| [1] 曹聪,刘海春,武文亮,等.高龄髋部骨折后死亡原因调查及相关因素分析[J]. 医学与哲学,2015,36(6):48-50.
[2] 王振恒,方永超,阚翔翔,等.影响老年髋部骨折患者术后1年死亡率的因素分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2014, 22(2): 110-114.
[3] 张英泽.临床创伤骨科流行病学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2009:150-170.
[4] 王欣荣,应汉杰,欧阳平凯,等.骨质疏松症的发病机理及其治疗[J].生物工程进展,2001,21(3):54-56.
[5] 孙俊英,洪天禄,唐天泗,等.自体游离髂骨移植重建髋臼后壁陈旧性骨折缺损[J].中华骨科杂志,2000,20(12):7092-7111.
[6] Song JW, Chung KC. Observational studies: cohort and case-control studies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2010; 126(6):2234-2242.
[7] Pereira SR, Puts MT, Portela MC, et al. The impact of prefracture and hip fracture characteristics on mortality in older persons in Brazil. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010; 468(7):1869-1883.
[8] Juliebø V, Krogseth M, Skovlund E, et al. Medical treatment predicts mortality after hip fracture. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010;65(4):442-449.
[9] Lee HB, Mears SC, Rosenberg PB, et al. Predisposing factors for postoperative delirium after hip fracture repair in individuals with and without dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(12):2306-2313.
[10] Castronuovo E, Pezzotti P, Franzo A, et al. Early and late mortality in elderly patients after hip fracture: a cohort study using administrative health databases in the Lazio region, Italy. BMC Geriatr. 2011;11:37.
[11] Lauritzen JB, Duus BR, van der Mark S. Is mortality after hip fracture associated with surgical delay or admission during weekends and public holidays? A retrospective study of 38,020 patients. Acta Orthop. 2012;83(6):609-613.
[12] Shoda N, Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H, et al. Risk factors affecting inhospital mortality after hip fracture: retrospective analysis using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination Database. BMJ Open. 2012; 2(3). pii: e000416.
[13] Valizadeh M, Mazloomzadeh S, Golmohammadi S, et al. Mortality after low trauma hip fracture: a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2012;13:143.
[14] Kim SD, Park SJ, Lee DH, et al. Risk factors of morbidity and mortality following hip fracture surgery. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2013;64(6):505-510.
[15] Buecking B, Eschbach D, Koutras C, et al. Re-admission to Level 2 unit after hip-fracture surgery - Risk factors, reasons and outcome. Injury. 2013; 44(12):1919-1925.
[16] Koh GC, Tai BC, Ang LW, et al. All-cause and cause-specific mortality after hip fracture among Chinese women and men: the Singapore Chinese Health Study. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(7):1981-1989.
[17] Ariza-Vega P, Kristensen MT, Martín-Martín L, et al. Predictors of long-term mortality in older people with hip fracture. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2015;96(7):1215-1221.
[18] Forget P, Moreau N, Engel H, et al. The neutrophil- to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) after surgery for hip fracture (HF). Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2015;60(2):366-371.
[19] Maxwell MJ, Moran CG, Moppett IK. Development and validation of a preoperative scoring system to predict 30 day mortality in patients undergoing hip fracture surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2008;101(4):511-517.
[20] Ho CA, Li CY, Hsieh KS, et al. Factors determining the 1-year survival after operated hip fracture: a hospital-based analysis. J Orthop Sci. 2010;15(1): 30-37.
[21] Hagino T, Ochiai S, Sato E, et al. Prognostic prediction in patients with hip fracture: risk factors predicting difficulties with discharge to own home. J Orthop Traumatol. 2011;12(2):77-80.
[22] Librero J, Peiró S, Leutscher E, et al. Timing of surgery for hip fracture and in-hospital mortality: a retrospective population-based cohort study in the Spanish National Health System. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12:15.
[23] Shen SH, Huang KC, Tsai YH, et al. Risk analysis for second hip fracture in patients after hip fracture surgery: a nationwide population-based study. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2014;15(10):725-731.
[24] Miyanishi K, Jingushi S, Torisu T. Mortality after hip fracture in Japan: the role of nutritional status. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2010;18(3):265-270.
[25] Hung LW, Tseng WJ, Huang GS, et al. High short-term and long-term excess mortality in geriatric patients after hip fracture: a prospective cohort study in Taiwan. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2014;15:151.
[26] Holvik K, Ranhoff AH, Martinsen MI, et al. Predictors of mortality in older hip fracture inpatients admitted to an orthogeriatric unit in oslo, norway. J Aging Health. 2010; 22(8):1114-1131.
[27] Oztürk A, Ozkan Y, Akgöz S, et al. The risk factors for mortality in elderly patients with hip fractures: postoperative one-year results. Singapore Med J. 2010;51(2):137-143.
[28] Gdalevich M, Cohen D, Yosef D, et al. Morbidity and mortality after hip fracture: the impact of operative delay. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2004;124(5): 334-340.
[29] Kang BJ, Lee YK, Lee KW, et al. Mortality after hip fractures in nonagenarians. J Bone Metab. 2012; 19(2):83-86.
[30] Nettleman MD, Alsip J, Schrader M, et al. Predictors of mortality after acute hip fracture. J Gen Intern Med. 1996;11(12):765-767.
[31] Karaman Ö, Özkazanl? G, Orak MM, et al. Factors affecting postoperative mortality in patients older than 65 years undergoing surgery for hip fracture. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2015;21(1):44-50.
[32] Härstedt M, Rogmark C, Sutton R, et al. Impact of comorbidity on 6-month hospital readmission and mortality after hip fracture surgery. Injury. 2015; 46(4): 713-718.
[33] Wehren LE, Hawkes WG, Orwig DL, et al. Gender differences in mortality after hip fracture: the role of infection. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18(12):2231-2237.
[34] Haentjens P, Autier P, Barette M, et al. Survival and functional outcome according to hip fracture type: a one-year prospective cohort study in elderly women with an intertrochanteric or femoral neck fracture. Bone. 2007;41(6):958-964.
[35] Roberts SE, Goldacre MJ. Time trends and demography of mortality after fractured neck of femur in an English population, 1968-98: database study. BMJ. 2003;327(7418):771-775.
[36] Fransen M, Woodward M, Norton R, et al. Excess mortality or institutionalization after hip fracture: men are at greater risk than women. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002; 50(4):685-690.
[37] Deakin DE, Boulton C, Moran CG. Mortality and causes of death among patients with isolated limb and pelvic fractures. Injury. 2007;38(3):312-317.
[38] Casaletto JA, Gatt R.Post-operative mortality related to waiting time for hip fracture surgery. Injury. 2004; 35(2): 114-120.
[39] Doruk H, Mas MR, Yildiz C, et al. The effect of the timing of hip fracture surgery on the activity of daily living and mortality in elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2004;39(2):179-185.
[40] Cornwall R, Gilbert MS, Koval KJ, et al. Functional outcomes and mortality vary among different types of hip fractures: a function of patient characteristics.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(425):64-71.
[41] 丰景斌,谷贵山,方秀统,等.老年骨质疏松性髋部骨折患者实施内固定与人工关节置换术的效果及运动功能恢复状态比较[J].中国临床康复, 2004, 8(27):5907- 5909.
[42] 夏军,黄钢勇,黄煌渊. 80岁及以上髋部骨折患者围手术期治疗的探讨[J].中国老年医学杂志,2005,24(5):355-357.
[43] 中华内科杂志编辑委员会.侵袭性肺部真菌感染的诊断标准与治疗原则(草案)[J]. 中华内科杂志,2006,45(8): 697-700.
[44] Söderqvist A, Miedel R, Ponzer S, et al. The influence of cognitive function on outcome after a hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(10):2115-2123. |
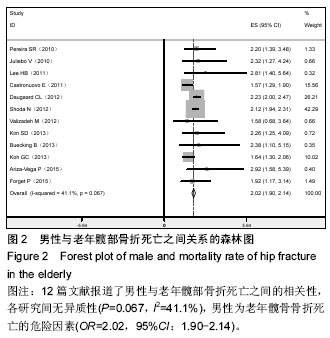
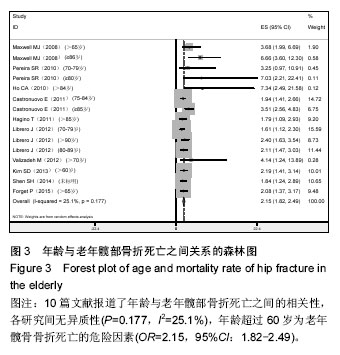
.jpg)



.jpg)