中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (11): 1714-1719.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2502
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
运动预适应与力竭运动大鼠心肌损伤:Rho/ROCK信号通路的作用
刘晓晨1,王改凤2
- 1河南财政金融学院体育系,河南省郑州市 450046;2河南省中医院脑病一病房,河南省郑州市 450002
Exercise preconditioning for myocardial injury in rats after exhaustive exercise based on Rho/ROCK pathway
Liu Xiaochen1, Wang Gaifeng2
- 1Department of Physical Education, Henan University of Finance and Economics, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2First Ward of Encephalopathy, Henan Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
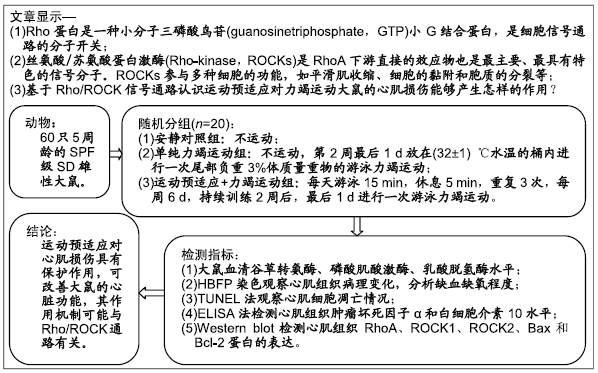
Rho/ROCK信号通路:Rho蛋白是小G结合蛋白Ras超家族成员之一,其通过激活下游蛋白激酶ROCK而产生多种生物学效应,如血管平滑肌的收缩、肌动蛋白细胞骨架形成、细胞黏附与迁移、细胞增殖与凋亡、基因表达等,与临床上多种心血管疾病如心力衰竭、缺血再灌注损伤、肺动脉高压、脑血管痉挛等相关疾病发生有关。对Rho/ROCK信号通路的研究有助于了解这些疾病的发病机制,进而为治疗提供一个新的思路。
运动预适应:是指反复短暂的间歇性大强度运动能够诱导机体产生缺血预适应,进而提高心肌对长时间缺血、缺氧的耐受能力,是减少心肌缺血损伤的有效途径之一。运动预适应作为一种物理刺激,具有简单、安全和易控的特点,对于科学制定训练计划和预防运动性心肌损伤都有重要意义。
背景:目前,关于运动预适应的心肌保护机制尚未完全阐明,据报道Rho/ROCK信号通路在心血管疾病中起到关键作用,运动预适应是否通过Rho/ROCK信号通路对心肌起到保护作用有待研究。
目的:基于Rho/ROCK信号通路探讨运动预适应在力竭运动大鼠心肌损伤中的作用。
方法:将60只5周龄的SPF级SD雄性大鼠随机分为3组:安静对照组、单纯力竭运动组、运动预适应+力竭运动组,各组建模结束后1 h,取血清进行全生化分析检测心肌酶谷草转氨酶、磷酸肌酸激酶、乳酸脱氢酶水平,取心肌组织标本进行苏木精-碱性复红-苦味酸染色观察心肌组织病理变化,分析缺血缺氧程度,TUNEL法观察心肌细胞凋亡情况,ELISA法检测心肌组织肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素10水平,Western blot检测心肌组织RhoA、ROCK1、ROCK2、Bax和Bcl-2蛋白的表达。
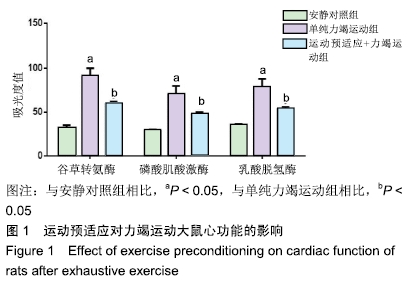
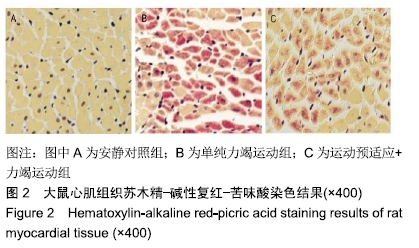
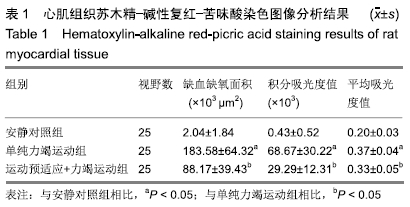
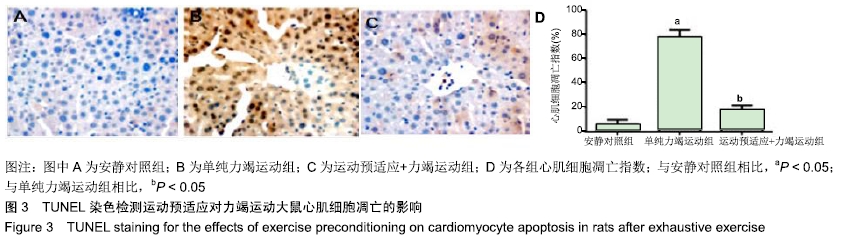
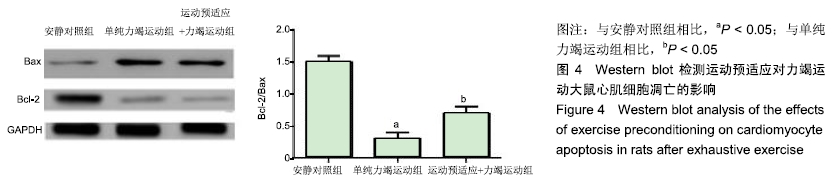
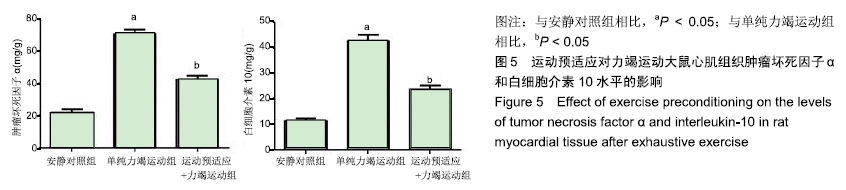
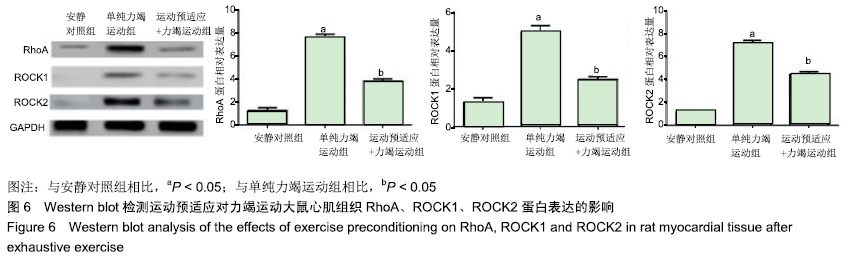
结果与结论:①单纯力竭运动组谷草转氨酶、磷酸肌酸激酶、乳酸脱氢酶水平显著高于安静对照组(P < 0.05);而运动预适应+力竭运动组谷草转氨酶、磷酸肌酸激酶、乳酸脱氢酶水平显著低于单纯力竭运动组(P < 0.05);②单纯力竭运动组心肌细胞界限不清楚,呈现出较多斑块状或片状艳红色样区域,与安静对照组相比,有明显的缺血缺氧改变;运动预适应+力竭运动组部分心肌细胞界限不清楚,出现部分斑块状艳红色染色,较单纯力竭运动组缺血缺氧程度明显减轻;③单纯力竭运动组较安静对照组凋亡指数值明显升高,运动预适应+力竭运动组与单纯力竭运动组相比凋亡指数值明显下降(P < 0.05);④单纯力竭运动组的肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素10水平显著高于安静对照组(P < 0.05),运动预适应+力竭运动组肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素10水平显著低于单纯力竭运动组(P < 0.05);⑤单纯力竭运动组的Bcl-2/Bax显著低于安静对照组(P < 0.05),运动预适应+力竭运动组Bcl-2/Bax显著高于单纯力竭运动组(P < 0.05);⑥与安静对照组相比,单纯力竭运动组RhoA、ROCK1、ROCK2蛋白水平明显升高,而运动预适应+力竭运动组RhoA、ROCK1、ROCK2蛋白水平显著低于单纯力竭运动组(P < 0.05);⑦结果表明,运动预适应对心肌损伤具有保护作用,可改善大鼠的心脏功能,其作用机制可能与Rho/ROCK通路有关。
ORCID: 0000-0002-0145-8270(刘晓晨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: