| [1] Ates GB,Ak A,Garipcan B,et al.Methylene blue mediated photobiomodulation on human osteoblast cells. Lasers Med Sci. 2017;32(8):1847-1855.[2] Chen Z, Liu R,Yang SH, et al. Methylene blue inhibits GABAA receptors by interaction with GABA binding site. Neuropharmacology, 2017;119(12):100-110.[3] Delport A,Harvey BH,Petzer A, et al. The monoamine oxidase inhibition properties of selected structural analogues of methylene blue. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2017;325:1-8.[4] Geurts JW,Kallewaard JW,Kessels A,et al.Efficacy and cost-effectiveness of intradiscal methylene blue injection for chronic discogenic low back pain: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials.2015;16(8):532-538.[5] Gholivand MB,Ahmadi E,Haseli M.A novel voltammetric sensor for nevirapine, based on modified graphite electrode by MWCNs/poly(methylene blue)/gold nanoparticle. Anal Biochem. 2017;527:4-12.[6] 陈广儒,卫建民.椎间孔镜条件下置入椎弓根钉治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,12 (35):5641-5645.[7] 丁允知,胡敬男,周勇.经皮椎间孔镜下行TESSYS技术与椎间盘镜下手术治疗腰椎间盘突出症的效果对比[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2017, 6(5):492-493.[8] 李善庆.经椎板间入路椎间孔镜和椎间盘镜治疗L5/S1椎间盘突出症的对比研究 [D].华中科技大学,2016.[9] 凌华军,范磊,赖茂松,等.椎间盘镜与椎间孔镜治疗腰椎间盘突出疗效比较的Meta分析[J]. 中国内镜杂志,2017,12 (3):47-55.[10] Adams MA,Prenovost KM,Dominitz JA,et al.Predictors of Use of Monitored Anesthesia Care for Outpatient Gastrointestinal Endoscopy in a Capitated Payment System. Gastroenterology. 2017; 153(6):1496-1503.[11] Bissonnette R,Tamaz R,Bolduc C,et al.Use of capsule endoscopy to identify lesions suggestive of Crohn's disease in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;77(4):755-756 .[12] Dijemeni E,D'Amone G.The comparability of drug-induced sedation endoscopy classification systems.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.2017;274(12):4277-4278[13] Hammad H,Kaltenbach T,Soetikno R.Image-enhanced endoscopy:How far do we need to go?.Gastrointest endosc.2017;86(4):698-699.[14] Sano T,Herzog M,Kellner P.Response to the comment: Is observed upper airway obstruction patterns during drug-induced sedation endoscopy dose-dependent?.Sleep Breath.2018;22(1):187.[15] Hosseinzadeh R,Khorsandi K.Methylene blue, curcumin and ion pairing nanoparticles effects on photodynamic therapy of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2017;18:284-294..[16] Kallewaard JW,Geurts JW,Kessels A,et al.Efficacy, Safety, and Predictors of Intradiscal Methylene Blue Injection for Discogenic Low Back Pain:Results of a Multicenter Prospective Clinical Series. Pain Pract.2016;16(4):405-412.[17] Kassab A,Dabous O,Morsy M.A novel management of streptococcal pharyngotonsillar infections by laser-activated silver nanoparticles and methylene blue conjugate, in vitro study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.2017;100:114-118.[18] Khan S,Khan SN,Meena R,et al.Photoinactivation of multidrug resistant bacteria by monomeric methylene blue conjugated gold nanoparticles.