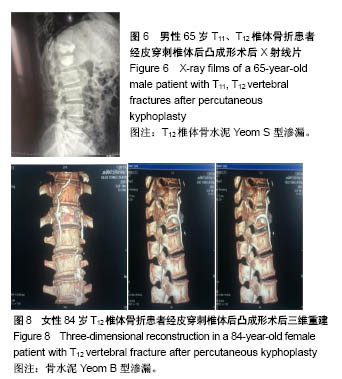
| [1] Rho YJ,Choe WJ,Chun YI.Risk factors predicting the new symptomatic vertebral compression fractures after percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty.Eur Spine J. 2012;21(5):905.[2] Heyde CE,Fekete Z,Robinson Y,et al.Treatment options for problematic thoracic and lumbar osteoporotic fractures.Der Orthopde.2008;37(4):307-320.[3] Farrokhi MR,Alibai E,Maghami Z.Randomized controlled trial of percutaneous vertebroplasty versus optimal medical management for the relief of pain and disability in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Neurosurg Spine.2011;14(5):561.[4] Yeom JS,Kim WJ,Choy WS,et al.Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(85):83-89.[5] 殷渠东,孙振中,顾三军.经皮椎体后凸成形术中减少骨水泥渗漏的策略[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015, 30(9):938-940.[6] 茹选良,蒋增辉,桂先革,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩骨折的非骨水泥渗漏相关并发症[J]. 中国骨伤, 2015, 28(8):763-767.[7] 郑召民.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术灾难性并发症—骨水泥渗漏及其预防[J].中华医学杂志, 2006,86(43): 3027-3030.[8] Li X,Lou X,Lin X,et al.Refracture of osteoporotic vertebral body concurrent with cement fragmentation at the previously treated vertebral level after balloon kyphoplasty: a case report.Osteoporos Int.2014;25(5):1647-1650.[9] 谢海风,张晓冬,王维佳.经皮椎体后凸成形术的临床应用[J].医学综述,2011,17(12):1824-1826.[10] Hulme PA,Krebs J,Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty:a systematic review of 69 clinical studies.Spine. 2006;31(17):1983.[11] 倪才方,陈珑,徐宝山,等.椎体内静脉造影在经皮椎体成形术中应用价值[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006,26(1):1-6.[12] Gaughen JR,Jense ME,Schweickert PA,et al.Relevance of antecedent venography in percutaneous vertebroplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures.Am J Neuroradiol.2010; 23(4):594-600.[13] 唐志宏,邹国耀,肖颖,等.胸腰段椎体内血管分布与安全区内穿刺减少骨水泥的渗漏[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(3):387-391.[14] 殷渠东,孙振中,顾三军.经皮椎体后凸成形术中减少骨水泥渗漏的策略[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2015, 30(9):938-940.[15] 苟凌云,李兵,张贤,等.经皮椎体注入骨水泥剂量与老年骨质疏松压缩性骨折椎体高度的恢复:1年随访验证[J].中国组织工程研究, 2007,11(35):6978-6982.[16] 杨益民,任志伟,张智,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗椎体压缩性骨折围手术期并发症分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010,20(3): 235-238.[17] 吴子祥,雷伟,桑宏勋,等. 阶段注射法预防椎体成型术中骨水泥渗漏的实验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2010,16(2):96-99.[18] Hodler J,Peck D,Gilula LA.Midterm outcome after vertebroplasty: predictive value of technical and patient-related factors.Radiology.2003;227(3):662-668.[19] Nakano M,Hirano N,Ishihara H,et al.Calcium phosphate cement leakage after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fractures: risk factor analysis for cement leakage.J Neurosurg Spine.2005;2(1):27-33.[20] Krebs J,Ferguson SJ,Bohner M,et al.Clinical measurements of cement injection pressure during vertebroplasty. Spine. 2005;30(5):118-122. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)