| [1] Wuertz K, Haglund L.Inflammatory mediators in intervertebral disk degeneration and discogenic pain. Global Spine.2013; 3(3):175-184.[2] Risbud MV,Shapiro IM.Role of cytokines in intervertebral disc degeneration:pain and disccontent. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014; 10(1):44-56.[3] Brisby H,Olmarker K,Larsson K,et al.Proinflammatory cytokines in cerebrospinal fluid and serum in patients with disc herniation and sciatica. Eur Spine J.2002;11(1):62-66.[4] Park MS,Lee HM,Hahn SB,et al.The association of the activation-inducible tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand with lumbardisc herniation.Yonsei Med J.2007;48(5):839-846.[5] Kraychete DC,Sakata RK,Issy AM,et al.Serum cytokine levels in patients with chronic low back pain due to herniated disc: analyticalcross-sectional study.Sao Paulo Med J.2010;128(5):259-262.[6] Pedersen LM,Schistad E,Jacobsen LM,et al.Serum levels of the pro-inflammatory interleukins -6 (IL-6) and -8 (IL-8) patients with lumbarradicular pain due to disc her niation:a 12-month prospective study. Brain Behav. Immun.2015;46: 132-136.[7] Moon HJ,Yurube T,Lozito TP,et al.Effects of secreted factors in culture medium of annulus fibrosus cells on microvascular endothelial cells: elucidating the possible pathomechanisms of matrix degradation and nerve in-growth in disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(2):344-354.[8] Deng X,Zhao F,Kang B,et al.Elevated interleukin-6 expression levels are associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Ther Med.2016;11(4):1425-1432.[9] 陈岩,胡有谷.转化生长因子β与椎间盘细胞Ⅰ型胶原基因调控的关系[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2000, 7(2):151-153. [10] Cheng L,Fan W,Liu B,et al.Th17 lymphocyte levels are higher in patients with ruptured than non-ruptured lumbar discs, and are correlated with pain intensity.Injury.2013;44(12): 1805-1810. [11] Xue H,Yao Y,Wang X,et al.Interleukin-21 is associated with the pathogenesis of lumbar disc herniation. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol.2015;14(5):509-518.[12] Grad S,Bow C,Karppinen J,et al.Systemic blood plasma CCL5 and CXCL6:Potential biomarkers for human lumbar disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater.2016;31:1-10.[13] Goode AP,Marshall SW,Kraus VB,et al.Association between serum and urine biomarkers and lumbar spine individual radiographicfeatures: the Johnston County Osteoarthritis Project.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(11):1286-1293.[14] Xie P,Liu B,Chen R,et al.Comparative analysis of serum proteomes:Identification of proteins associated with sciatica due to lumbar intervertebral disc herniation.Biomed Rep.2014; 2(5):693-698.[15] Moen A,Lind AL,Thulin M,et al.Protein Profiling of Patients with Lumbar Inflammatory Serum Radicular Pain One Year after DiscHerniation.Int J Inflam.2016;2016:3874964.[16] 贾长青,王臣,陈勇,等.基质金属蛋白酶3和白细胞介素1在突出的腰椎间盘组织中的含量及其相关性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(12):1180-1182.[17] Tertti M,Paajanen H,Laato M,et al.Disc degeneration in magnetic resonance imaging.A comparative biochemical, histologic, and radiologic study in cadaver spines. Spine. 1991;16(6):629-634.[18] Pearce RH, Thompson JP, Bebault GM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging reflects the chemical changes of aging degeneration in the humanintervertebral disk.J Rheumatol Suppl.1991; 27:42-43.[19] Southern EP,Fye MA,Panjabi MM,et al.Disc degeneration: a human cadaveric study correlating magnetic resonance imaging and quantitative discomanometry.Spine.2000;25(17) 2171-2175.[20] Weidenbaum M,Foster RJ,Best BA,et al.Correlating magnetic resonance imaging with the biochemical content of the normal humanintervertebral disc.J Orthop Res.1992;10(4):552-561.[21] Schiebler ML,Camerino VJ,Fallon MD,et al.In vivo and ex vivo magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of early disc degeneration with histopathologic correlation. Spine.1991; 16(6):635-640.[22] Blumenkrantz G,Zuo J,Li X,et al.In vivo 3.0-tesla magnetic resonance T1rho and T2 relaxation mapping in subjects with intervertebral disc degeneration and clinical symptoms.Magn Reson Med.2010;63(5):1193-1200. [23] Taylor TK,Melrose J,Burkhardt D,et al.Spinal biomechanics and aging are major determinants of the proteoglycan metabolism of intervertebral disc cells.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25(23):3014-3020.[24] Iatridis JC,MacLean JJ,O'Brien M,et al.Measurements of proteoglycan and water content distribution in human lumbarintervertebral discs.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007;32(14): 1493-1497.[25] Filippi CG, Duncan CT, Watts R, et al.In vivo quantification of T1 in lumbar spine disk spaces at 3T using parallel transmission MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;201(1): W110-116.[26] Radek M,Pacholczyk-Sienicka B,Jankowski S,et al.Assessing the correlation between the degree of disc degeneration on the Pfirrmann scale and the metabolites identified in HR-MAS NMR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;34(4): 376-380.[27] Pfirrmann CW,Metzdorf A,Zanetti M,et al.Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneratio.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2001;26(17):1873-1878.[28] Luoma K,Vehmas T,Riihimäki,et al.Disc height and signal intensity of the nucleus pulposus on magnetic resonance imaging as indicators of lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(6):680-686.[29] Antoniou J,Pike GB,Steffen T,et al.Quantitative magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of degenerative disc disease. Magn Reson Med.1998;40(6):900-907.[30] Kettler A,Wilke HJ.Review of existing grading systems for cervical or lumbar disc and facet joint degeneration.Eur Spine J.2006;15(6):705-718.[31] Ye S,Ju B,Wang H,et al.Bone morphogenetic protein-2 provokes interleukin-18-induced human intervertebral disc degeneration.Bone Joint Res.2016;5(9):412-418.[32] Weber KT,Alipui DO,Sison CP,et al.Serum levels of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin-6 vary based on diagnoses in individuals with lumbar intervertebral disc diseases. Arthritis Res Ther.2016;18:3. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
腰椎间盘退行性病变:腰椎间盘退行性病变是中老年人的一种常见病、多发病。它是由于椎间盘、椎体、椎小关节、脊柱韧带等退变、老化引起椎间盘突出,椎管、神经根管及椎间孔狭窄,导致患者出现腰腿痛。腰椎间盘退行性病变的特征性改变是其髓核中蛋白聚糖含量的下降以及伴随的水分丢失,启动和调节这一过程的生物机制仍不十分清楚。
生物标记物的意义:生物标记物是指能够客观反映某一生理、病理过程或治疗效果的生理指标,可用于疾病诊断、判断疾病分期或者用来评价新药或新疗法在目标人群中的安全性及有效性。生物标记物分析是一种有前景的技术,将极大的促进新型诊断和预测工具的发展,有助于追踪早期疾病的变化,并为患者量身定制治疗方案。
文题释义:
腰椎间盘退行性病变:腰椎间盘退行性病变是中老年人的一种常见病、多发病。它是由于椎间盘、椎体、椎小关节、脊柱韧带等退变、老化引起椎间盘突出,椎管、神经根管及椎间孔狭窄,导致患者出现腰腿痛。腰椎间盘退行性病变的特征性改变是其髓核中蛋白聚糖含量的下降以及伴随的水分丢失,启动和调节这一过程的生物机制仍不十分清楚。
生物标记物的意义:生物标记物是指能够客观反映某一生理、病理过程或治疗效果的生理指标,可用于疾病诊断、判断疾病分期或者用来评价新药或新疗法在目标人群中的安全性及有效性。生物标记物分析是一种有前景的技术,将极大的促进新型诊断和预测工具的发展,有助于追踪早期疾病的变化,并为患者量身定制治疗方案。.jpg) 文题释义:
腰椎间盘退行性病变:腰椎间盘退行性病变是中老年人的一种常见病、多发病。它是由于椎间盘、椎体、椎小关节、脊柱韧带等退变、老化引起椎间盘突出,椎管、神经根管及椎间孔狭窄,导致患者出现腰腿痛。腰椎间盘退行性病变的特征性改变是其髓核中蛋白聚糖含量的下降以及伴随的水分丢失,启动和调节这一过程的生物机制仍不十分清楚。
生物标记物的意义:生物标记物是指能够客观反映某一生理、病理过程或治疗效果的生理指标,可用于疾病诊断、判断疾病分期或者用来评价新药或新疗法在目标人群中的安全性及有效性。生物标记物分析是一种有前景的技术,将极大的促进新型诊断和预测工具的发展,有助于追踪早期疾病的变化,并为患者量身定制治疗方案。
文题释义:
腰椎间盘退行性病变:腰椎间盘退行性病变是中老年人的一种常见病、多发病。它是由于椎间盘、椎体、椎小关节、脊柱韧带等退变、老化引起椎间盘突出,椎管、神经根管及椎间孔狭窄,导致患者出现腰腿痛。腰椎间盘退行性病变的特征性改变是其髓核中蛋白聚糖含量的下降以及伴随的水分丢失,启动和调节这一过程的生物机制仍不十分清楚。
生物标记物的意义:生物标记物是指能够客观反映某一生理、病理过程或治疗效果的生理指标,可用于疾病诊断、判断疾病分期或者用来评价新药或新疗法在目标人群中的安全性及有效性。生物标记物分析是一种有前景的技术,将极大的促进新型诊断和预测工具的发展,有助于追踪早期疾病的变化,并为患者量身定制治疗方案。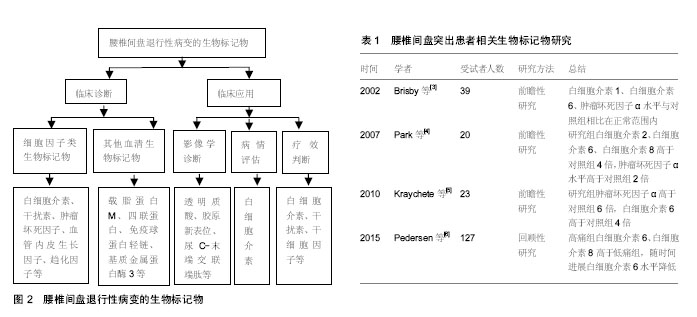
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
腰椎间盘退行性病变:腰椎间盘退行性病变是中老年人的一种常见病、多发病。它是由于椎间盘、椎体、椎小关节、脊柱韧带等退变、老化引起椎间盘突出,椎管、神经根管及椎间孔狭窄,导致患者出现腰腿痛。腰椎间盘退行性病变的特征性改变是其髓核中蛋白聚糖含量的下降以及伴随的水分丢失,启动和调节这一过程的生物机制仍不十分清楚。
生物标记物的意义:生物标记物是指能够客观反映某一生理、病理过程或治疗效果的生理指标,可用于疾病诊断、判断疾病分期或者用来评价新药或新疗法在目标人群中的安全性及有效性。生物标记物分析是一种有前景的技术,将极大的促进新型诊断和预测工具的发展,有助于追踪早期疾病的变化,并为患者量身定制治疗方案。
文题释义:
腰椎间盘退行性病变:腰椎间盘退行性病变是中老年人的一种常见病、多发病。它是由于椎间盘、椎体、椎小关节、脊柱韧带等退变、老化引起椎间盘突出,椎管、神经根管及椎间孔狭窄,导致患者出现腰腿痛。腰椎间盘退行性病变的特征性改变是其髓核中蛋白聚糖含量的下降以及伴随的水分丢失,启动和调节这一过程的生物机制仍不十分清楚。
生物标记物的意义:生物标记物是指能够客观反映某一生理、病理过程或治疗效果的生理指标,可用于疾病诊断、判断疾病分期或者用来评价新药或新疗法在目标人群中的安全性及有效性。生物标记物分析是一种有前景的技术,将极大的促进新型诊断和预测工具的发展,有助于追踪早期疾病的变化,并为患者量身定制治疗方案。