Lin Zhenxun, Zhen Puxiang, Chen Yan, Kuang Xiaocong, Hua Qikai
- (Department of Bone and Joint Surgery, the First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi Medical University, Nanning 530021, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
胫骨横向骨搬移术:作为一项治疗糖尿病足的新技术,让患者免去截肢的风险。“胫骨横向骨搬移术”原理来自Ilizarov张力-应力法则。该法则是俄罗斯医学专家Ilizarov于20世纪50年代创立的肢体再生与功能重建的理论,被公认为近代矫形骨科的第四个里程碑。该法则原理是:生物组织被缓慢牵拉时会产生一定的张力,可刺激组织再生和活跃生长。人的骨骼和人体的上皮组织、结缔组织一样,具有很大的再生潜力和可塑性,给骨骼一个合适的应力性牵拉,骨骼及其附着的肌肉、筋膜、血管、神经就会同步生长。
胫骨横向骨搬移前后局部创面巨噬细胞不同亚型的分布、计数及其比例比较:可以认识胫骨横向骨搬移术可减轻由巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足创面局部炎症,促进创面的愈合。
文题释义:
胫骨横向骨搬移术:作为一项治疗糖尿病足的新技术,让患者免去截肢的风险。“胫骨横向骨搬移术”原理来自Ilizarov张力-应力法则。该法则是俄罗斯医学专家Ilizarov于20世纪50年代创立的肢体再生与功能重建的理论,被公认为近代矫形骨科的第四个里程碑。该法则原理是:生物组织被缓慢牵拉时会产生一定的张力,可刺激组织再生和活跃生长。人的骨骼和人体的上皮组织、结缔组织一样,具有很大的再生潜力和可塑性,给骨骼一个合适的应力性牵拉,骨骼及其附着的肌肉、筋膜、血管、神经就会同步生长。
胫骨横向骨搬移前后局部创面巨噬细胞不同亚型的分布、计数及其比例比较:可以认识胫骨横向骨搬移术可减轻由巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足创面局部炎症,促进创面的愈合。
.jpg) 文题释义:
胫骨横向骨搬移术:作为一项治疗糖尿病足的新技术,让患者免去截肢的风险。“胫骨横向骨搬移术”原理来自Ilizarov张力-应力法则。该法则是俄罗斯医学专家Ilizarov于20世纪50年代创立的肢体再生与功能重建的理论,被公认为近代矫形骨科的第四个里程碑。该法则原理是:生物组织被缓慢牵拉时会产生一定的张力,可刺激组织再生和活跃生长。人的骨骼和人体的上皮组织、结缔组织一样,具有很大的再生潜力和可塑性,给骨骼一个合适的应力性牵拉,骨骼及其附着的肌肉、筋膜、血管、神经就会同步生长。
胫骨横向骨搬移前后局部创面巨噬细胞不同亚型的分布、计数及其比例比较:可以认识胫骨横向骨搬移术可减轻由巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足创面局部炎症,促进创面的愈合。
文题释义:
胫骨横向骨搬移术:作为一项治疗糖尿病足的新技术,让患者免去截肢的风险。“胫骨横向骨搬移术”原理来自Ilizarov张力-应力法则。该法则是俄罗斯医学专家Ilizarov于20世纪50年代创立的肢体再生与功能重建的理论,被公认为近代矫形骨科的第四个里程碑。该法则原理是:生物组织被缓慢牵拉时会产生一定的张力,可刺激组织再生和活跃生长。人的骨骼和人体的上皮组织、结缔组织一样,具有很大的再生潜力和可塑性,给骨骼一个合适的应力性牵拉,骨骼及其附着的肌肉、筋膜、血管、神经就会同步生长。
