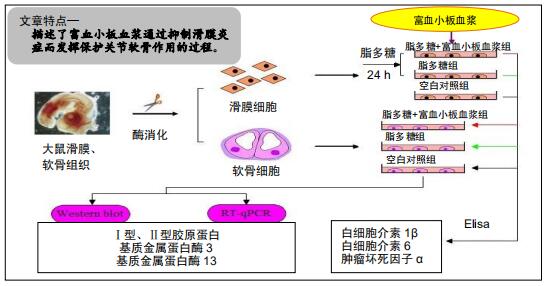
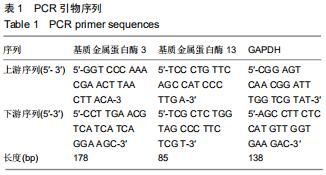
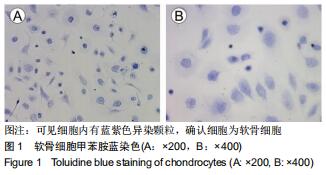
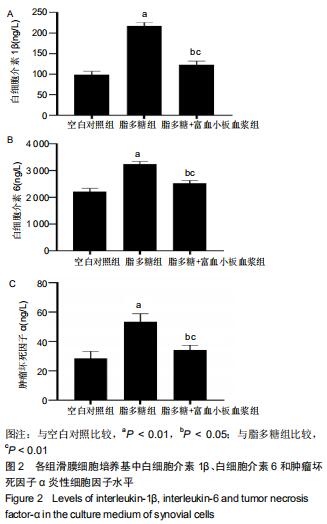
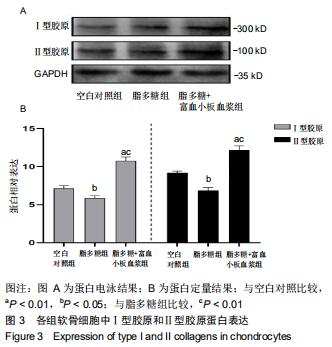
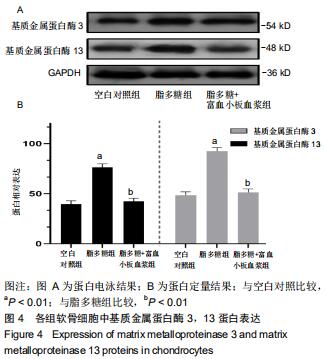
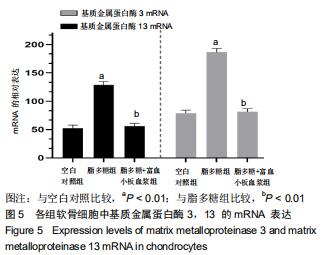
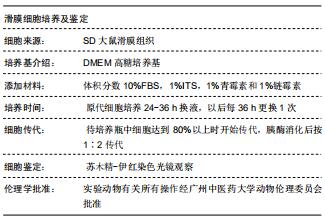
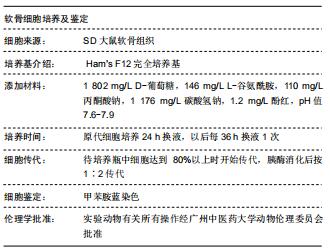
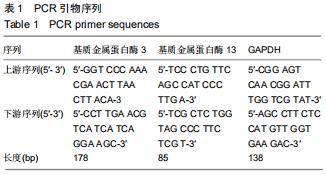
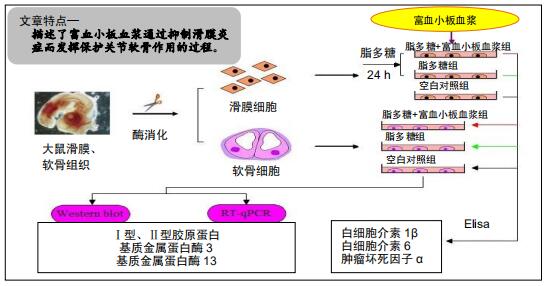
|
[1] SIT RWS, WU RWK, LAW SW, et al. Intra-articular and extra-articular platelet-rich plasma injections for knee osteoarthritis:A 26-week, single-arm, pilot feasibility study. Knee.2019;160(19)30159-30170.
[2] CROSS M, SMITH E, HOY D, et al.The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(7):1323-1330.
[3] HOY DG, SMITH E, CROSS M, et al. The global burden of musculoskeletal conditions for 2010: an overview of methods. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;(6):982-989.
[4] BRICCA A, JUHL CB, STEULTJENS M,et al.Impact of exercise on articular cartilage in people at risk of, or with established, knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review of randomised controlled trials.2019;53(15):940-947.
[5] BOSCHETTI F, PERETTI GM. Tensile and compressive properties of healthy and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Biorheology. 2008;45(3-4):337-344.
[6] BOUGAULT C1, CUERU L, BARILLER J,et al.Alteration of cartilage mechanical properties in absence of β1 integrins revealed by rheometry and FRAP analyses.J Biomech. 2013; 46(10):1633-1640.
[7] SIEBELT M, VAN DER WINDT AE, GROEN HC,et al. FK506 protects against articular cartilage colla-genous extra-cellular matrix degradation. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(4): 591-600.
[8] SMITH MD. The normal synovium. Open Rheumatol J. 2011;5:100-106.
[9] DELIGNE C, CASULLI S, PIGENET A,et al. Differential expression of interleukin-17 and interleukin -22 in inflamed and non-inflamed synovium from osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015;23(11):1843-1852.
