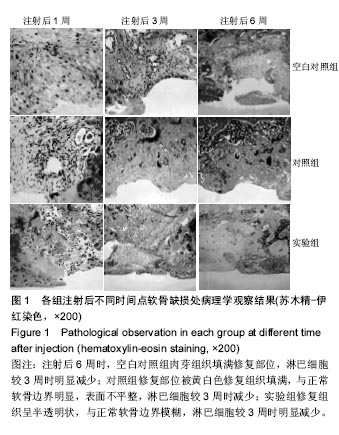
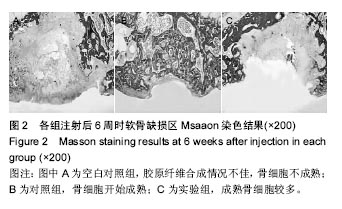
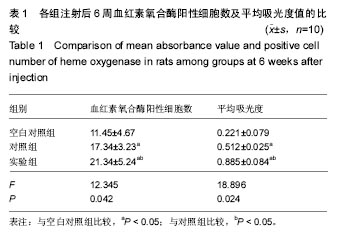
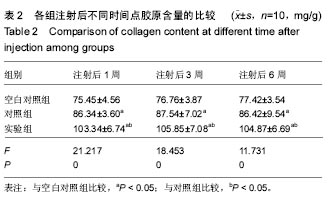
| [1]Orsi AD,Chakravarthy S,Canavan PK,et al.The effects of knee joint kinematics on anterior cruciate ligament injury and articular cartilage damage.Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2016;19(5):493-506.[2]Lv YM,Yu QS.Repair of articular osteochondral defects of the knee joint using a composite lamellar scaffold.Bone Joint Res. 2015;4(4):56-64.[3]王志学,吕国枫,丁勇,等.自体软骨细胞移植技术治疗膝关节软骨缺损的研究进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2014,14(12):2372-2375.[4]Eckstein F,Wirth W,Lohmer LS,et al.Five-year follow-up of knee joint cartilage thickness changes after acute anterior cruciate ligament rupture.Arthritis Rheumatol.2015; 67(1): 152-161.[5]Brill R,Wohlgemuth WA,Hempfling H,et al.Dynamic impact force and association with structural damage to the knee joint: An ex-vivo study.Ann Anat.2014;196(6):456-463.[6]Zhu Y,Wu X,Liang Y,et al.Repair of cartilage defects in osteoarthritis rats with induced pluripotent stem cell derived chondrocytes.BMC Biotechnol.2016;16(1):78.[7]Tahami SM,Rad SM.Outcome of ACL Reconstruction and Concomitant Articular Injury Treatment.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2015;3(4):260-263.[8]王永成,袁雪凌,汪爱媛,等.膝关节骨软骨损伤的治疗策略[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(1):113-118.[9]鄢志辉,杨柳,郭林,等.关节镜下双极射频消融治疗外侧半月板撕裂合并外侧间室软骨损伤的疗效分析[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(1):13-16.[10]Niemeyer P,Porichis S,Steinwachs M,et al.Long-term outcomes after first-generation autologous chondrocyte implantation for cartilage defects of the knee.Am J Sports Med.2014;42(1):150-157.[11]Chen P,Zhu S,Wang Y,et al.The amelioration of cartilage degeneration by ADAMTS-5 inhibitor delivered in a hyaluronic acid hydrogel.Biomaterials.2014;35(9):2827-2836.[12]Tangerino Filho EP,Fachi JL,Vasconcelos IC,et al.Effects of microcurrent therapy on excisional elastic cartilage defects in young rats.Tissue Cell.2016;48(3):224-234.[13]Whittaker J,Woodhouse LJ,Nettel-Aguirre A,et al.Evidence of early post-traumatic osteoarthritis and other negative health outcomes 3–10 years following knee joint injury in youth sport.Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015;23(7):1122-1129.[14]Li H,Chen C,Chen S.Posttraumatic knee osteoarthritis following anterior cruciate ligament injury:Potential biochemical mediators of degenerative alteration and specific biochemical markers.Biomed Rep.2015;3(2):147-151.[15]Vos LM,Kuijer R,Huddleston Slater JJ,et al.Inflammation is more distinct in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis compared to the knee joint.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014; 72(1):35-40.[16]Jabaji Z,Brinkley GJ,Khalil HA,et al.Type I collagen as an extracellular matrix for the in vitro growth of human small intestinal epithelium.Plos One.2014;9(9):e107814.[17]Paesen R,Sanen K,Smisdom N,et al.Polarization second harmonic generation by image correlation spectroscopy on collagen type I hydrogels.Acta Biomater. 2014;10(5): 2036-2042.[18]Liu S,Wu J,Liu X,et al.Osteochondral regeneration using an oriented nanofiber yarn-collagen type I/hyaluronate hybrid/TCP biphasic scaffold.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(2):581-592.[19]Yang YH,Ard MB,Halper JT,et al.Type I Collagen-Based Fibrous Capsule Enhances Integration of Tissue-Engineered Cartilage with Native Articular Cartilage.Ann Biomed Eng. 2014;42(4):716-726.[20]Hosseini Y,Verbridge SS,Agah M.Bio-inspired microstructures in collagen type I hydrogel.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015; 103(6): 2193-2197.[21]Wei Y,Bai L.Recent advances in the understanding of molecular mechanisms of cartilage degeneration, synovitis and subchondral bone changes in osteoarthritis.Connect Tissue Res.2016;57(4):245-261.[22]徐敬,赵建宁,徐海栋,等.关节软骨损伤修复研究进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2015,35(3):455-461.[23]樊东力,张一鸣.生物医用材料和组织工程技术在组织修复中的应用及进展[J].第三军医大学学报,2015,37(19):1909-1913.[24]Chen W,Chen S,Morsi Y,et al.Superabsorbent 3D Scaffold Based on Electrospun Nanofibers for Cartilage Tissue Engineering.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(37): 24415-24425.[25]Chen G,Lv Y,Dong C,et al.Effect of internal structure of collagen/hydroxyapatite scaffold on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2015;10(2):99-108.[26]Song K,Yan X,Zhang Y,et al.Numberical simulation of fluid flow and three-dimensional expansion of tissue engineering seed cells in large scale inside a novel rotating wall hollow fiber membrane bioreactor.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2015; 38(8):1527-1540.[27]Whyte GP,Gobbi A,Sadlik B.Dry Arthroscopic Single-Stage Cartilage Repair of the Knee Using a Hyaluronic Acid-Based Scaffold With Activated Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Arthrosc Tech.2016;5(4):e913-e918.[28]Wang Y,Hu J,Jiao J,et al.Engineering vascular tissue with functional smooth muscle cells derived from human iPS cells and nanofibrous scaffolds.Biomaterials, 2014,35(32): 8960-8969.[29]Maturavongsadit P,Luckanagul JA,Metavarayuth K,et al. Promotion of In Vitro Chondrogenesis of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using In Situ Hyaluronic Hydrogel Functionalized with Rod-Like Viral Nanoparticles.Biomacromolecules.2016;17(6):1930-1938.[30]王震,梁大川,白洁玉,等.慢病毒介导的Sox9基因在兔骨髓间充质干细胞的过表达促进软骨损伤修复[J].中国骨伤, 2015,28(5): 433-440.[31]朱如里,郑闽前,马永平,等.自体软骨细胞移植修复关节软骨缺损的基础及临床应用研究[J].南通大学学报:医学版, 2012,32(6): 458-460.[32]Lin YX,Ding ZY,Zhou XB,et al.In vitro,and In vivo,Evaluation of the Developed PLGA/HAp/Zein Scaffolds for Bone-Cartilage Interface Regeneration.Biomed Environ Sci.2015;28(1):1-12.[33]Kaderli S,Boulocher C,Pillet E,et al.A novel biocompatible hyaluronic acid-chitosan hybrid hydrogel for osteoarthrosis therapy.Int J Pharm.2015;483(1-2):158-168.[34]谷雅.骨科金属内置物材料的生物学特性及应用进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(6):536-539.[35]陈旭,李国英.胶原/透明质酸共混体系的相容性及相互作用研究[J].功能材料,2013,44(8):1136-1140.[36]宁洪艳,韩宏岩,吕强,等.纳米纤维家蚕丝蛋白软支架制备及性能[J].应用昆虫学报,2015,52(6):1507-1512.[37]刘效仿,张健,侯蕾,等.透明质酸促进撞击性膝关节软骨损伤修复的实验研究[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2014,16(12):1094-1098.[38]赵峰,何薇,刘桂兰,等.透明质酸水凝胶修复大鼠软骨缺损的实验研究[J].重庆医学,2014,43(35):4719-4722. |
.jpg)

.jpg)