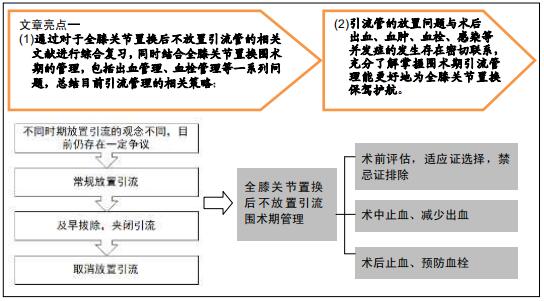
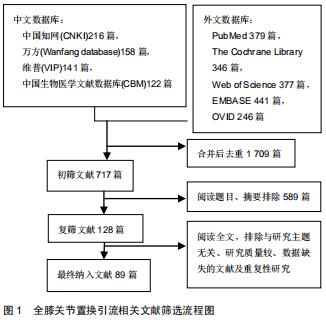
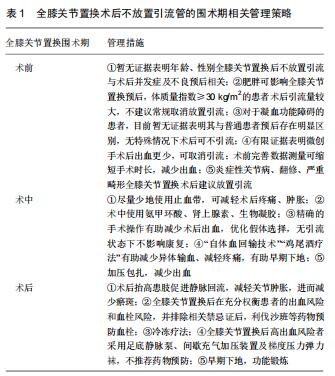
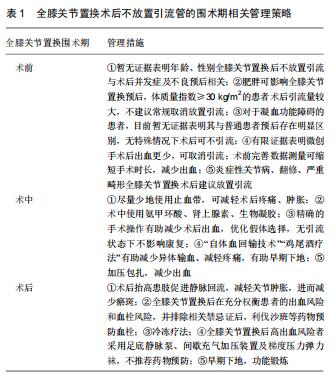
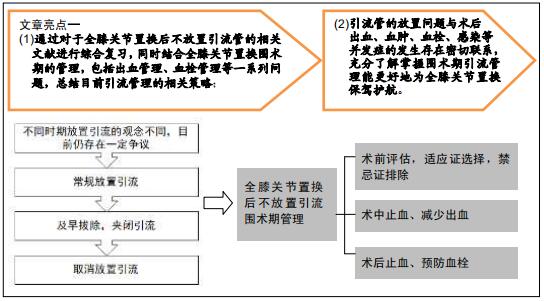
|
[1] KIM YH, CHO SH, KIM RS. Drainage versus nondrainage in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(347):188-193.
[2] WAUGH TR, STINCHFIELD FE. Suction drainage of orthopaedic wounds. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1961;43-A:939-946.
[3] MCGRORY B, WEBER K, LYNOTT JA, et al. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guideline on Surgical Management of Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2016;98(8):688-692.
[4] HOLT BT, PARKS NL, ENGH GA, et al. Comparison of closed-suction drainage and no drainage after primary total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics.1997;20(12):1121-1124, 1124-1125.
[5] DRINKWATER CJ, NEIL MJ. Optimal timing of wound drain removal following total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty.1995;10(2):185-189.
[6] ALEXANDER JW, KORELITZ J, ALEXANDER NS. Prevention of wound infections. A case for closed suction drainage to remove wound fluids deficient in opsonic proteins. Am J Surg.1976;132(1):59-63.
[7] KIM YH, CHO SH, KIM RS. Drainage versus nondrainage in simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;(347):188-193.
[8] LIU XH, FU PL, WANG SY, et al. The effect of drainage tube on bleeding and prognosis after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res.2014;9:27.
[9] JENNINGS JM, LOYD BJ, MINER TM, et al. A prospective randomized trial examining the use of a closed suction drain shows no influence on strength or function in primary total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B(7_Supple_C):84-90.
[10] HU Y, LI Q, WEI BG, et al. Blood loss of total knee arthroplasty in osteoarthritis: an analysis of influential factors. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):325.
[11] JING F, LI HM, YANG XD, et al. Efficacy and safety of drainage after total knee arthroplasty. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.2017;97(27): 2145-2149.
[12] NANNI M, PERNA F, CALAMELLI C, et al. Wound drainages in total hip arthroplasty: to use or not to use? Review of the literature on current practice. Musculoskelet Surg.2013;97(2):101-107.
[13] WILLEMEN D, PAUL J, WHITE SH, et al. Closed suction drainage following knee arthroplasty. Effectiveness and risks. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1991;(264):232-234.
[14] 荆鑫,滕红林,吴海山,等. 全关节置换术后关节腔引流问题的探讨[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2002,10(S1):47-49.
[15] ARES-RODRIGUEZ O, MARTINEZ AH, FERNANDEZ AH, et al. Survival curve and factors related to drainage during the first 24 h after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008; 16(6):585-589.
[16] PRASAD N, PADMANABHAN V, MULLAJI A. Comparison between two methods of drain clamping after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2005;125(6):381-384.
[17] PORNRATTANAMANEEWONG C, NARKBUNNAM R, SIRIWATTANASAKUL P, et al. Three-hour interval drain clamping reduces postoperative bleeding in total knee arthroplasty: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2012;132(7):1059-1063.
[18] RALEIGH E, HING CB, HANUSIEWICZ AS, et al. Drain clamping in knee arthroplasty, a randomized controlled trial. ANZ J Surg. 2007; 77(5):333-335.
[19] STUCINSKAS J, TARASEVICIUS S, CEBATORIUS A, et al. Conventional drainage versus four hour clamping drainage after total knee arthroplasty in severe osteoarthritis: a prospective, randomised trial. Int Orthop.2009;33(5):1275-1278.
[20] MADADI F, MEHRVARZ AS, MADADI F, et al. Comparison of drain clamp after bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg,2010;23(4): 215-221.
[21] ROY N, SMITH M, ANWAR M, et al. Delayed release of drain in total knee replacement reduces blood loss. A prospective randomised study. Acta Orthop Belg.2006;72(1):34-38.
[22] TAI TW, YANG CY, JOU IM, et al. Temporary drainage clamping after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Arthroplasty.2010;25(8):1240-1245.
[23] 项群,王四清,殷俊,等.全膝关节置换术后引流管夹闭时间选择的临床研究[J].河北医学,2013,19(4):537-539.
[24] 冯宗权,陈志维,王全兵,等.全膝关节置换术后失血综合管理的探讨[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(11):829-831.
[25] 梅迎雪,石晓庆,张海娇,等. 全膝关节置换术后暂时夹闭引流管联合持续性冷敷压迫的疗效分析[J]. 宁夏医学杂志,2014,36(3):283-285.
[26] 刘丹.全膝关节置换术后早期不同伤口引流管夹闭时间对引流量的影响[J].护理学报,2011,18(22):46-48.
[27] 徐志斌,王进.全膝关节置换术后延迟开放引流管止血效果观察[J]. 山东医药,2014,54(10):52-53.
[28] LI T, XIAO K, WENG X. Reply to comment on Li et al.: Non-continuous versus continuous wound drainage after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Int Orthop.2014;38(10):2219-2220.
[29] 兰海,员晋,张进军,等.夹闭引流管对全膝关节置换术后出血的影响[J]. 中国现代医生,2010,48(21):20-21.
[30] HUANG Z, MA J, PEI F, et al. Meta-analysis of temporary versus no clamping in TKA. Orthopedics.2013;36(7):543-550.
[31] 赵晓伟,王国栋,张元民,等.间断性夹闭引流管对减少膝关节置换术后出血量的临床效果观察[J].中国综合临床,2013,29(z1):112-114.
[32] AGARWALA S, JHAVERI M, MENON A. Advantages of clamping and drainage over continuous drainage in a total knee arthroplasty. J Clin Orthop Trauma.2020;11(1):133-135.
[33] YUAN Y, ZHANG HJ, ZHANG B, et al. Case-control study on effect of early intermittently closing drainage tube for blood loss after total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Gu Shang.2019;32(1):60-63.
[34] ZHANG S, XU B, HUANG Q, et al. Early Removal of Drainage Tube after Fast-Track Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg.2017; 30(6):571-576.
[35] 李彬,田立杰,温昱,等.全膝关节置换术后引流管短期夹闭与持续开放相比较的Meta分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011,19(12):969-973.
[36] SALEH K, OLSON M, RESIG S, et al. Predictors of wound infection in hip and knee joint replacement: results from a 20 year surveillance program. J Orthop Res.2002;20(3):506-515.
[37] PATEL VP, WALSH M, SEHGAL B, et al. Factors associated with prolonged wound drainage after primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2007;89(1):33-38.
[38] SI H, YANG T, ZENG Y, et al. No clear benefit or drawback to the use of closed drainage after primary total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016:183.
