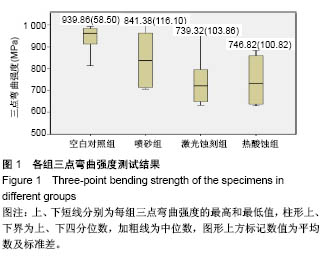
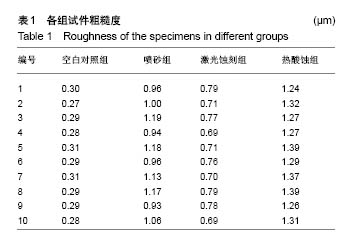
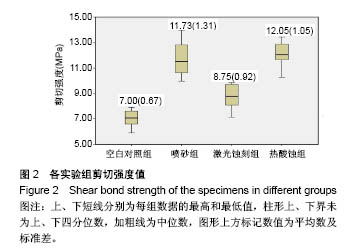
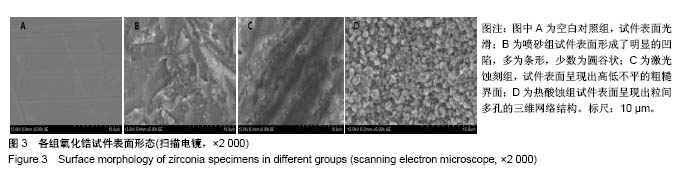
| [1] 汪洋.氧化锆陶瓷在口腔修复中的应用[J].全科口腔医学电子杂志, 2016,3(14):9,13.[2] Re D, Augusti D, Sailet I, et al. The effect of surface treatment on the adhesion of resin cements to Y-TZP. Eur J Esthet Dent. 2008; 3(2):186-196.[3] Akin GE, Kaval ME, Turk T, et al. Surface roughness and bond strength of zirconia posts to a resin cement after various surface pretreatments. Photomed Laser Surg. 2015;33(5):246-251.[4] Pozzobon JL, Pereira GKR, Wandscher VF, et al. Mechanical behavior of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystalline ceramic after different zirconia surface treatments. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77(1):828-835.[5] 刘艳,张祖太,何敏,等.齿科氧化锆表面处理的研究进展[J].北京口腔医学,2015,23(2):114-117. [6] Murthy V, Manoharan, Balaji, et al. Effect of four surface treatment methods on the shear bond strength of resin cement to zirconia ceramics- a comparative in vitro study. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014; 8(9):65-68.[7] 邵龙泉,胡琛,孙挺,等.表面处理方法及黏结剂种类影响氧化锆的剪切强度[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(8):1435-1438.[8] 杜桥,牛光良.氧化锆的表面粗化与改性[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2015, 42(1):97-101.[9] Bielen V, Inokoshi M, Munck JD, et al. Bonding effectiveness to differently sandblasted dental zirconia. J Adhes Dent. 2015;17(3): 235-242.[10] Kara O, Kara HB, Tobi ES, et al. Effect of various lasers on the bond strength of two zirconia ceramics. Photomed Laser Surg. 2015; 33(2):69-76.[11] 吴建中,谢海峰,陈晨.热酸蚀刻法粗化处理氧化锆陶瓷表面的初步研究[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2013,33(12):1789-1794.[12] Özdemir H, Yaniko?lu N, Sa?söz N. Effect of MDP-based silane and different surface conditioner methods on bonding of resin cements to zirconium framework. J Prosthodont. 2017;24(7):38-47.[13] 戴文雍,印厚才,陈晨,等.热酸溶液蚀刻对氧化锆粘接强度的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2013,31(6):569-573.[14] 郑茜聪,蔡志斌.CAD/CAM氧化锆全瓷单冠抗折裂随访4年临床分析[J].口腔医学,2015,35(9):783-785.[15] Hibst R, Keller U. Experimental studies of the application of the Er:YAG laser on dental hard substances: I. Measurement of the ablation rate. Lasers Surg Med. 1989;9(4):338-344.[16] Angiero F, Benedicenti S, Parker S, et al. Clinical and surgical management of odontoma. Photomed Laser Surg. 2014;32(1): 47-53.[17] Taniguchi Y, Aoki A, Sakai K, et al. A novel surgical procedure for er:yag laser-assisted periodontal regenerative therapy: case series. 2016;36(4):507-515.[18] Onisor I, Pecie R, Chaskelis I, et al. Cutting and coagulation during intraoral soft tissue surgery using Er:YAG laser. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2013;14(2):140-145.[19] Ruyter EI, Vajeeston N, Knarvang T, et al. A novel etching technique for surface treatment of zirconia ceramics to improve adhesion of resin-based luting cements. Acta Biomater Odontol Scand. 2017; 3(1):36-46.[20] 周珊羽.全解剖式氧化锆全冠断裂强度的研究[D].南方医科大学,2013.[21] Kaimal A, Ramdev P, Shruthi CS. Evaluation of effect of zirconia surface treatment, using plasma of argon and silane, on the shear bond strength of two composite resin cements. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(8):39-43.[22] 伊元夫.牙科CAD/CAM用氧化锆陶瓷的颜色调控及其低温时效研究[D].中国人民解放军军医进修学院.2007.[23] 李新,苏乃川,廖运茂,等.不同条件的表面喷砂对牙科氧化锆材料表面丧失的影响[J].口腔医学.2017,37(1):28-32.[24] Wang H, Aboushelib MN, Feilzer AJ. Strength influencing variables on CAD/CAM zirconia frameworks. Dent Mater. 2008;24(5):633-638.[25] Preis V, Weiser F, Handel G, et al. Wear performance of monolithic dental ceramics with different surface treatments. Quintessence Int. 2013;44(5):393-405.[26] 黄阳.牙科CAD/CAM系统可切削氧化锆的性能研究[D].中国人民解放军医学院.2016.[27] Ça?lar ?,Yan?ko?lu N. The effect of sandblasting, er:yag laser, and heat treatment on the mechanical properties of different zirconia cores. Photomed Laser Surg. 2016;34(1):17-26.[28] Rona N, Yenisey M, Kucukturk G, et al. Effect of electrical discharge machining on dental Y-TZP ceramic-resin bonding. J Prosthodont Res. 2017;61(2):158-167.[29] Yassaei S, Aghili HA, Davari A, et al. Effect of four methods of surface treatment on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets to zirconium. J Dent (Tehran). 2015;12(4):281-289.[30] 吕品,姜婷.热酸蚀处理对氧化锆面剪切粘接强度的影响[J].北京大学学报(医学版).2014,46(2):302-305. |
.jpg)
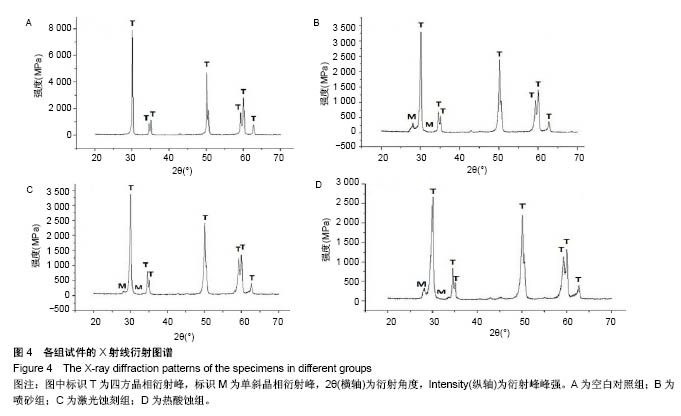
.jpg)