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;174:150-161.[19] Lullove EJ. Use of Ovine-based Collagen Extracellular Matrix and Gentian Violet/Methylene Blue Antibacterial Foam Dressings to Help Improve Clinical Outcomes in Lower Extremity Wounds: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Wounds. 2017;29(4):107-114.[20] 阿力木江•买买提明. 提高亚甲蓝分光光度法测定水中阴离子表面活性剂的分析方法探讨[J].科学技术创新,2017, 12(33): 55-57.[21] 李鹏,郭毅.亚甲蓝病毒灭活血浆中人细小病毒B19抗原、抗体的检测与分析[J].临床输血与检验, 2018, 13(1):20-23.[22] Mao XL,Ye LP,Zheng HH,et al.Submucosal tunneling endoscopic resection using methylene-blue guidance for cardial subepithelial tumors originating from the muscularis propria layer. Dis Esophagus. 2017;30(3):1-7[23] Mazzeffi M,Hammer B,Chen E,et al.Methylene blue for postcardiopulmonary bypass vasoplegic syndrome: A cohort study. Ann Card Anaesth. 2017;20(2):178-181[24] Mehaffey JH,Johnston LE, Hawkins RB, et al. Methylene Blue for Vasoplegic Syndrome After Cardiac Operation: Early Administration Improves Surviva.Ann Thorac Surg. 2017; 104(1):36-41.[25] 郭继东,侯树勋,吴叶,等.椎间盘造影结合亚甲蓝注射治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛的初步疗效观察[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2010, 5(2): 67-70.[26] 郝其全,孙海燕,袁超,等.经皮激光椎间盘减压术+亚甲蓝治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛效果观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2017,15 (2):185-186.[27] 刘春雨,金丽,彭宝淦.硬膜外注入亚甲蓝对腰椎脊髓及脊神经节结构的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 9(38):6160-6164.[28] 刘沛,肖少雄,熊伟.椎间盘内亚甲蓝注射治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2009, 13(03):34-35.[29] 刘永征,李成权,徐强,等.CT引导下椎间盘造影后亚甲蓝注射治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011, 5(3): 227-228.[30] 刘元彬,张为,申勇,等. Disc-FX经皮髓核钳夹、射频消融术与椎间盘内亚甲蓝注射术治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的对比研究[J].河北医科大学学报,2013, 11(10):1128-1131.[31] 聂中阶,黄开元,郭继民,等.单间隙腰椎间盘突出症手术治疗的定位[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2003, 4(11):58-59.[32] 庞晓东,徐展,彭宝淦,等.亚甲蓝治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛机制的动物实验研究[J]. 中国疼痛医学杂志, 2011, 12(5):274-279.[33] 庞晓东,杨洪,李端明,等.椎间盘内亚甲蓝注射治疗终板源性腰痛的临床观察[J]. 脊柱外科杂志, 2012, 22(5):274-276.[34] 彭宝淦,陈金栋.椎间盘内亚甲蓝注射治疗慢性椎间盘源性腰痛的随机临床对照研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2011,11(1):3-8.[35] 彭宝淦,侯树勋,吴闻文,等.椎间盘内亚甲蓝注射治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛[J].中华医学杂志,2006, 21(11):782-784.[36] 沈进稳,瞿杭波,童培建,等.亚甲蓝腰椎间盘内注射在经皮激光椎间盘减压术后的应用[J].临床骨科杂志,2008,20(4):324-326.[37] 史剑倩,章勇,张达颖,等.亚甲蓝注射联合靶点射频治疗盘源性腰痛的临床疗效研究[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2015, 11(10): 791-793.[38] 陈永成.亚甲蓝穴位注射配合针刀治疗跟痛症72例[J].现代中医药,2017,12(6):48-49.[39] 郭永强.复方亚甲蓝注射液骶管麻醉在肛肠手术中的应用效果观察[J].临床医学工程, 2017, 13(11):1595-1596.[40] 何树平.骶管麻醉配合复方亚甲蓝注射液应用于肛肠手术中的麻醉效果研究[J].中国社区医师, 2017, 21(33):47-48.[41] 苏启超,刘泉,刘贵林,等.臭氧与亚甲蓝联合治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床观察[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2012,12(12):765-766.