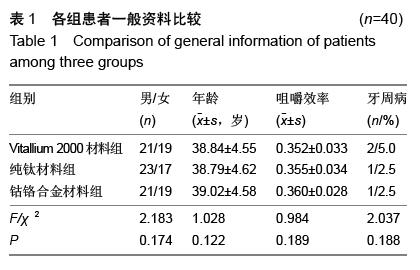
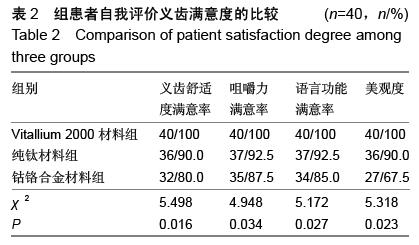
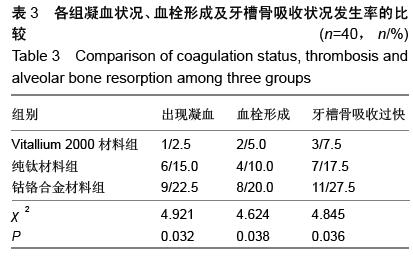
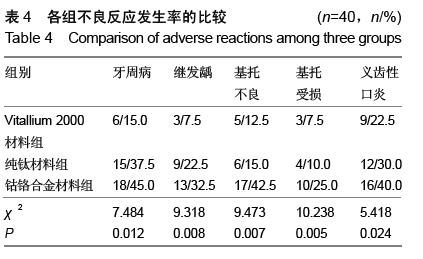
| [1] 王兴,孟箭.骨缺损异种骨移植同期种植修复疗效的锥形束CT评价[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(1):66-70.
[2] 钟群,彭艳,邬雪颖,等.义齿稳固剂影响无牙下颌牙槽嵴应力分布的光弹性分析[J].上海口腔医学, 2014,23(1): 46-50.
[3] 兰旭,杨瑛,杨秋霞.两种卡环作用于钴铬金属冠的固位力衰减及冠表面磨损研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2014, 30(2): 165-168.
[4] 邬雪颖,钟群.复合树脂高强纤维修复牙周炎患者下前牙缺失及固定松动牙[J].上海口腔医学, 2014,23(2): 204-208.
[5] 蒙萌,李冬梅,马楚凡,等.牙列缺损的功能分类与牙齿磨耗相关性的临床调查研究[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2013, 23 (2):132-135.
[6] 吕俊邦,邬惠良,张焱,等.可摘局部义齿质量量表应用效果评价[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(1):77-80.
[7] 贾爽,王德芳,叶荣荣,等.钴铬合金、钛合金与高钴铬钼合金铸造卡环循环疲劳的研究[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2013, 33 (6):782-785.
[8] 沈意涵,邹多宏,吴轶群.牙种植体周围炎相关因素和治疗新进展[J].上海口腔医学,2014,23(6):763-768.
[9] 苏勤,徐萍,金松,等.三种不同材料支架义齿对临床修复效果的影响[J].实用医学杂志,2014,30(22):3598-3600.
[10] 郑黎薇,吴可伦,刘楠馨,等.变异链球菌对不同材料活动义齿牙冠黏附的研究[J].四川大学学报:医学版, 2015,46(1): 87-89+98.
[11] 罗新宇,倪峰,柏全民,等.10例牙齿重度磨损伴牙列缺损种植修复与咬合重建[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2015, 25(1):41-44.
[12] 杨雪,荣起国,杨亚东.附着体类型对种植支持可摘局部义齿应力分布的影响[J].北京大学学报:医学版, 2015,47(1):72-77.
[13] 牛茂,许在俊,李月.基于三维打印技术制作可摘局部义齿支架树脂熔模的适合性研究[J].重庆医学, 2015,23(9): 1235-1238.
[14] 梁照,赵瑞芳,周以钓,等.非标准牙片牙槽骨吸收率测定系统[J].临床口腔医学杂志,1992, 8(3):148-150.
[15] 程玮,于海利,林雪芬,等.不同氟浓度人工唾液对3种牙用铸造合金表面形貌的影响[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2012, 30(1):18-21.
[16] 王来杰,彭辉,刘梅,等.两种可摘局部义齿修复上前牙缺失效果的对比研究[J].南京医科大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 32 (2): 284-285.
[17] 朱彦红,张博,刘亦洪,等.铸造支架式可摘局部义齿折断分析[J].北京大学学报:医学版, 2012,44(1):80-83.
[18] 杨彦伟,张少锋,张宏晨,等.可摘义齿着色影响因素的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2012,28(2):219-222.
[19] 冷旭,毛钊.义齿软衬材料表面白色念珠菌黏附的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2012,25(4):442-445.
[20] 王珏,乔广艳,沈庆平,等.氟对纯钛表面变形链球菌和血链球菌黏附的影响[J].上海口腔医学, 2015,24(2): 141-146.
[21] 王蔚,侯玉明,李佳佳,等.不同清洁方式对义齿树脂基托粗糙度的影响[J].中南大学学报:医学版, 2013,38(10):1065-1069.
[22] 黄磊,王鹏.铸造纯钛环修复龈下残根的临床疗效评价[J].上海口腔医学,2013,22(5):581-584.
[23] 吴艳芬,吴凤鸣.3种义齿清洁剂对钴铬合金及纯钛耐腐蚀性的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2013,29 (5): 646-650.
[24] Cho YB,Moon SJ,Chung CH,et al.Resorption of labial bone in maxillary anterior implant.J Adv Prosthodont. 2011;3(2):85-89.
[25] Jensen T,Schou S,Stavropoulos A,et al.Maxillary sinus floor augmentation with Bio-Oss or Bio-Oss mixed with autogenous bone as graft in animals:a systematic review .Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 41(1):114-120.
[26] Miyamoto Y,Obama T. Dental cone beam computed tomography analyses of postoperative labial bone thickness in maxillary anterior implants: comparing immediate and delayed implant placement.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent.2011;31(3):215-225.
[27] Zhang Q,Witter DJ,Gerritsen AE,et al.Functional dental status and oral health-related quality of life in an over 40-years old Chinese population.Clin Oral Invest. 2012;27(1):27.
[28] Cunha-Cruz J, Pashova H,Packard JD,et al.Tooth wear: prevalence and associated factors in general practice patients.Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2010; 38(3): 228-234.
[29] Wang D,Künzel A,Golubovic V,et al.Accuracy of peri-implant bone thickness and validity of assessing bone augmentation material using cone beam computed tomography.Clin Oral Investig. 2013;17(6):1601-1609.
[30] Spin -Neto R,Stavropoulos A,Pereira LA,et al.Fate of autologous and fresh-frozen allogeneic block bone grafts used for ridge augmentation. A CBCT -based analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res.2013;24(2):167-173.
[31] Dreiseidler T,Tandon D,Ritter L,et al.Accuracy of a newly developed open-source system for dental implant planning.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2012; 27(1):128-137.
[32] 彭艳, 焦婷,金文忠,等.舌向集中 全口义齿应力分布的光弹性研究(下颌种植覆盖义齿加载)[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2012,32(3):317-320.
[33] Cheng H,Xu M,Zhang H,et al.Cyclic fatigue properties of cobalt-chromium alloy clasps for partial removable dental prostheses.J Prosthet Dent.2010;104(6): 389-396.
[34] Nguyen TC,Witter DJ,Bronkhorst EM,et al.Dental functional status in a Southern Vietnamese adult population-an analysis by a combined quantitative and qualitative classification system.Int J Prosthodont.2011; 24(1):30-37.
[35] Zhang Q,Witter DJ,Bronkhorst EM,et al.Oral health and prosthetic status of an urban and rural population over 40 years in shandong province,china. BMC Public Health.2011; 1(11):420.
[36] Zhang Q,Witter DJ,Bronkhorst EM,et al.Dental functional status with and without tooth replacement in a Chinese adult population.Clin Oral Invest. 2012; 16(4):1251-1259.
[37] 王旭,钟丽芳,温竹,等.无牙颌患者全口义齿修复人工牙选择的研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2010,3(9):562-563.
[38] 张薇,刘娟,李长福.着色介质及表面粗糙度对热固化基托树脂着色的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2012,28(1): 22-25.
[39] 毕瑞野,樊怡,宋东哲,等.活动义齿的清洁方法[J].国际口腔医学杂志, 2013,40(1):109-116.
[40] Hagiwara Y, Nakajima K. Application of Ce-TZP/Al<sub>2</sub>O<sub>3</sub> nanocomposite to the framework of an implant-fixed complete dental prosthesis and a complete denture.J Prosthodont Res.2016. pii: S1883-1958(16)00018-9.
[41] Siddharth R,Gautam R,Chand P,et al.Quantitative analysis of leaching of different metals in human saliva from dental casting alloys: An in vivo study.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2015;15(3):206-210.
[42] Zhang S,Qiu J,Ren Y, et al.Reciprocal interaction between dental alloy biocorrosion and Streptococcus mutans virulent gene expression.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2016;27(4):78.
[43] Kirmanidou Y,Sidira M,Drosou ME,et al.New Ti-Alloys and Surface Modifications to Improve the Mechanical Properties and the Biological Response to Orthopedic and Dental Implants: A Review.Biomed Res Int. 2016; 2016:2908570.
[44] van der Zel JM.[Dissertations 25 years after date 44. Behaviour at high temperatures of palladium based dental alloys].Ned Tijdschr Tandheelkd. 2016;123(2): 93-97.
[45] 45 Altuna P,Lucas-Taulé E,Gargallo-Albiol J,et al.Clinical evidence on titanium-zirconium dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg.2016.pii: S0901-5027(16) 00025-4.
[46] Emir F, Ayyildiz S.Comments regarding Lucchetti MC, Fratto G, Valeriani F, De Vittori E, Giampaoli S, Papetti P, et al. Cobalt-chromium alloys in dentistry: An evaluation of metal ion release. J Prosthet Dent 2015; 114:602-608. |
.jpg)