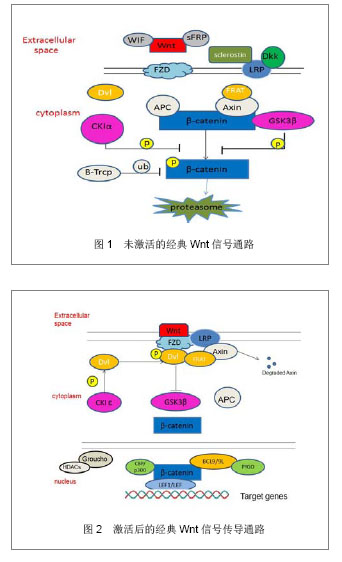
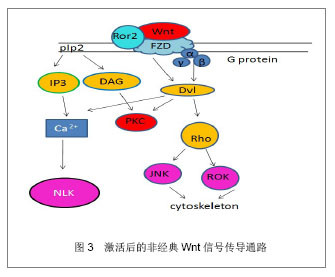
| [1]Pittenger MF,Mackay AM,Beck SC,et al.Multilineage pontential adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science.1999;(284):143.
[2]万晓晨,刘翠平,陈海啸,等. TGF-β/BMPs、Wnt和MAPK信号通路在间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化中的作用[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2008,30 (6):697-700.
[3]Nusse R. Wnt signaling in disease and in development. Cell Res. 2005;(15):28-32.
[4]Huelsken J, Behrens J. The Wnt signaling pathway. Journal of Cell Science. 2002;(115): 3977-3978.
[5]Ling L, Nurcombe V. Wnt signaling controls the fate of mesenchymal stem cells. Gene.2009;(433):1-7.
[6]Logan CY, Nusse A. The Wnt signaling pathway in development and disease. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.2004;(20):781-810.
[7]Ishitani T, Kishida S, Hyodo-Miura J, et al.The TAK1-NLK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Mol Cell Biol.2003; (23):131-139.
[8]Liu F, Kohlmeier S, Wang CY.Wnt signaling and skeletal development. Cell. Signal. 2008;(20):999-1009.
[9]Lu W, Yamamoto V, Ortega B, et al.Mammalian Ryk is a Wnt coreceptor required for stimulation of neurite outgrowth. Cell. 2004;(119):97-108.
[10]Aguilera O, Fraga MF, Ballestar E, et al. Epigenetic inactivation of the Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-1 (DKK-1) gene in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene.2006;(25):4116-4121.
[11]Cho SW, Her SJ, Sun HJ, et al.Differential effects of secreted frizzled-related proteins on osteoblastic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal cells and apoptosis of osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;367(2):399-405.
[12]Ehrlund A, Mejhert N, Lorente-Cebrián S, ,et al. Characterization of the Wnt Inhibitors Secreted Frizzled-Related Proteins (SFRPs) in Human Adipose Tissue. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013 Mar;98(3):E503-508.
[13]Van Raay TJ,Coffey RJ,Solnica-Krezel L. Zebrafish Naked1 and Naked2 antagonize both canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling.Dev Biol.2007;(309):68.
[14]Schmidt A, Ladage D, Schinköthe T, et al.Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor Controls Migration in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells.2006;24(7):1750-1758.
[15]Song L, Webb NE, Song Y, et al.Identification and Functional Analysis of Candidate Genes Regulating Mesenchymal Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Multipotency. Stem Cells. 2006; 24(7): 1707-1718.
[16]Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ, et al.Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2004; (93):1210-1230.
[17]Baksh D, Tuan RS. Canonical and non-canonical Wnts differentially affect the development potential of primary isolate of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Physiol.2007;(212):817-826.
[18]Qiu W, Andersen TE, Bollerslev J, et al.Patients with high bone mass phenotype exhibit enhanced osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of adipogenesis of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Miner Res.2007;(22): 1720-1731.
[19]Yamada A, Iwata T. Diverse functions of secreted frizzled-related proteins in the osteoblastogenesis of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Biomaterials.2013; 34(13):3270-3278.
[20]Boland GM, Perkins G, Hall DJ, et al.Wnt 3a promotes proliferation and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2004; (93):1210-1230.
[21]de Boer J, Siddappa R, Gaspar C, et al. Wnt signaling inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Bone.2004;(34):818-826.
[22]Tang N, Song WX, Luo J, et al. BMP-9-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitors requires functional canonical Wnt/β-catenin signalling. J Cell Mol Med. 2009; 13(8B): 2448-2464.
[23]Nemoto E,Koshikawa Y. Wnt signaling inhibits cementoblast differentiation and promotes proliferation. Bone.2009;44(5): 805-812.
[24]Rybchyn MS, Slater M, Conigrave AD, et al. An Akt-dependent Increase in Canonical Wnt Signaling and a Decrease in Sclerostin Protein Levels Are Involved in Strontium Ranelate-induced Osteogenic Effects in Human Osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(27):23771-23779.
[25]Hartmann C.A Wnt canon orchestrating osteoblastogenesis. Trends Cell Biol. 2006;16(3):151-158.
[26]Bennett CN, Longo KA, Wright WS, et al. Regulation of osteoblastogenesis and bone mass by Wnt10b. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(9):3324-3329.
[27]Arnsdorf EJ, Tummala P, Kwon RY, et al. Mechanically induced osteogenic differentiation-the roleofRhoA,ROCKIIand eytoskeletal dynamics. J Cell Se.2009;(122):546-553.
[28]Lako M, Strachan T, Bullen P, et al. Iso lation,characterisation and embryonic expression of WNT11, a gene which maps to 11q13.5 and has possible roles in the development of skeleton, kidney and lung. Gene.1998;(219):101-110.
[29]Takada I, Mihara M,Suzawa M,et al.A histone lysine methyltransferase activated by non-canonical Wnt signalling suppresses PPAR-γ transactivation. Nature Cell Biology.2007; (9):1273-1285 .
[30]Bolzoni M, Donofrio G, Storti P, et al. Myeloma cells inhibit non-canonical wnt co-receptor ror2 expression in human bone marrow osteoprogenitor cells: effect of wnt5a/ror2 pathway activation on the osteogenic differentiation impairment induced by myeloma cells. Leukemia.2013;(27): 451-463.
[31]Nemoto E, Ebe Y. Wnt5a signaling is a substantial constituent in bone morphogenetic protein-2-mediated osteoblastogenesis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2012;422(4):627-632. |