Design
Animal behavioral and pathological controlled study.
Time and setting
Experiments were conducted in the Key Laboratory of Tissue Construction and Testing, Southern Medical University and Central Laboratory of Yuebei People’s Hospital of Shantou University in China from August 2011 to December 2013.
Materials
Experimental animals
Female Sprague-Dawley rats were provided by Experimental Animal Center, Southern Medical University in China license No. SCXK(Yue)2006-00152006B023. A total of 60 adult female healthy Sprague-Dawley rats weighing 180–250 g , averagely (217±5.48) g, were randomly selected and assigned to three groups. Sham surgery group (n=12): vertebral plate was opened. Conventional spinal cord transection group (n=24): complete spinal cord transection and PBS injection were conducted conventionally. Microscopic spinal cord transection group (n=24): complete spinal cord transection and PBS injection were conducted by standardization micromanipulation technique. Each group was randomly assigned to 7-day, 14-day and 28-day groups according to time points after model establishment. For dead rat models, dead reasons were analyzed, and dead models were supplemented by new ones. The main experiment was done in the Key Laboratory of Tissue Construction and Testing, Southern Medical University in China.
.jpg)
MethodsRat models of spinal cord transaction [20]
The rats were intraperitoneally anesthetized with 100 g/L chloral hydrate (300 mg/kg). They were fixed on the operating table in a prone position. Under aseptic condition, T9 spinous cone was considered as a center. A 2 cm longitudinal incision was made. Bilateral paraspinal muscles of spinous process were dissociated bluntly until reaching the surface of vertebral plate. Bilateral paraspinal muscles were drawn using a mini-automatic retractor to expose lamina and spinous cone. Spinous processes of T8-T10 cones were bitten with a rongeur. Under a 10-fold operating microscope, T8-T10 intervertebral yellow ligament of rats in the microscopic spinal cord transection group was bluntly isolated with sub-miniature nerve stripping. T8 and T9 vertebral plates were bitten with a mini-gun clamp until reaching bilateral facet inner edge. Under the operating microscope, spinal dura mater was longitudinally cut about 0.5 cm. Through the incision of the spinal dura mater, outside the dural subarachnoid region, the ultra-thin knife blade was against the side wall of the bone. Spinal cord was completely cut under the operating microscope, including spinal dorsal vein, spinal dorsal artery and ventral spinal artery. Two points were selected at the broken ends of the spinal cord, and the two points were 0.8 mm from the middle line and 0.5 mm from the stump. On the stereotaxic apparatus, capillary glass needle connected to 1 µL microinjector was vertically inserted below the spinal dura mater about 1.2 to 1.5 mm. Injection was conducted for more than 15 minutes and regulated by a screw nut. The needle was left in place for 10 minutes. The screw nut was slowly returned back, and the glass needle was pulled out[16, 21]. Above procedure was repeated four times. After four points of microinjection, the incision at the dura mater was sutured microscopically. The operation was finished by conventional method in the sham surgery group and conventional spinal cord transection group. The incision at the dura mater was covered with an autologous fascia of chest and back of rats, and then gradually sutured layer by layer[21-22].
Management after model establishment [22]
Animals from each group were intramuscularly daily injected with penicillin (3×104 U/kg) for 3 consecutive days after model induction. Four or five rats were housed in a cage at constant temperature. The padding was replaced by new every other day. Artificial bladder massage was done daily for urination, once in the morning and once in the evening.
Basso, Beattie and Bresnahan (BBB) score for evaluation of hindlimb motor function [22]
Hindlimb motor function was analyzed by BBB score at 7, 14 and 28 days after model induction in each group. BBB score contained 22 levels, complete paralysis as 0 point and complete normal as 21 points.
Drawn, fixed and sliced [8]
The animals were intraabdominally anesthetized with chloral hydrate (600 mg/kg) at 7, 14 and 28 days after model establishment in each group. The chest was opened, and right auricle was cut. Intubation was performed in the ascending aorta via the tip of the heart. At room temperature, 150 mL physiological saline was rapidly dripped until clear effluent was observed. Samples were fixed with 250 mL 40 g/L paraformaldehyde containing 0.1 mol/L PBS (pH 7.2–7.4). Fixative was rapidly dripped for 15 minutes, and then maintained for 4–5 hours. 1.5 cm spinal cord was collected taking transected site as a center, fixed in 40 g/L paraformaldehyde for 3 hours. 0.5 cm spinal cord was reserved at head and tail sides of the transected site. Spinal cord was serially sliced into 5 µm coronal sections.
