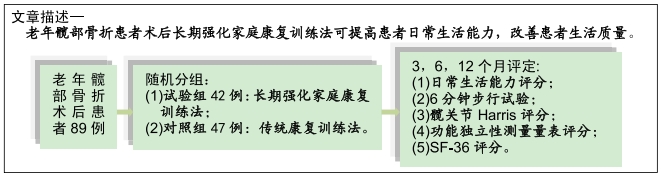
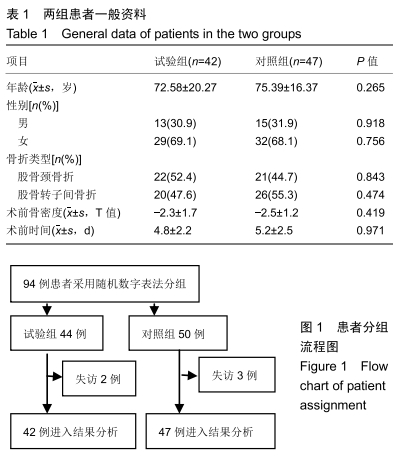
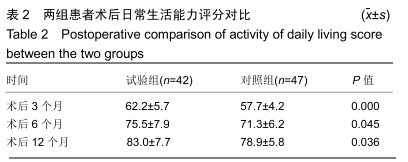
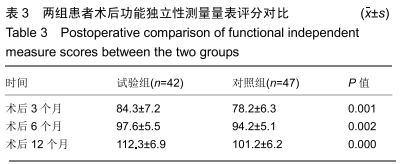
[1] GULLBERG B, JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. World-wide projections for hip fracture.Osteoporos Int. 1997;7(5): 407-413.
[2] HERNLUND E, SVEDBOM A, IVERGARD M, et al. Osteoporosis in the European Union: medical management, epidemiology and economic burden. A report prepared in collaboration with the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF) and the European Federation of Pharmaceutical Industry Associations (EFPIA). Arch Osteoporos. 2013;8:136.
[3] JOHNELL O, KANIS JA. An estimate of the worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic fractures. Osteoporos Int. 2006;17(12):1726-1733.
[4] DAVIDSON CW, MERRILEES MJ, WILKINSON TJ, et al. Hip fracture mortality and morbidity--can we do better? N Z Med J. 2001;114(1136):329-332.
[5] KEENE GS, PARKER MJ, PRYOR GA. Mortality and morbidity after hip fractures.BMJ (Clinical research ed.) 1993;307:1248-1250.
[6] FISHER AA, DAVIS MW, RUBENACH SE, et al. Outcomes for older patients with hip fractures: the impact of orthopedic and geriatric medicine cocare.J Orthop Trauma. 2006;20(3): 172-180.
[7] MAROTTOLI RA, BERKMAN LF, COONEY LM JR. Decline in physical function following hip fracture.J Am Geriatr Soc. 1992;40(9):861-866.
[8] DYER SM, CROTTY M, FAIRHALL N, et al. A critical review of the long-term disability outcomes following hip fracture. BMC Geriatrics.2016;16:158.
[9] OSNES EK, LOFTHUS CM, MEYER HE, et al.Consequences of hip fracture on activities of daily life and residential needs. Osteoporos Int. 2004;15(7):567-574.
[10] VOCHTELOO AJ, MOERMAN S, TUINEBREIJER WE, et al. More than half of hip fracture patients do not regain mobility in the first postoperative year.Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13(2): 334-341.
[11] SHEEHAN KJ, SOBOLEV B, GUY P. Mortality by Timing of Hip Fracture Surgery: Factors and Relationships at Play.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2017;99(20):e106.
[12] CAULEY JA. Burden of hip fracture on disability. The Lancet. Public health.2017;2:e209-e210.
[13] GREGERSEN M, MORCH MM, HOUGAARD K, et al. Geriatric intervention in elderly patients with hip fracture in an orthopedic ward.J Inj Violence Res. 2012;4(2):45-51.
[14] BINDER EF, BROWN M, SINACORE DR, et al.Effects of extended outpatient rehabilitation after hip fracture: a randomized controlled trial.Jama.2004;292:837-846.
[15] AUAIS MA, EILAYYAN O, MAYO NE. Extended exercise rehabilitation after hip fracture improves patients' physical function: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Physical therapy.2012; 92:1437-1451.
[16] COPANITSANOU P. Community rehabilitation interventions after hip fracture: Pragmatic evidence-based practice recommendations.Int J Orthop Trauma Nurs. 2019;35: 100712.
[17] 陆芸等.骨科术后康复指南[M].天津:天津科技翻译出版公司, 2009:375-427.
[18] 贺红梅,安帅,张新玉,等.老年股骨粗隆间骨折术后早期强化功能锻炼的对比研究[J].北京医学,2017,39(2):150-153.
[19] SAINSBURY A, SEEBASS G, BANSAL A, et al.Reliability of the Barthel Index when used with older people. Age Ageing. 2005;34:228-232.
[20] ROLEY SS, DELANY JV, BARROWS CJ, et al. Occupational therapy practice framework: domain & practice, 2nd edition . Am J Occup Ther. 2008;62(6):625-683.
[21] HAMILTON BB, LAUGHLIN JA, FIEDLER RC, et al. Interrater reliability of the 7-level functional independence measure (FIM). Scand J Rehabil Med. 1994;26(3):115-119.
[22] WANDERLEY FA, OLIVEIRA J, MOTA J, et al. Six-minute walk distance (6MWD) is associated with body fat, systolic blood pressure, and rate-pressure product in community dwelling elderly subjects.Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2011;52(2): 206-210.
[23] BONCZAR T, RUTOWICZ B, MIZIA E, et al. Preliminary validation of the IOF QLQ and comparison with the SF-36 in patients after a distal radius fracture.Folia medica Cracoviensia.2014;54:35-44.
[24] NILSDOTTER A, BREMANDER A. Measures of hip function and symptoms: Harris Hip Score (HHS),Hip Disability and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score (HOOS), Oxford Hip Score (OHS), Lequesne Index of Severity for Osteoarthritis of the Hip (LISOH), and American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS) Hip and Knee Questionnaire.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63 Suppl 11:S200-S207.
[25] SIDDIQUE T, SAH RK, MASOOD F, et al. Improvement in Harris Hip Score after cementless total hip arthroplasty in young active adults with secondary hip arthritis- A short-term follow-up result.J Pak Med Assoc. 2015;65(11 Suppl 3): S63-66.
[26] HACK J, BUECKING B, AIGNER R, et al. What are the influencing factors in self-rated health status after hip fracture? A prospective study on 402 patients.Arch Osteoporos.2019; 14(1):92.
[27] BERTRAM M, NORMAN R, KEMP L, et al. Review of the long-term disability associated with hip fractures. Inj Prev. 2011;17(6):365-370.
[28] LI CJ, DU XX, YANG K, et al. Effects of professional rehabilitation training on the recovery of neurological function in young stroke patients.Neural Regen Res. 2016;11(11): 1766-1772.
[29] STOLEE P, LIM SN, WILSON L, et al. Inpatient versus home-based rehabilitation for older adults with musculoskeletal disorders: a systematic review.Clin Rehabil. 2012;26(5):387-402.
[30] EDGREN J, SALPAKOSKI A, SIHVONEN SE, et al. Effects of a home-based physical rehabilitation program on physical disability after hip fracture: a randomized controlled trial.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2015;16(4):350.e1-7.
[31] KUO WY, SHYU YL, WANG JS, et al. Adherence to Home-Based Rehabilitation in Older Adults With Diabetes After Hip Fracture.Nurs Res. 2019;68(5):383-389.
[32] ORTIZ-PINA M, SALAS-FARINA Z, MORA-TRAVERSO M, et al. A home-based tele-rehabilitation protocol for patients with hip fracture called @ctivehip. Res Nurs Health. 2019;42(1): 29-38.
[33] MOFFET H, TOUSIGNANT M, NADEAU S, et al. In-Home Telerehabilitation Compared with Face-to-Face Rehabilitation After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Noninferiority Randomized Controlled Trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97(14): 1129-1141.
[34] 孔莉,林智.脑卒中后偏瘫患者肢体痉挛的家庭康复治疗[J].中国康复,2019,34:455-457.
[35] 周园园,张瑞芬,李鹏鹏,等.微信平台在阿尔茨海默病患者家庭认知康复治疗中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(9): 1100-1102.
[36] 郭淑芬,郝正玮,戈艳蕾,等.老年髋部骨折患者正念水平与家庭康复效果的Logistical回归分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2016,5(1): 58-61.
|