| [1] Stary HC.Natural history and histological classification of at herosclerotic lesions. Thromb Vasc Biol.2006;20(5):1177-1178.[2] Holzapfel GA,Mulvihill JJ,Cunnane EM,et al.Computa-tional approaches for analyzing the mechanics of athero-sclerotic plaques: A review. J Biomech.2014;47(4) :859-869.[3] Dong JL,Inthavong K,Tu JY.Image-based computational hemodynamics evaluation of atherosclerotic carotid bifurca-tion models.Comput Biol Med.2013;43 (4):1353-1362.[4] Wong K,Thavornpattanapong P,Cheung C,et al. Bio-mechanical investigation of pulsatile flow in a three-dimen-sional atherosclerotic carotid bifurcation model. J MechMed Biol.2013;13(1):1-21.[5] 张弛,韩景芸,蒲放,等. 颈内动脉虹吸部血流的数值计算和模型实验[J].医用生物力学,2013,28(1):56-62.[6] 牛小千.颈动脉内中膜厚度相关影响因素分析[J].中华临床医师杂志,2015,9(23):4471-4473.[7] 阚艳敏,马琳,杨华,等.正常高值血压者颈动脉和股动脉弹性的改变及其相关性[J].中国动脉硬化杂志2015,23(7):685-688.[8] Homburg PJ, Rozie S, van Gils MJ, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque ulcerationin the symptomatic internal carotid artery is associated withnonlacunar ischemic stroke. Stroke. 2010;41: 1151-1156.[9] Clerin V,Nichol JW,Petko M,et al.Tissue engineering ofarteries by directed remodeling of intact arterial segments. Tissue Eng.2003;9(3):461-472.[10] Jackson ZS,Dajnowiec D,Gotlieb AI,et al.Partial offloadingof longitudinal tension induces arterial tortuosity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2005;25 (5):957-962.[11] Jackson ZS,Gotlieb AI,Langille BL.Wall tissue remodelingregulates longitudinal tension in arteries. Circ Res. 2002;90(8):918-925.[12] Teng Z,Zhang Y,Huang Y,et al.Material properties of components in human carotid atherosclerotic plaques: A u-niaxial extension study. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(12):5055-5063.[13] Campbell IC,Weiss D,Suever JD,et al.Biomechanical modeling and morphology analysis indicates plaque rupturedue to mechanical failure unlikely in atherosclerosis-pronemice.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2013;04(3):H473-486.[14] Lu J,Duan W,Qiao A.Finite element analysis of mechanics of neovessels with intraplaque hemorrhage in carotid atherosclerosis. Biomed Eng Online.2015;14(Suppl 1): S3 (1-11).[15] Jin H, Yang Q, Ji F,et al.Human amniotic epithelial cell transplantation for the repair of injured brachial plexus nerve: evaluation of nerve viscoelastic properties. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(2):260-265.[16] 王秀玲,张继波,李新颖.青年与老年颈总动脉力学特性对比分析[J].中国老年学杂志 2015,35 (2):6514-6515.[17] Nagai Y,Metter EJ ,Earley CJ, et al . Increased carotid artery inti2 mal2media thickness in asymptomatic older subjects with exercise2 induced myocardial ischemia. Circulation. 1998;98(15):1504-1510.[18] McQuilan BM,Hung J,Beilby JP, et al. Antioxidant vitamins andthe risk of carotid atherosclerosis. The perth carotid ultrasound di2 sease assessment study (CUDAS).J Am Coll Cardiol.2001;38(7):1788-1793.[19] Fields JZ ,Walton KG,Schneider RH, et al.Effect of multimodalitynatural medicine program on carotid atherosclerosis in order sub2jects :a pilot trial of Maharishi Vedic Medicine. Am J Caridiol.2002;89(8):952-957.[20] Benetos A,Laurent S,Hoeks AP,et al.Arterial alterations with aging and high blood pressure. A noninvasive study of carotid] O'Rourke MFHashimotoJ. Mechanical factors in arterial aging: aclinical perspective.J Am CollCardiol.2007;50:1-13.[21] Yasmin,McEniery CM,O'Shaughnessy KM,et al.Variation in thehuman matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene is associated with arterialstiffness in healthy individuals.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2006;26:1799-1805. |
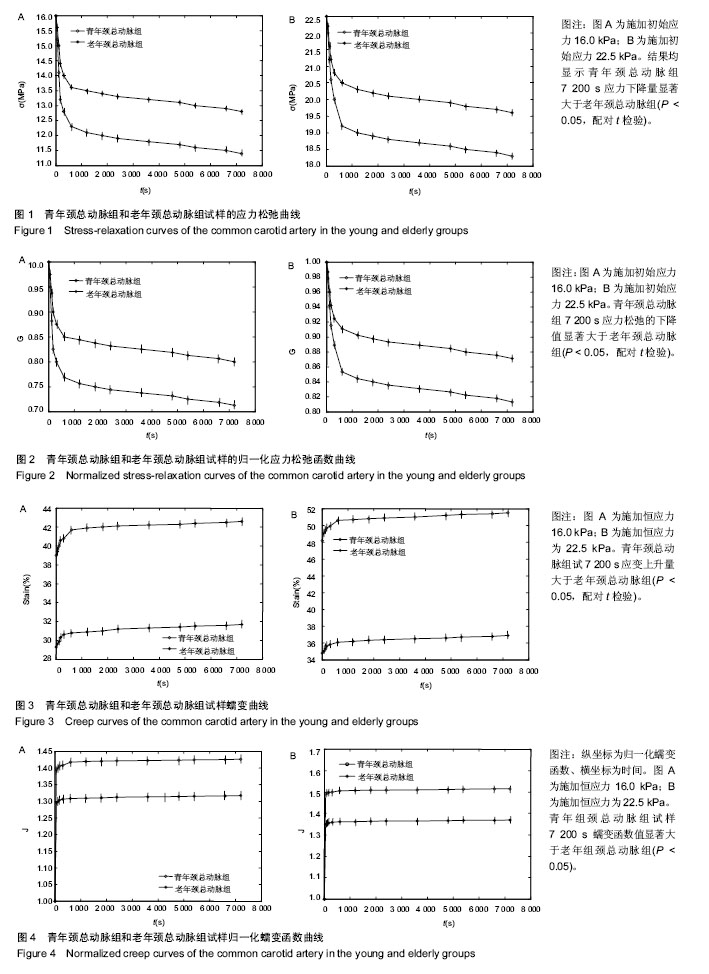
.jpg)



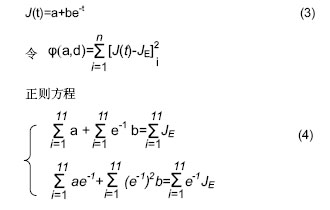


.jpg)