中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (44): 6557-6563.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.44.003
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
髋关节置换前后髋关节功能与维生素D水平的多元线性回归分析
张 炜1,汤在祥2,耿德春1,朱 锋1,董汉青1,王熠军1,徐耀增1
- 1苏州大学附属第一医院骨科,江苏省苏州市 215006;2苏州大学医学部公共卫生学院,江苏省苏州市 215123
Multiple linear regression analysis of hip function and vitamin D levels before and after hip arthroplasty
Zhang Wei1, Tang Zai-xiang2, Geng De-chun1, Zhu Feng1, Dong Han-qing1, Wang Yi-jun1, Xu Yao-zeng1
- 1Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Suzhou University, Suzhou 215006, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Insitute of Public Health, Medical School of Suzhou University, Suzhou 215123, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
维生素D:维生素D为胆固醇类衍生物,最初因抗佝偻病作用被认识,目前认为维生素D也是一种类固醇激素。而且维生素D被证明与癌症、高血压、糖尿病、多发性硬化等许多疾病有关,并且在骨科中越来越受到重视。
髋关节置换:始于上世纪中期,距今已经有50多年历史,随着假体材料不断改进,置换技术的成熟,已经成为关节外科中最成功的手术之一。除了假体的材料、手术技巧、术后康复等主要因素外,仍在探索哪些因素对其预后有影响。
摘要
背景:髋关节置换患者中维生素D低水平的发病率及其影响国内尚未有过报道。全髋关节置换的患者维生素长期处于低水平状态没有受到足够的重视。
目的:确定接受全髋关节置换患者置换前维生素D低水平的患病率,分析置换前维生素D水平与髋关节功能评分之间的关系。
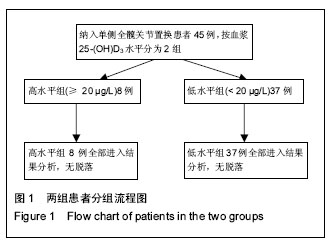
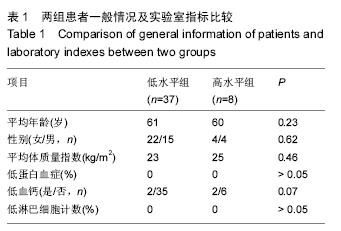
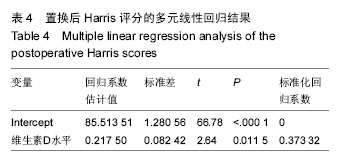
方法:纳入2013年7月至2014年8月在苏州大学附属第一医院行初次髋关节置换的患者45例45髋。根据置换前血浆维生素D水平将患者分为维生素D低水平组(< 20 μg/L)和维生素D高水平组(≥ 20 μg/L)。观察并比较2组患者的一般情况、置换前及置换后末次随访时的髋关节功能评分,采用多元线性回归分析法分析维生素D水平与髋关节置换前后髋关节功能的关系。随访时间11-14个月。
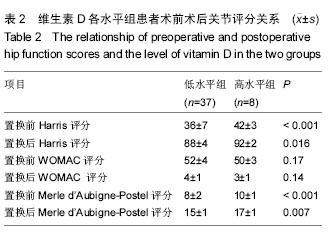
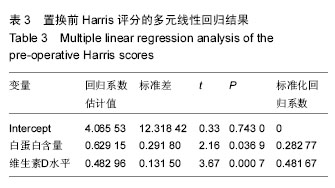
结果与结论:①维生素D低水平的患病率为82%(使用20 μg/L为标准);②与维生素D高水平组相比,维生素D低水平组置换前Harris评分和Merle d’Aubigne-Postel评分更低(P均< 0.05);置换后末次随访时,维生素D低水平组Harris评分和Merle d’Aubigne-Postel评分仍然低于维生素D高水平组(P均< 0.05);③通过对置换前、置换后Harris评分行多元线性回归分析,置换前维生素D水平与置换前、置换后的Harris评分呈紧密正相关,且有统计学意义(P < 0.05);④结果提示,髋关节置换患者有着较高的维生素D低水平发病率,且维生素D低水平组置换前、置换后髋关节功能评分较维生素D高水平组低,维生素D水平和置换前、置换后关节功能评分之间呈紧密正相关性。建议髋关节置换患者常规补充维生素D、钙;维生素D水平对于患者的病情评价、术后预期有一定指导意义。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-0424-4884(徐耀增)
中图分类号:
.jpg)