Main outcome measures
There were BBB score of hindlimb motor function, and histopathological observation: tissue structure and morphological characteristics of spinal cord, transverse diameter of normal spinal cord, thickness of the glial scar at the transected site, the longitudinal distance between the two stumps, the transverse diameter of the spinal cord cavity, scar index, stump spacing index and cavity index (scar index = scar thickness/spinal cord diameter; stump spacing index = stump spacing/spinal cord diameter; cavity index = transverse diameter of the cavity/spinal cord diameter).
Statistical analysis
Statistical treatment was performed by the first and second authors. Measurement data were expressed as mean ± SD, and analyzed using SPSS 12.0 software. Intergroup comparison was done using group t-test. Pearson correlation coefficient between observational data and BBB score was calculated. A value of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
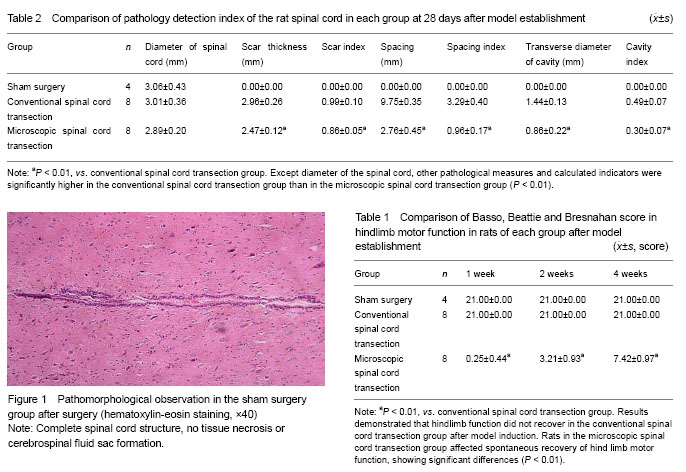
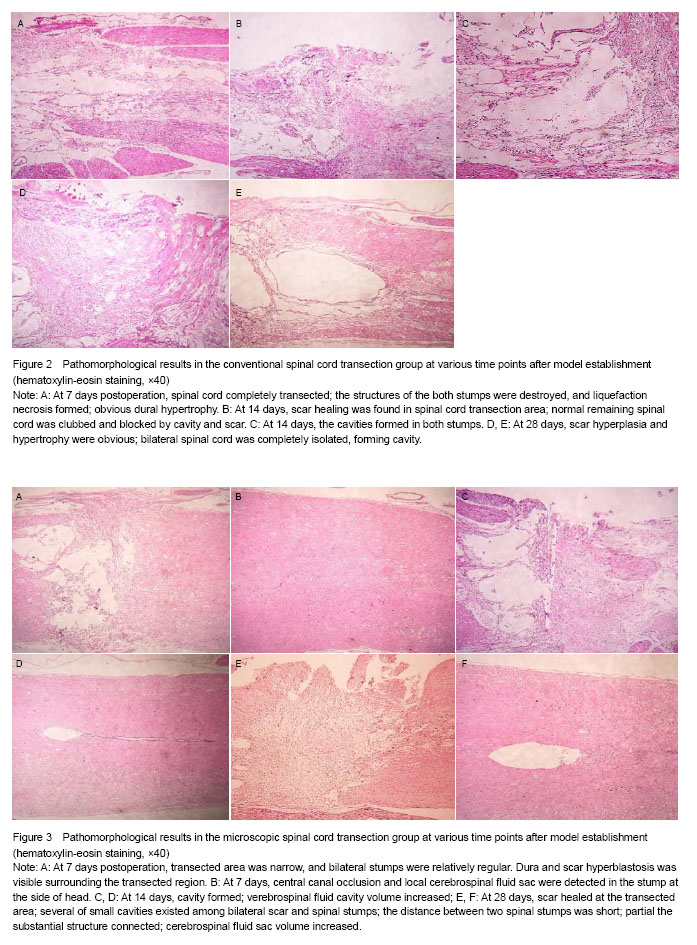
.jpg)