[1] LENKE LG, KUKLO TR, ONDRA S, et al. Rationale behind the current state-of-the-art treatment of scoliosis (in the pedicle screw era). Spine. 2008;33:1051-1054.
[2] 吕国华,王冰,马泽民,等. 多节段椎弓根螺钉内固定系统矫正胸椎侧凸畸形的有效性和安全性评价[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004, 14(4):23-25.
[3] 张伟,朱晓东,吴大江,等. 置钉密度与Lenke 1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸矫正率的相关性[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(7): 558-561.
[4] MIN K, SDZUY C, FARSHAD M. Posterior correction of thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis with pedicle screw instrumentation: results of 48 patients with minimal 10-year follow-up. Eur Spine J. 2013; 22:345-354.
[5] DEDE O, WARD WT, BOSCH P, et al. Using the freehand pedicle screw placement technique in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis surgery: what is the incidence of neurological symptoms secondary to misplaced screws? Spine. 2014;39:286-290.
[6] 张国志,王宇飞,杨克敏,等. 全椎弓根螺钉一期后路手术治疗重度脊柱侧凸畸形[J]. 昆明医学院学报,2011,32(3):76-80+92.
[7] 申明奎,罗明,李鹏,等. 连续置钉、间断置钉和关键椎置钉治疗LenkeⅠ型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的疗效对比[J]. 中华小儿外科杂志,2018,39(1):57-63.
[8] DAFFNER SD, BEIMESCH CF, WANG JC. Geographic and demographic variability of cost and surgical treatment of idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2010;35:1165-1169.
[9] RUSHTON PR, ELMALKY M, TIKOO A, et al. The effect of metal density in thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2016;25(10): 3324-3330.
[10] KAMERLINK JR, QUIRNO M, AUERBACH JD, et al. Hospital cost analysis of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis correction surgery in 125 consecutive cases. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92:1097-1104.
[11] 曾忠友,裴斐,张建乔,等. 腰椎后路内固定融合术并发神经损伤的原因分析和处理[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2016,14(2):83-86.
[12] ODA I, ABUMI K, LU D, et al. Biomechanical role of the posterior elements, costovertebral joints, and rib cage in the stability of the thoracic spine. Spine. 1996;21:1423-1429.
[13] THAWRANI DP, GLOS DL, COOMBS MT, et al. Transverse process hooks at upper instrumented vertebra provide more gradual motion transition than pedicle screws. Spine. 2014;39:E826-832.
[14] QUICK ME, GRANT CA, ADAM CJ, et al. A biomechanical investigation of dual growing rods used for fusionless scoliosis correction. Clin Biomech. 2015;30:33-39.
[15] SUK SI, LEE CK, KIM WJ, et al. Segmental pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1995;20:1399-1405.
[16] 赵云飞,杨长伟,李明.全椎弓根螺钉治疗青少年特发性脊柱侧凸置钉策略的研究进展[J].骨科,2017,8(3):249-252.
[17] KETENCI IE, YANIK HS, DEMIROZ S, et al. Three-Dimensional Correction in Patients With Lenke 1 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Comparison of Consecutive Versus Interval Pedicle Screw Instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2016;41:134-138.
[18] HWANG CJ, LEE CK, CHANG BS, et al. Minimum 5-year follow-up results of skipped pedicle screw fixation for flexible idiopathic scoliosis. J Neurosurg Spine. 2011;15:146-150.
[19] 李志鲲,陈超,徐炜,等.关键椎置钉与连续置钉治疗LenkeⅠ型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸的疗效对比[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2015,13(5): 257-261.
[20] SHEN M, JIANG H, LUO M, et al. Comparison of low density and high density pedicle screw instrumentation in Lenke 1 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017;18: 336.
[21] LARSON AN, POLLY DW JR, ACKERMAN SJ, et al. What would be the annual cost savings if fewer screws were used in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis treatment in the US? J Neurosurg Spine. 2016;24:1
[22] Quan GM, Gibson MJ. Correction of main thoracic adolescent idiopathic scoliosis using pedicle screw instrumentation: does higher implant density improve correction? Spine. 2010;35:562-567.
[23] Bharucha NJ, Lonner BS, Auerbach JD, et al. Low-density versus high-density thoracic pedicle screw constructs in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: do more screws lead to a better outcome? Spine J. 2013;13: 375-381.