[39] WATANABE T, MUNETA T, YAGISHITA K, et al. Closed suction drainage is not necessary for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective study on simultaneous bilateral surgeries of a mean follow-up of 5.5 years. J Arthroplasty.2016;31(3):641-645.
[40] LI N, LIU M, WANG D, et al. Comparison of complications in one-stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty with and without drainage. J Orthop Surg Res.2015;10:3.
[41] WANG D, XU J, ZENG WN, et al. Closed Suction Drainage Is Not Associated with Faster Recovery after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study of 80 Patients. Orthop Surg.2016;8(2):226-233.
[42] ZHANG XN, WU G, XU RZ, et al. Closed suction drainage or non-drainage for total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi.2012;50(12):1119-1125.
[43] FAN Y, LIU Y, LIN J, et al. Drainage does not promote post-operative rehabilitation after bilateral total knee arthroplasties compared with nondrainage. Chin Med Sci J.2013;28(4):206-210.
[44] 盛林,翁习生,林进,等.全膝关节置换50例:放置引流的随机对照比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(26):5043-5046.
[45] TAI TW, JOU IM, CHANG CW, et al. Non-drainage is better than 4-hour clamping drainage in total knee arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2010;33(3). doi: 10.3928/01477447-20100129-11.
[46] NISHITANI K, KURIYAMA S, NAKAMURA S, et al. A multivariate analysis on the effect of no closed suction drain on the length of hospital stay in total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Relat Res.2019; 31(1):25-30.
[47] 杜晋强,高耀祖,张志强,等. 体重指数对骨关节炎患者术后疗效的影响[J]. 中国骨伤,2014,27(11):916-919.
[48] SAMSON AJ, MERCER GE, CAMPBELL DG. Total knee replacement in the morbidly obese: a literature review. ANZ J Surg.2010;80(9):595-599.
[49] VASARHELYI EM, MACDONALD SJ. The influence of obesity on total joint arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2012;94(11 Suppl A):100-102.
[50] FRIEDMAN RJ, HESS S, BERKOWITZ SD, et al. Complication rates after hip or knee arthroplasty in morbidly obese patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2013;471(10):3358-3366.
[51] VAZQUEZ-VELA JG, WORLAND RL, KEENAN J, et al. Patient demographics as a predictor of the ten-year survival rate in primary total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2003;85(1):52-56.
[52] 甘玉云,李伦兰,汪璐璐,等.身体质量指数对全膝关节置换患者膝关节功能的影响[J]. 中华关节外科杂志(电子版), 2019,13(5):575-583.
[53] MOON HK, HAN CD, YANG IH, et al. Factors affecting outcome after total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Yonsei Med J.2008,49(1):129-137.
[54] MORTAZAVI S, FIROOZABADI MA, NAJAFI A, et al. Evaluation of outcomes of suction drainage in patients with haemophilic arthropathy undergoing total knee arthroplasty. Haemophilia.2017;23(4):e310-e315.
[55] LI C, ZENG Y, SHEN B, et al. A meta-analysis of minimally invasive and conventional medial parapatella approaches for primary total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2015;23(7): 1971-1985.
[56] CANCIENNE JM, WERNER BC, BROWNE JA. Complications of primary total knee arthroplasty among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and osteoarthritis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2016;24(8):567-574.
[57] LI J, ZHAO J, HE C, et al. Comparison of Blood Loss After Total Hip Arthroplasty Between Ankylosing Spondylitis and Osteoarthritis. J Arthroplasty.2016;31(7):1504-1509.
[58] WARD MM. Risk of total knee arthroplasty in young and middle-aged adults with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol.2018;37(12): 3431-3433.
[59] SEHAT KR, EVANS R, NEWMAN JH. How much blood is really lost in total knee arthroplasty? Correct blood loss management should take hidden loss into account. Knee.2000;7(3):151-155.
[60] OZKUNT O, SARIYILMAZ K, GEMALMAZ HC, et al. The effect of tourniquet usage on cement penetration in total knee arthroplasty: A prospective randomized study of 3 methods. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(4):e9668.
[61] LIU Y, SI H, ZENG Y, et al. More pain and slower functional recovery when a tourniquet is used during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2020; 28(6):1842-1860.
[62] ZHOU K, WANG H, LI J, et al. Non-drainage versus drainage in tourniquet-free knee arthroplasty: a prospective trial. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87(12):1048-1052.
[63] MCCARTHY DE, HU SY, ABDULKARIM A. Does Tourniquet Use in TKA Increase Postoperative Pain? A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2019;477(3):547-558.
[64] WANG K, NI S, LI Z, et al. The effects of tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9):2849-2857.
[65] AJNIN S, FERNANDES R. Reduced length of stay and faster recovery after total knee arthroplasty without the use of tourniquet. J Clin Orthop Trauma.2020;11(1):129-132.
[66] ALEXANDERSSON M, WANG EY, ERIKSSON S. A small difference in recovery between total knee arthroplasty with and without tourniquet use the first 3 months after surgery: a randomized controlled study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2019;27(4):1035-1042.
[67] EJAZ A, LAURSEN AC, KAPPEL A, et al. Faster recovery without the use of a tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Orthop.2014;85(4): 422-426.
[68] SADIGURSKY D, ANDION D, BOUREAU P, et al. Effect of tranexamic acid on bleeding control in total knee arthroplasty. Acta Ortop Bras. 2016;24(3):131-136.
[69] HIIPPALA S, STRID L, WENNERSTRAND M, et al. Tranexamic acid (Cyklokapron) reduces perioperative blood loss associated with total knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth.1995;74(5):534-537.
[70] 岳辰,周宗科,裴福兴,等.中国髋、膝关节置换术围术期抗纤溶药序贯抗凝血药应用方案的专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志,2015,8(4):281-285.
[71] GAO F, SUN W, GUO W, et al. Topical Administration of Tranexamic Acid Plus Diluted-Epinephrine in Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Randomized Double-Blinded Controlled Trial. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30(8):1354-1358.
[72] WU Y, YANG T, ZENG Y, et al. Clamping drainage is unnecessary after minimally invasive total knee arthroplasty in patients with tranexamic acid: A randomized, controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore).2017;96(7):e5804.
[73] SHI X, LI H, ZHOU Z, et al. Individual valgus correction angle improves accuracy of postoperative limb alignment restoration after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc.2017;25(1): 277-283.
[74] SARKANOVIC ML, GVOZDENOVIC L, SAVIC D, et al. Autologous blood transfusion in total knee replacement surgery. Vojnosanit Pregl. 2013;70(3):274-278.
[75] PARK K, LEE SR, JIN JM, et al. The efficacy and safety of postoperative autologous transfusion of filtered shed blood and anticoagulant prophylaxis in total knee arthroplasty patients. Knee Surg Relat Res.2012;24(1):14-18.
[76] 洪坤豪,潘建科,潘碧琦,等.全膝关节置换术后应用自体血回输装置有效性及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 实用医学杂志,2015,31(15):2545-2550.
[77] CHARALAMBIDES C, BEER M, MELHUISH J, et al. Bandaging technique after knee replacement. Acta Orthop.2005;76(1):89-94.
[78] OGATA K, WHITESIDE LA. Effects of external compression on blood flow to muscle and skin. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1982;(168):105-107.
[79] LEWIS GN, RICE DA, MCNAIR PJ, et al. Predictors of persistent pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114(4):551-561.
[80] 李金洁,王云芸,赵英,等.鸡尾酒疗法对老年全膝关节置换术后镇痛的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2016,36(15):3769-3770.
[81] 姜军,吕厚山,朱靖有. 髁间闭合式和开放式人工膝关节假体对全膝关节置换术后出血量的影响[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,22(1):9-11.
[82] LI J, WANG J, LI Y, et al. Effect of rivaroxaban on risk of bleeding after total knee arthroplasty. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2011;25(11):1323-1325.
[83] EriKSSON BI, BORRIS LC, FRIEDMAN RJ, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty. N Engl J Med.2008;358(26):2765-2775.
[84] CAO YB, ZHANG JD, SHEN H, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total hip or knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010;66(11):1099-1108.
[85] 中华医学会骨科学分会.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2016,6(2):65-71.
[86] SNOW V, QASEEM A, BARRY P, et al. Management of venous thromboembolism: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians and the American Academy of Family Physicians. Ann Fam Med.2007;5(1):74-80.
[87] 申屠瑛.局部持续冷敷在人工全膝关节置换术后患者中的应用[J]. 中华现代护理杂志,2014,49(17):2154-2156.
[88] ADIE S, KWAN A, NAYLOR JM, et al. Cryotherapy following total knee replacement. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;(9):D7911.
[89] FALCK-YTTER Y, FRANCIS CW, JOHANSON NA, et al. Prevention of VTE in orthopedic surgery patients: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: american college of chest physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2012;141(2 Suppl): e278S-e325S.
|