[10] SAULNIER N, VIGUIER E, PERRIER-GROULT E,et al. Intra-articular administration of xenogeneic neon-atal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells early aftermeniscal injury down-regulates metalloproteinase gene expression in synovium and preventscartilage degradation in a rabbit model of osteoarth-ritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2015;23(1):122-33.
[11] AYRAL X, PICKERING EH, WOODWORTH TG,et al. Synovitis: a potential predictive factor of structur-ral progression of medial tibiofemoral kneeosteoarthritis-results of a 1 year longitudinal arthroscopic study in 422 patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.2005;13(5):361-367.
[12] GILBERTIE JM, LONG JM, SCHUBERT AG, et al.Pooled Platelet-Rich Plasma Lysate Therapy Increases Synoviocyte Proliferation and Hyaluronic Acid Production While Protecting Chondrocytes From Synoviocyte-Derived Inflammatory Mediators.Front Vet Sci. 2018;4(5):150.
[13] DILLON CF, RASCH EK, GU Q, et al. Prevalence of bone osteoarthritis in the United States: arthri-tis data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 1991-94.J Rheu-matol. 2006;33(11):2271-2279.
[14] VOS T, BARBER RM, BELL B, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 301 acute and chronic diseases and injuries in 188 countries, 1990-2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013.Lancet.2015;386(9995): 743-800.
[15] MURPHY L, HELMICK CG. The impact of osteoarthritis in the United States: a population-health perspective.Am J Nurs. 2012,112(3 Suppl 1):S13-19.
[16] KURTZ S, ONG K, LAU E, et al.Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89(4):780-785.
[17] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[18] LOESER RF, SHANKER G, CARLSON CS, et al.Reduction in the chondrocyte response to insulin-like growth factor 1 in aging and osteoarthritis: studies in a non-human primate model of naturally occurring disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2000; 43(9):2110-2120.
[19] MATHIESSEN A, CONAGHAN PG.Synovitis in osteoarthritis: current understanding with therapeutic implications.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):18.
[20] RAHMATI M, MOBASHERI A, MOZAFARI M.Inflammatory mediators in osteoarthritis: A critical review of the state-of-the-art, current prospects, and future challenges. Bone.2016;85:81-90.
[21] SARMANOVA A, HALL M, FERNANDES GS, et al. Association between ultrasound-detected synovitis and knee pain: a population-based case-control study with both cross-sectional and follow-up data.Arthritis Res Ther. 2017; 19(1):281.
[22] LAVER L, MAROM N, DNYANESH L, et al. PRP for Degenerative Cartilage Disease: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies.Cartilage. 2017;8(4):341-364.
[23] JOTANOVIC Z, MIHELIC R, SESTAN B, et al. Role of interleukin-1 inhibitors in osteoarthritis: an evidence-based review.Drugs Aging. 2012;29(5):343-358.
[24] KARDEL R, ULFGREN AK, REINHOLT FP, et al.Inflammatory cell and cytokine patterns in patients with painful clicking and osteoarthritis in the temporomandibular joint.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003;32(4):390-396.
[25] KIM JH, JEON J, SHIN M, et al. Regulation of the catabolic cascade in osteoarthritis by the zinc-ZIP8-MTF1 axis.Cell. 2014;156(4):730-743.
[26] PELLETIER JP, KAPOOR M, FAHMI H, et al. Strontium ranelate reduces the progression of experimental dog osteoarthritis by inhibiting the expression of key proteases in cartilage and of IL-1β in the synovium.Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72(2):250-257.
[27] TANAKA T, NARAZAKI M, KISHIMOTO T. Therapeutic targeting of the interleukin-6 receptor. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol.2012;52:199–219.
[28] DANDONA P, ALJADA A, BANDYOPADHYAY A. Inflammation: the link between insulin resistance, obesity and diabetes. Trends Immunol.2004;25:4-7.
[29] LEGENDRE F, BOGDANOWICZ P, BOUMEDIENE K, et al. Role of interleukin 6(IL-6)/IL-6R-induced signal tranducers and activators of transcription and mitogen-activated protein kinase/extr-acellular. J Rheumatol.2005;32:1307-1316.
[30] ZHAO B.TNF and Bone Remodeling.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2017;15(3):126-134.
[31] MAYER U,BENDITZ A,GRÄSSEL S.miR-29b regulates expression of collagens I and III in chondro-genically differentiating BMSC in an osteoarthritic environment.Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):13297.
[32] EYRE D. Collagen of articular cartilage. Arthritis Res.2002; 4(1):30-35.
[33] LEYH M, SEITZ A, DÜRSELEN L,et al.Subchondral bone influences chondrogenic differentiation and collagen production of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and articular chondrocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(5):453.
[34] TAKAHASHI M, FUJIKAWA K, ANGAMMANA R, et al.An in situ hybridization study of MMP-2, -9, -13, -14, TIMP-1, and -2 mRNA in fetal mouse mandibular condylar cartilage as compared with limb bud cartilage.Gene Expr Patterns. 2019; 32:1-11.
[35] XIANG X, ZHOU Y, SUN H,et al. Ivabradine abrogates TNF-α-induced degradation of articular cartilage matrix.Int Immunopharmacol.2019;66:347-353.
[36] AMĂLINEI C, CĂRUNTU ID, BĂLAN RA. Biology of metalloproteinases. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2007;48(4): 323-334.
|