[24] Le Naveaux F, Aubin CE, Larson AN, et al. Implant distribution in surgically instrumented Lenke 1 adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: does it affect curve correction? Spine. 2015;40:462-468.
[25] 江华,肖增明,詹新立,等. Lenke 1型特发性脊柱侧凸患者术后顶椎区残留旋转的危险因素分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(15): 1428-1430.
[26] 郑欣,王渭君,钱邦平,等. 顶椎置钉与否对Lenke1型青少年特发性脊柱侧凸矫形效果的影响[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(8): 707-711.
[27] BEHENSKY H, COLE AA, FREEMAN BJ, et al. Fixed lumbar apical vertebral rotation predicts spinal decompensation in Lenke type 3C adolescent idiopathic scoliosis after selective posterior thoracic correction and fusion. Eur Spine J. 2007;16:1570-1578.
[28] SALMINGO RA, TADANO S, FUJISAKI K, et al. Relationship of forces acting on implant rods and degree of scoliosis correction. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2013;28:122-128.
[29] WANG X, AUBIN CE, LARSON AN, et al. Biomechanical analysis of pedicle screw density in spinal instrumentation for scoliosis treatment: first results. Stud Health Technol Inform . 2012;176:303-306.
[30] 马华松,海涌,白克文,等.青少年特发性脊柱侧凸节段性固定点的选择[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2004,12(Z1):41-43.
[31] BENGARD MJ, GARDNER MJ. Screw depth sounding in proximal humerus fractures to avoid iatrogenic intra-articular penetration. J Orthop Trauma. 2011;25(10):630-633.
[32] DELIKARIS A, WANG X, BOYER L, et al. Implant Density at the Apex Is More Important Than Overall Implant Density for 3D Correction in Thoracic Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Using Rod Derotation and En Bloc Vertebral Derotation Technique. Spine. 2018;43:E639-E647.
[33] SJOVOLD SG, ZHU Q, BOWDEN A, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of the Total Facet Arthroplasty System® (TFAS®): loading as compared to a rigid posterior instrumentation system. Eur Spine J. 2012;21: 1660-1673.
[34] WANG Z, SAKAKIBARA T, YOSHIKAWA T, et al. Do the position and orientation of the crosslink influence the stiffness of spinal instrumentation? Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30:176-180.
[35] KUKLO TR, DMITRIEV AE, CARDOSO MJ, et al. Biomechanical contribution of transverse connectors to segmental stability following long segment instrumentation with thoracic pedicle screws. Spine. 2008;33:E482-487.
[36] ALIZADEH M, KADIR MR, FADHLI MM, et al. The use of X-shaped cross-link in posterior spinal constructs improves stability in thoracolumbar burst fracture: a finite element analysis. J Orthop Res. 2013;31: 1447-1454.
[37] WEI FX, LIU SY, LIANG CX, et al. Transpedicular fixation in management of thoracolumbar burst fractures: monosegmental fixation versus short-segment instrumentation. Spine. 2010;35:E714-720.
[38] STRATHE AB, SORENSEN H, DANFAER A. A new mathematical model for combining growth and energy intake in animals: the case of the growing pig. J Theor Biol. 2009;261:165-175.
[39] WILKE HJ, MATHES B, MIDDERHOFF S, et al. Development of a scoliotic spine model for biomechanical in vitro studies. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2015;30:182-187. |
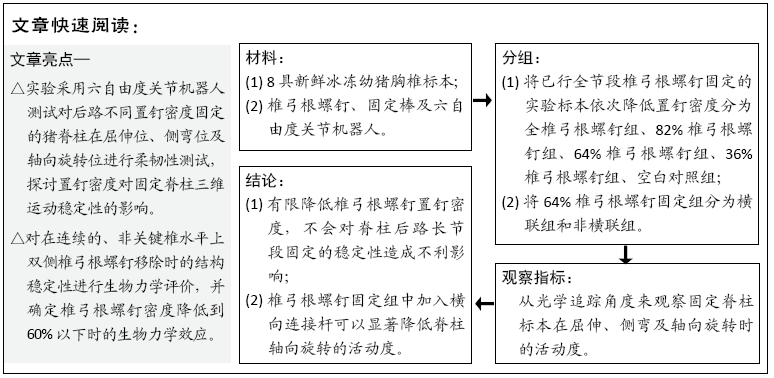 文题释义:
文题释义: