| [1] Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscles, exercise and obesity: skeletal muscle as a secretory organ. Nat Rev Endocrinol.2012;8(8): 457-465.[2] Giudice J,Taylor JM.Muscle as a paracrine and endocrine organ.Curr Opin Pharmacol.2017;34:49-55.[3] Wong GW,Wang J,Hug C,et al. A family of Acrp30 / adiponectin structural and functional paralogs[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.2004; 101:10302-10307.[4] Seldin MM,Peterson JM,Byerly MS,et al.Myonectin(CTRP15),a novel myokine that links skeletal muscle to systemic lipid homeostasis.J Biol Chem.2012;287(15):11968-11980.[5] Noriyuki Ouchi and Kenneth Walsh.Cardiovascular and Metabolic Regulation by the Adiponectin/CTRP Family of Proteins.Circulation. 2012;5(31):1524-1539[6] Matsuzawa Y,Funahashi T,Kihara S,Shimomura I.Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2004;24:29-33.[7] Yi W,Sun Y,Lau WB,et al.C1q/TNF-related protein-3, a newly identified adipokine, is a novel anti-apoptotic, pro-angiogenic,and cardioprotective molecule in the ischemic mouse heart. Circulation. 2012;125:134-145.[8] Park SY, Choi JH, Ryu HS,et al. C1q tumor necrosis factor alpha-related protein isoform 5 is increased in mitochondrial DNA-depleted myocytes and activates AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem.2009;284:27780-27789.[9] Seldin M M,Wong G W.Regulation of tissue crosstalk by skeletal muscle-derived myonectin and other myokines.Adipocyte.2012;1(4) : 200-202[10] Febbraio M, Abumrad NA, Hajjar DP, et al. A null mutation in murine CD36 reveals an important role in fatty acid and lipoprotein metabolism.J Biol Chem.1999;274 (27):19055-19062.[11] Ibrahimi A , Bonen A , Blinn WD, et al. Muscle -specific overexpression of FAT/CD36 enhances fatty acid oxidation by contracting muscle ,reduces plasma triglycerides and fatty acids,and increases plasma glucose and insulin.J Biol Chem.1999;274(38):26761-26766.[12] Seldin MM,Lei X,Tan SY,et al.Skeletal muscle-derived myonectin activates the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway to suppress autophagy in liver.J Biol Chem.2013;288(50): 36073-36082.[13] Kautz L,Jung G,Valore EV,et al.Identification of erythroferrone as an erythroid regulator of iron metabolism.Nat Genet.2014;46:678-684.[14] Honda H,Kobayashi Y,Onuma S,et al.Associations among erythroferrone and biomarkers of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism, and treatment with long-term erythropoiesis-stimulating agents in patients on hemodialysis.PLOS ONE.2016;11:e151601.[15] Kautz L, Jung G, Nemeth E,et al. Erythroferrone contributes to recovery from anemia of inflammation.Blood. 2014,124:2569-2574.[16] Nai A,Rubio A,Campanella A,et al.Limiting hepatic Bmp-Smad signaling by matriptase-2 is required for erythropoietin-mediated hepcidin suppression in mice.Blood.2016;127:2327-2336[17] 张靓,董泽源,马谨,等.跑台运动对高脂饮食诱导的肥胖大鼠骨骼肌肌联素表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2016,35(6):547-552.[18] Peterson JM, Mart R, Bond CE.Effect of obesity and exercise on the expression of the novel myokines, Myonectin and Fibronectin type III domain containing 5.PeerJ.2014;2:e605.[19] Rodríguez A, Becerril S, Méndez-Giménez L, et al.Leptin administration activates irisin-induced myogenesis via nitric oxide-dependent mechanisms, but reduces its effect on subcutaneous fat browning in mice. Int J Obes (Lond). 2015;39(3):397-407. [20] Yang M,Wei D,Mo C,et al.Saturated fatty acid palmitate-induced insulin resistance is accompanied with myotube loss and the impaired expression of health benefit myokine genes in C2C12 myotubes.Lipids Health Dis.2013;12: 104.[21] 陈婷,李仲文,张艳艳,等.甘油诱导的骨骼肌损伤修复过程肌间脂形态学及肌分泌因子表达变化[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2015,31(1): 64-71.[22] Gamas L, Matafome P, Seiça R.Irisin and Myonectin Regulation in the Insulin Resistant Muscle: Implications to Adipose Tissue: Muscle Crosstalk.J Diabetes Res.2015;8:121-128.[23] Chen T,Li ZW,Zhang YY,et al.Muscle-selective knockout of AMPKα2 does not exacerbate diet-induced obesity probably related to altered myokines expression.Biochem Biophysic Res Com.2015;458(12): 449-455.[24] Sharma N,Castorena CM,Cartee GD. Greater insulin sensitivity in calorie restricted rats occurswith unaltered circulating levels of several important myokines and cytokines.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2012; 9(1):90. [25] Pedersen BK.The diseasome of physical inactivity — and the role of myokines in muscle-fat cross talk.J Physiol.2009;587:5559-5568.[26] Catoire M, Kersten S.The search for exercise factors in humans. FASEB J.2015;29(5):1615-28.[27] Hawley JA, Hargreaves M, Joyner MJ et al.Integrative biology of exercise. Cell.2014; 159(4):738-749. [28] Park SY,Choi JH,Ryu HS,et al.C1q tumor necrosis factor alpha-related protein isoform 5 is increased in mitochondrial DNA-depleted myocytes and activates AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2009;284(41):27780-27789.[29] Lim S,Choi SH,Koo BK,et al.Effects of aerobic exercise training on C1q tumor necrosis factor alpha-related protein isoform 5 (myonectin): association with insulin resistance and mito-chondrial DNA density in women.J Clin Endocrinol Metab.2009;97:88-93.[30] Phielix E,Meex R,Moonen-Kornips E,et al.Exercise training increases mitochondrial content and exvivo mitochondrial function similarly in patients with type 2 diabetes and in control individuals.Diabetologia. 2010;53(8):1714-1721.[31] Xu FX,Zhou X,Shen F,et al.Decreased peripheral blood mitochondrial DNA content is related to HbA1c, fasting plasmaglucose level and age of onset in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Diabet Med.2012;29(7):e47-54.[32] Jager S,Handschin C, St-Pierre J, et al.AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) action in skeletal muscle via direct phosphorylalion of PGC-1 alpha.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2007; 104(29) :12017-12022. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌联素(Myonectin):又称补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15( complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor- related protein 15,CTRP 15),是骨骼肌分泌的一种新型生物活性物质,为CTRP蛋白家族的第15位成员。
肌肉因子(Myokines):骨骼肌能够以自分泌、旁分泌和内分泌的方式调节着其他的远端器官,这些肌源性分泌因子称为“肌肉因子”(Myokines)。它们不仅作用于骨骼肌自身糖、脂肪和蛋白质代谢,还担当骨骼肌与肝脏、脂肪、心脏及大脑之间进行对话(crosstalk)的信使,调节整体代谢状况。
文题释义:
肌联素(Myonectin):又称补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15( complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor- related protein 15,CTRP 15),是骨骼肌分泌的一种新型生物活性物质,为CTRP蛋白家族的第15位成员。
肌肉因子(Myokines):骨骼肌能够以自分泌、旁分泌和内分泌的方式调节着其他的远端器官,这些肌源性分泌因子称为“肌肉因子”(Myokines)。它们不仅作用于骨骼肌自身糖、脂肪和蛋白质代谢,还担当骨骼肌与肝脏、脂肪、心脏及大脑之间进行对话(crosstalk)的信使,调节整体代谢状况。.jpg) 文题释义:
肌联素(Myonectin):又称补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15( complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor- related protein 15,CTRP 15),是骨骼肌分泌的一种新型生物活性物质,为CTRP蛋白家族的第15位成员。
肌肉因子(Myokines):骨骼肌能够以自分泌、旁分泌和内分泌的方式调节着其他的远端器官,这些肌源性分泌因子称为“肌肉因子”(Myokines)。它们不仅作用于骨骼肌自身糖、脂肪和蛋白质代谢,还担当骨骼肌与肝脏、脂肪、心脏及大脑之间进行对话(crosstalk)的信使,调节整体代谢状况。
文题释义:
肌联素(Myonectin):又称补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15( complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor- related protein 15,CTRP 15),是骨骼肌分泌的一种新型生物活性物质,为CTRP蛋白家族的第15位成员。
肌肉因子(Myokines):骨骼肌能够以自分泌、旁分泌和内分泌的方式调节着其他的远端器官,这些肌源性分泌因子称为“肌肉因子”(Myokines)。它们不仅作用于骨骼肌自身糖、脂肪和蛋白质代谢,还担当骨骼肌与肝脏、脂肪、心脏及大脑之间进行对话(crosstalk)的信使,调节整体代谢状况。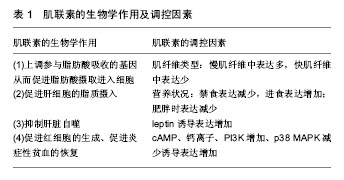
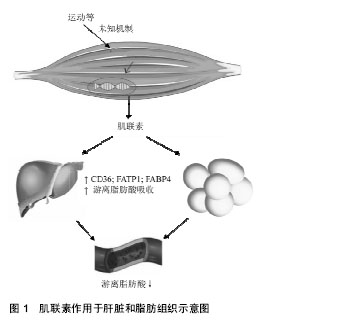
.jpg) 文题释义:
肌联素(Myonectin):又称补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15( complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor- related protein 15,CTRP 15),是骨骼肌分泌的一种新型生物活性物质,为CTRP蛋白家族的第15位成员。
肌肉因子(Myokines):骨骼肌能够以自分泌、旁分泌和内分泌的方式调节着其他的远端器官,这些肌源性分泌因子称为“肌肉因子”(Myokines)。它们不仅作用于骨骼肌自身糖、脂肪和蛋白质代谢,还担当骨骼肌与肝脏、脂肪、心脏及大脑之间进行对话(crosstalk)的信使,调节整体代谢状况。
文题释义:
肌联素(Myonectin):又称补体C1q/肿瘤坏死因子相关蛋白15( complement C1q/tumor necrosis factor- related protein 15,CTRP 15),是骨骼肌分泌的一种新型生物活性物质,为CTRP蛋白家族的第15位成员。
肌肉因子(Myokines):骨骼肌能够以自分泌、旁分泌和内分泌的方式调节着其他的远端器官,这些肌源性分泌因子称为“肌肉因子”(Myokines)。它们不仅作用于骨骼肌自身糖、脂肪和蛋白质代谢,还担当骨骼肌与肝脏、脂肪、心脏及大脑之间进行对话(crosstalk)的信使,调节整体代谢状况。