胫骨横向骨搬移前后局部创面巨噬细胞不同亚型的分布、计数及其比例比较:可以认识胫骨横向骨搬移术可减轻由巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足创面局部炎症,促进创面的愈合。摘要
背景:Ilizarov生物学理论——张力-应力法则技术通过生物组织缓慢牵拉产生一定张力可刺激组织的再生和活跃生长。
目的:探究巨噬细胞在胫骨横向骨搬移术促进重度糖尿病足创面愈合的作用。
方法:以2017年12月至2018年1月在广西医科大学第一附属医院骨关节外科行胫骨横向骨搬移治疗的10例重度糖尿病足(Wagner3级及以上)患者为研究对象,在征求患者同意及伦理委员会许可后于治疗前及治疗后1个月取其创面边缘处组织制成组织切片,应用免疫组织化学技术,以CD86单抗标记M1型巨噬细胞,CD163单抗标记M2型巨噬细胞,染色后在高倍镜视野下对阳性细胞进行计数,并应用Image pro plus 6.0软件对图像中的象素点进行采集分析,计算出M1/M2比值的变化。
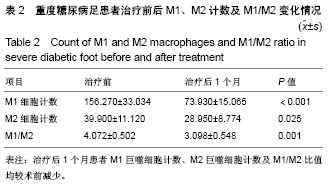
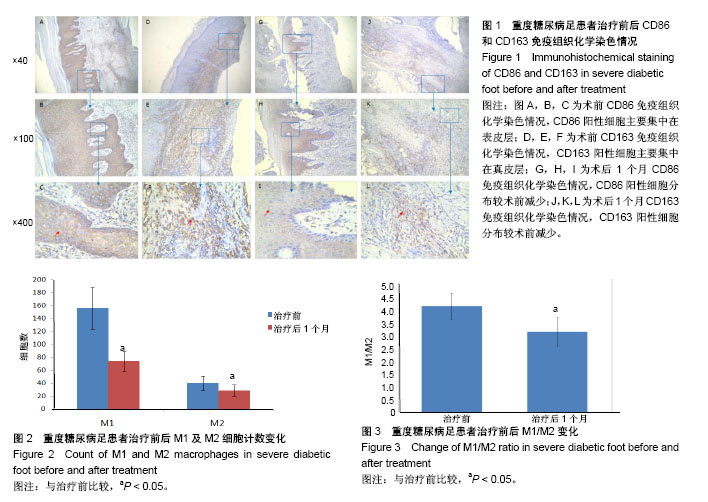
结果与结论:①治疗后1个月患者M1/M2比值显著低于治疗前(P < 0.05);②治疗后CD86、CD163阳性细胞分布和计数均较治疗前减少(P < 0.05);③结果表明,胫骨横向骨搬移可以使巨噬细胞趋向转化为M2巨噬细胞,从而减轻巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足慢性创面炎症,促进愈合。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-5490-7930(高伟)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
胫骨横向骨搬移术:作为一项治疗糖尿病足的新技术,让患者免去截肢的风险。“胫骨横向骨搬移术”原理来自Ilizarov张力-应力法则。该法则是俄罗斯医学专家Ilizarov于20世纪50年代创立的肢体再生与功能重建的理论,被公认为近代矫形骨科的第四个里程碑。该法则原理是:生物组织被缓慢牵拉时会产生一定的张力,可刺激组织再生和活跃生长。人的骨骼和人体的上皮组织、结缔组织一样,具有很大的再生潜力和可塑性,给骨骼一个合适的应力性牵拉,骨骼及其附着的肌肉、筋膜、血管、神经就会同步生长。
胫骨横向骨搬移前后局部创面巨噬细胞不同亚型的分布、计数及其比例比较:可以认识胫骨横向骨搬移术可减轻由巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足创面局部炎症,促进创面的愈合。
文题释义:
胫骨横向骨搬移术:作为一项治疗糖尿病足的新技术,让患者免去截肢的风险。“胫骨横向骨搬移术”原理来自Ilizarov张力-应力法则。该法则是俄罗斯医学专家Ilizarov于20世纪50年代创立的肢体再生与功能重建的理论,被公认为近代矫形骨科的第四个里程碑。该法则原理是:生物组织被缓慢牵拉时会产生一定的张力,可刺激组织再生和活跃生长。人的骨骼和人体的上皮组织、结缔组织一样,具有很大的再生潜力和可塑性,给骨骼一个合适的应力性牵拉,骨骼及其附着的肌肉、筋膜、血管、神经就会同步生长。
胫骨横向骨搬移前后局部创面巨噬细胞不同亚型的分布、计数及其比例比较:可以认识胫骨横向骨搬移术可减轻由巨噬细胞介导的糖尿病足创面局部炎症,促进创面的愈合。