[42] 唐国柯,黄庆华,张朝跃.椎间盘内亚甲蓝与臭氧注射治疗盘源性腰痛的对照研究[J].湖南中医药大学学报,2012,10(12):39-40.[43] 唐晓军,罗玲丽,唐国军,等.椎间盘造影染色在椎间孔镜治疗极外侧型腰椎间盘突出症中的应用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018, 14(3):209-213.[44] 熊伟,宋健治,肖少雄.椎间盘造影亚甲蓝盘内注射治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的疗效分析与探讨[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2007, 23(9): 6-8.[45] 王培森,侯勇,王建民.亚甲蓝肛周皮下注射联合中药坐浴用于混合痔术后镇痛效果临床观察[J].中医药临床杂志,2018, 6(2): 329-331.[46] 王三英,欧阳钦,李天煜,等.静脉注射地佐辛联合亚甲蓝、布比卡因超前镇痛用于痔疮术后效果观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2017, 4(20):3789-3791.[47] 徐仁良,华双一,江根玉,等.后入路注射臭氧加亚甲蓝治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床价值[J].颈腰痛杂志, 2015, 21(2):123-124.[48] 颜晓敏,章联,许诚.应用亚甲蓝作为乳腺癌前哨淋巴结示踪剂的临床分析[J].中华普外科手术学杂志:电子版,2017, 11(5): 449-450.[49] 杨洪,高春华,庞晓东,等.亚甲兰注射治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的临床观察[J].脊柱外科杂志,2012,16(05):271-273.[50] 杨梅.亚甲蓝病毒灭活血浆制备方法及对凝血因子的影响研究[J].中国医疗器械信息, 2017, 18(22):131-147.[51] 李欢,唐帆,马辉,等. 吲哚菁绿联合亚甲蓝显影在新辅助化疗乳腺癌术中的临床研究[J].科技视界, 2017, 9(32):7-8.[52] 刘恒,王钢乐,董懿,等.乳管内窥镜联合亚甲蓝双定位法诊断乳腺导管内瘤样病变及手术价值[J].中国医学装备,2017, 8(12): 89-92.[53] 满祎,许娅,刘爱国.乳晕皮内与瘤周注射亚甲蓝检测乳腺癌前哨淋巴结的效果对比[J].广西医科大学学报, 2018, 21(1):97-99.[54] 周裕凯,王瑛,张先杰,等.静脉注射亚甲蓝缓解丙泊酚注射痛的临床研究[J].川北医学院学报, 2018, 13(1):98-100.[55] 祝琴,李远平,张英毅, 等.纳米炭与亚甲蓝在早中期乳腺癌前哨淋巴结活检中的应用研究[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2017, 11(21): 109-112.[56] Michutova M,Mrazova V,Kudelova M,et al.Herpes simplex viruses type 1 and 2 photoinactivated in the presence of methylene blue transform human and mouse cells in vitro. Acta virologica. 2017; 61(3):308-315.[57] Mwale F,Wang HT,Roughley P,et al. Link N and mesenchymal stem cells can induce regeneration of the early degenerate intervertebral disc.Tissue engineering Part A.2014; 20(21-22): 2942-2949.[58] Noens L,Vilarino MD,Megalou A,et al.International, prospective haemovigilance study on methylene blue-treated plasma. Vox sanguinis.2017;112(4):352-359.[59] Pangasa N,Magoon R,Bhardwaj V,et al.Methylene blue for post-cardioplumonary bypass vasoplegic syndrome. Transfusion. 2017;20(3):381-392.[60] Paulinelli RR,Freitas-Junior R,Rahal RM,et al. A prospective randomized trial comparing patent blue and methylene blue for the detection of the sentinel lymph node in breast cancer patients. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2017 ;63(2):118-123.[61] 杨拴牢,孙照明,朱海波.CT引导下臭氧联合亚甲蓝盘内注射治疗颈椎间盘突出症67例临床观察[J].内蒙古中医药,2013, 2(23): 92-93.[62] 杨拴牢,朱海波,孙照明.臭氧加亚甲蓝盘内注射治疗盘源性腰痛102例体会[J].内蒙古中医药, 2013, 8(26):78-79.[63] 杨宪武,杨宏伟,李红玉,等. NBI、亚甲蓝染色联合EUS及EMR在胃部癌前病变肠上皮化生及胃部隆起病变诊治中的应用价值[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2017,13(33):3687-3689.[64] 张华秀,易红玉.经皮穿刺腰椎间盘射频减压联合亚甲蓝注射术治疗椎间盘源性腰痛的围术期护理[J].实用临床医学, 2016, 8(1):58-59.[65] 赵亮,郭华.两种微创手段治疗盘源性下腰痛78例效果观察[J].现代诊断与治疗, 2014,13(18):4239-4240.[66] Phelan AL,Jones CM,Ceschini AS,et al.Sparing a Craniotomy: The Role of Intraoperative Methylene Blue in Management of Midline Dermoid Cysts. