| [1]Yin H, Wang Y, Sun Z,et al.Induction of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and functional cartilage microtissue formation for in vivo cartilage regeneration by cartilage extracellular matrix-derived particles.ActaBiomater. 2016;33:96-109.[2]Zhang L,Hu J,Athanasiou KA.The role of tissue engineering in articular cartilage repair and regeneration. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2009;37:1-57.[3]Gaut C, Sugaya K. Critical review on the physical and mechanical factors involved in tissue engineering of cartilage. Regen Med.2015;22:1-15.[4]Matsunaga D,Akizuki S,Takizawa T,et al.Repair of articular cartilage and clinical outcome after osteotomy with microfracture or abrasion arthroplasty for medial gonarthrosis. Knee.2007;14(6):465-471.[5]Hunziker EB.Articular cartilage repair: basic science and clinical progress. A review of the current status and prospects.Osteoarthr Cartil.2002;10:432-463.[6]Eyrich D,Brandl F,Appel B,et al.Long-term stable fibrin gels for cartilage engineering. Biomaterials.2007;28(1):55-65.[7]Mercier NR, Costantino HR, Tracy MA,et al.A novel injectable approach for cartilage formation in vivo using PLG microspheres. Ann Biomed Eng.2004;32:418-429.[8]Chun KW, Yoo HS, Yoon JJ, et al.Biodegradable PLGA microcarriers for injectable delivery of chondrocytes: effect of surface modification on cell attachment and function. Biotechnol. Prog.2004;20:1797-1801.[9]Newman KD,McBurney MW.Poly(D-,L-lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres as biodegradable microcarriers for pluripotent stem cells. Biomaterials.2004;25:5763-5771.[10]Li YY, Cheng HW, Cheung KM,et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-collagen microspheres for articular cartilage repair: cell density and differentiation status. ActaBiomater.2014;10: 1919-1929.[11]Wakitani S, Goto T, Pineda SJ, et al. Mesenchymal cell-based repair of large, full-thickness defects of articular cartilage.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76(4):579-592.[12]Asik M, Ciftci F, Sen C, et al.The microfracture technique for the treatment of full-thickness articular cartilage lesions of the knee: midterm results. Arthroscopy.2008;24(11):1214-1220.[13]Lin YM, Lim JF, Lee J, et al. Expansion in microcarrier spinner cultures improves the chondrogenic potential of human early mesenchymal stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(6):740-753.[14]Pettersson S, Wetterö J, Tengvall P, et al. Cell expansion of human articular chondrocytes on macroporous gelatine scaffolds-impact ofmicrocarrier selection on cell proliferation. Biomed Mater. 2011;6(6):065001.[15]Kang H, Lu S, Peng J, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of human adipose�derived stem cells using microcarrier and bioreactor combination technique. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11(2): 1195-1199.[16]Goepfert C, Lutz V, Lünse S, Kittel S, et al. Evaluation of cartilage specific matrix synthesis of human articular chondrocytes after extended propagation on microcarriers by image analysis. Int J Artif Organs. 2010; 33(4):204-218.[17]Beris AE,Lykissas MG,Kostas-Agnantis I,et al.Treatment of full-thickness chondral defects of the knee with autologous chondrocyte implantation: a functional evaluation with long-term follow up.Am J Sports Med.2012;40:562-567.[18]Marlovits S, Tichy B, Truppe M,et al.Collagen expression in tissue engineered cartilage of aged human articular chondrocytes in a rotating bioreactor. IntJ Artif Organs.2003; 26(4):319-330.[19]Schulze-Tanzil G, de Souza P, Villegas Castrejon H, et al. Redifferentiation of dedifferentiated human chondrocytes in high-density cultures. Cell Tissue Res.2002;308: 371-379.[20]Hong Y, Gao C, Xie Y, et al.Collagen-coated polylactide microspheres as chondrocyte microcarriers. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6305-6313.[21]Cochis A, Grad S, Stoddart MJ, et al. Bioreactor mechanically guided 3D mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenesis using a biocompatible novel thermo-reversible methylcellulose-based hydrogel. Sci Rep. 2017;23:45018.[22]Chen J, Yuan Z, Liu Y, et al. Improvement of In Vitro Three-Dimensional Cartilage Regeneration by a Novel Hydrostatic PressureBioreactor. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(3):982-991.[23]Nazempour A, Quisenberry CR, Abu-Lail NI,et al. Combined effects of oscillating hydrostatic pressure, perfusion and encapsulation in a novelbioreactor for enhancing extracellular matrix synthesis by bovine chondrocytes. Cell Tissue Res. 2017 Jul 7.[24]Chung HJ, Go DH, Bae JW,et al. Synthesis and characterization of Pluronic grafted chitosan copolymer as a novel injectable biomaterial.CurrApplPhys. 2005;5:485–488.[25]Formica FA, Öztürk E, Hess SC,et al. A Bioinspired Ultraporous Nanofiber-Hydrogel Mimic of the Cartilage Extracellular Matrix.Adv Healthc Mater.2016;25:450-488.[26]Pescador D, Ibáñez-Fonseca A, Sánchez-Guijo F, et al. Regeneration of hyaline cartilage promoted by xenogeneic mesenchymal stromal cells embedded within elastin-like recombinamer-based bioactive hydrogels. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2017;28(8):115.[27]Yao Y, Huang Y, Qian D, et al. Effect of Various Ratios of Co-Cultured ATDC5 Cells and Chondrocytes on the Expression of Cartilaginous Phenotype in Microcavitary Alginate Hydrogel. J Cell Biochem. 2017 Jun 15.[28]Olubamiji AD, Zhu N, Chang T, et al. Traditional Invasive and Synchrotron-Based Noninvasive Assessments of Three-Dimensional-Printed Hybrid Cartilage Constructs In Situ. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2017;23(3):156-168. |
.jpg)
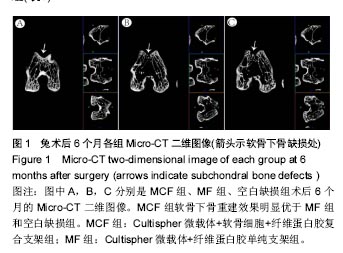
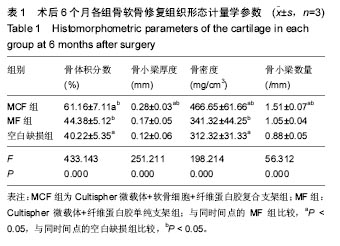
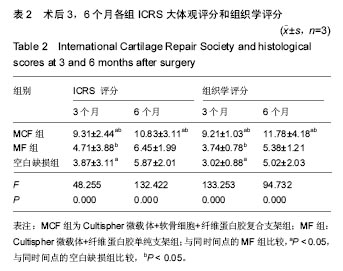
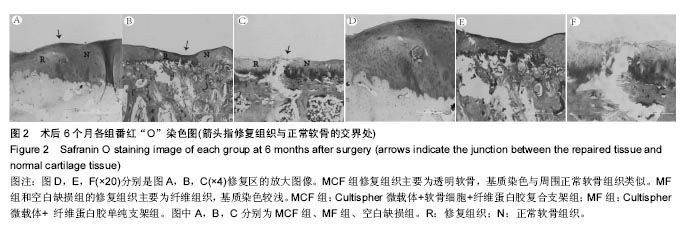
.jpg)