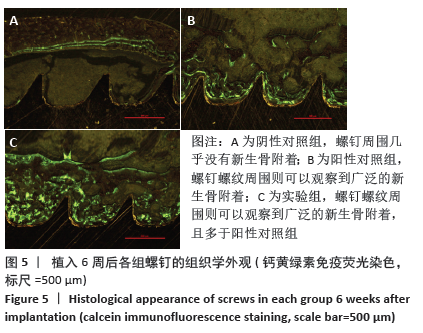
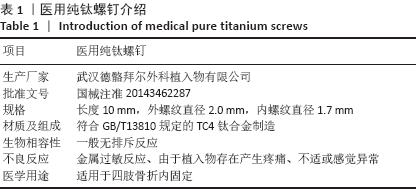
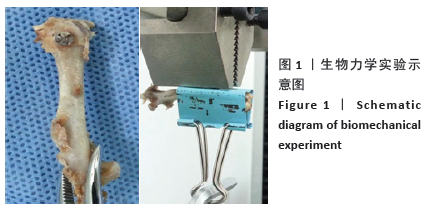
[1] ZHANG XJ, ZHAO XJ. In vitro bioactivity of silicon-incorporated titanium dioxide nanotubes. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2018;22(30):4864-4869.
[2] CIPRIANO AF, MILLER C, LIU H. Anodic growth and biomedical applications of Ti02 nanotubes. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2014;10(10): 2977-3003.
[3] MUNIRATHINAM B, NEELAKANTAN L. Titania nanotubes from weak organic acid electrolyte: fabrication, characterization and oxide film properties.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;4(49):567-578.
[4] KHAN AF, SALEEM M, AFZAL A, et al. Bioactive behavior of silicon substituted calcium phosphate based bioceramics for bone regeneration.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;1(35):245-252.
[5] LOU W, DONG Y, ZHANG H, et al. Preparation and Characterization of Lanthanum-Incorporated Hydroxyapatite Coatings on Titanium Substrates. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(9):21070-21086.
[6] RAO PJ, PELLETIER MH, WALSH WR, et al. Spine interbody implants: material selection and modification, functionalization and bioactivation of surfaces to improve osseointegration. Orthop Surg. 2014;6(2):81-89.
[7] MATENA J, PETERSEN S, GIESEKE M, et al. SLM produced porous titanium implant improvements for enhanced vascularization and osteoblast seeding. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):7478-7492.
[8] KULKARUI M, MAZARE A, GONGADZE E, et al. Titanium nanostruetnres for biomedical applications. Nanoteehnology. 2015;26(6):062002-19.
[9] DU QH, CAO JK, DONG XX, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of pluripotent stem cells induced by akermanite extracts. J Clin Rehabil Tissue Eng Res. 2015;(14):2236-2242.
[10] ZHANG W, JIN Y, QIAN S, et al. Vacuum extraction enhances rhPDGF-BB immobilization on nanotubes to improve implant osseointegration in ovariectomized rats. Nanomedicine. 2014;10(8):1809-1818.
[11] BUTTKE TM, MCCUBREY JA, OWEN TC. Use of an aqueous soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay to measure viability and proliferation of lymphokine-dependent cell lines. J Immunol Methods. 1993;157 (1-2):233-240.
[12] RAHMAN S, HLADY V. Downstream Platelet Adhesion and Activation Under Highly Elevated Upstream Shear Forces. Acta Biomater. 2019; 6(91):135-143.
[13] YU WQ, QIU J, ZHANG FQ. In vitro corrosion study of different TiO2 nanotube layers on titanium in solution with serum proteins. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2011;84(2):400-405.
[14] LAVENUS S, BERREUR M, TRICHET V, et al. Adhesion and osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells on titanium nanopores. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;22:84-96.
[15] GONG T, XIE J, LIAO J, et al. Nanomaterials and bone regeneration. Bone Res. 2015;3(3): 123-129.
[16] QIAO Y, ZHANG W, TIAN P, et al. Stimulation of bone growth following zinc incorporation into biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2014;35(25): 6882-6897.
[17] SCHWARTZ Z, RAZ P, ZHAO G, et al. Effect of micrometer-scale roughness of the surface of Ti6Al4V pedicle screws in vitro and in vivo. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(11):2485-2498.
[18] SUSWILLO RF, JAVAHERI B, RAWLINSON SC, et al. Strain uses gap junctions to reverse stimulation of osteoblast proliferation by osteocytes. Cell Biochem Funct. 2017;35(1):56-65.
[19] PARK J, BAUER S, VON DER MARK K, et al. Nanosize and vitality: TiO2 nanotube diameter directs cell fate. Nano Lett. 2007;7(6):1686-1691.
[20] LIU W, CHAIX A, GARY-BOBO M, et al. Stealth Biocompatible Si-Based Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2017;7(10):288-302.
[21] BALLO AM, XIA W, PALMQUIST A, et al. Bone tissue reactions to biomimetic ion-substituted apatite surfaces on titanium implants. J R Soc Interface. 2012;9(72):1615-1624.
[22] PREMNATH P, TAN B, VENKATAKRISHNAN K. Programming cell fate on bio-functionalized silicon. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015; 1(128):100-105.
[23] LING M, HUANG PX, ISLAM S, et al. Epigenetic regulation of Runx2 transcription and osteoblast differentiation by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase. Cell Biosci. 2017;7(1):27-36.
[24] SHI X, NAKAGAWA M, KAWACHI G, et al. Surface modification of titanium by hydrothermal treatment in Mg-containing solution and early osteoblast responses. Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(5): 1281-1290.
|