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017;139(6): 1445-1451. [67] Yun K.Assessing Urinary Tract Junction Obstruction Defects by Methylene Blue Dye Injection. J Vis Exp. 2017 Oct 12; (128). doi: 10.3791/56247.[68] Zoellner LA,Telch M,Foa EB,et al.Enhancing Extinction Learning in Posttraumatic Stress Disorder With Brief Daily Imaginal Exposure and Methylene Blue:A Randomized Controlled Trial. J Clin Psychiatry. 2017;78(7):e782-e789. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
CCK-8:CCK-8法使用酶联免疫检测仪测定细胞在450 nm波长处的光吸收值,计算细胞的活力或药物的毒性强度。该方法已被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的活性检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选、细胞增殖试验、细胞毒性试验以及药敏试验等。
MTT法:又称MTT比色法,是一种检测细胞存活和生长的方法。其检测原理为活细胞线粒体中的琥珀酸脱氢酶能使外源性MTT还原为水不溶性的蓝紫色结晶甲瓒(Formazan)并沉积在细胞中,而死细胞无此功能。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm波长处测定其光吸收值,可间接反映活细胞数量。在一定细胞数范围内,MTT结晶形成的量与细胞数成正比。
文题释义:
CCK-8:CCK-8法使用酶联免疫检测仪测定细胞在450 nm波长处的光吸收值,计算细胞的活力或药物的毒性强度。该方法已被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的活性检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选、细胞增殖试验、细胞毒性试验以及药敏试验等。
MTT法:又称MTT比色法,是一种检测细胞存活和生长的方法。其检测原理为活细胞线粒体中的琥珀酸脱氢酶能使外源性MTT还原为水不溶性的蓝紫色结晶甲瓒(Formazan)并沉积在细胞中,而死细胞无此功能。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm波长处测定其光吸收值,可间接反映活细胞数量。在一定细胞数范围内,MTT结晶形成的量与细胞数成正比。.jpg) 文题释义:
CCK-8:CCK-8法使用酶联免疫检测仪测定细胞在450 nm波长处的光吸收值,计算细胞的活力或药物的毒性强度。该方法已被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的活性检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选、细胞增殖试验、细胞毒性试验以及药敏试验等。
MTT法:又称MTT比色法,是一种检测细胞存活和生长的方法。其检测原理为活细胞线粒体中的琥珀酸脱氢酶能使外源性MTT还原为水不溶性的蓝紫色结晶甲瓒(Formazan)并沉积在细胞中,而死细胞无此功能。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm波长处测定其光吸收值,可间接反映活细胞数量。在一定细胞数范围内,MTT结晶形成的量与细胞数成正比。
文题释义:
CCK-8:CCK-8法使用酶联免疫检测仪测定细胞在450 nm波长处的光吸收值,计算细胞的活力或药物的毒性强度。该方法已被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的活性检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选、细胞增殖试验、细胞毒性试验以及药敏试验等。
MTT法:又称MTT比色法,是一种检测细胞存活和生长的方法。其检测原理为活细胞线粒体中的琥珀酸脱氢酶能使外源性MTT还原为水不溶性的蓝紫色结晶甲瓒(Formazan)并沉积在细胞中,而死细胞无此功能。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm波长处测定其光吸收值,可间接反映活细胞数量。在一定细胞数范围内,MTT结晶形成的量与细胞数成正比。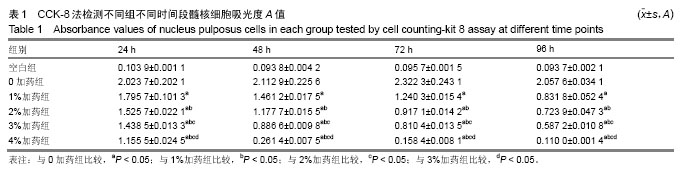
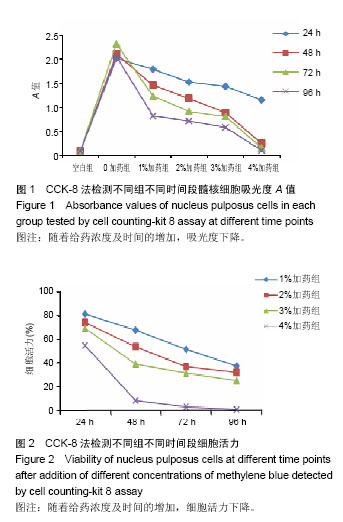
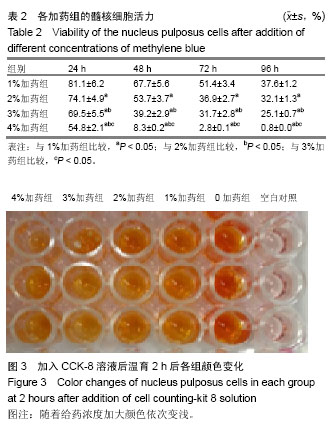
.jpg) 文题释义:
CCK-8:CCK-8法使用酶联免疫检测仪测定细胞在450 nm波长处的光吸收值,计算细胞的活力或药物的毒性强度。该方法已被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的活性检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选、细胞增殖试验、细胞毒性试验以及药敏试验等。
MTT法:又称MTT比色法,是一种检测细胞存活和生长的方法。其检测原理为活细胞线粒体中的琥珀酸脱氢酶能使外源性MTT还原为水不溶性的蓝紫色结晶甲瓒(Formazan)并沉积在细胞中,而死细胞无此功能。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm波长处测定其光吸收值,可间接反映活细胞数量。在一定细胞数范围内,MTT结晶形成的量与细胞数成正比。
文题释义:
CCK-8:CCK-8法使用酶联免疫检测仪测定细胞在450 nm波长处的光吸收值,计算细胞的活力或药物的毒性强度。该方法已被广泛用于一些生物活性因子的活性检测、抗肿瘤药物筛选、细胞增殖试验、细胞毒性试验以及药敏试验等。
MTT法:又称MTT比色法,是一种检测细胞存活和生长的方法。其检测原理为活细胞线粒体中的琥珀酸脱氢酶能使外源性MTT还原为水不溶性的蓝紫色结晶甲瓒(Formazan)并沉积在细胞中,而死细胞无此功能。用酶联免疫检测仪在490 nm波长处测定其光吸收值,可间接反映活细胞数量。在一定细胞数范围内,MTT结晶形成的量与细胞数成正比。