中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 517-523.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2223
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
不同玷污层对4种树脂粘接系统粘接强度及粘接耐久性的影响
郑适泽1,2,李 轲1,陈 玥1,鄢晓媛1,战德松3,付佳乐3
- 1中国医科大学口腔医学院,辽宁省沈阳市 110002;2吉林大学口腔医学院,吉林省长春市 130021;3中国医科大学口腔医学院口腔材料学教研室,中国医科大学附属口腔医院修复二科,辽宁省沈阳市 110002
Effect of different smear layers on the bonding performance and durability of four adhesive systems
Zheng Shize1, 2, Li Ke1, Chen Yue1, Yan Xiaoyuan1, Zhan Desong3, Fu Jiale3
- 1School of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Jilin University, Changchun 130021, Jilin Province, China; 3Department of Dental Materials, School of Stomatology, China Medical University, The Second Department of Prosthodontics, Hospital of Stomatology, China Medical University, Shenyang 110002, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
玷污层:牙体预备时由于车针的高速切割和挤压,牙本质表面形成厚1-5 μm的玷污层,它由无机物碎屑和凝固的胶原纤维碎屑组成。切割碎屑深入牙本质小管口形成管塞。磷酸酸蚀处理能够去除牙本质表面的玷污层及污物,而自酸蚀粘接剂则因为酸性较弱仅能对牙本质表面的玷污层及杂质进行部分溶解,并最终将剩余的玷污层包含在内形成混合粘接层。
甲基丙烯酰癸氧基二氢磷酸酯(10-MDP):是一种性能优良的酸性功能单体,与羟基磷灰石反应生成的难溶性钙盐形成“纳米层状结构”,强烈吸附于牙本质表面,这一特点被认为能够增强粘接性能,并且对胶原纤维有保护作用,长期观察发现其可以提高粘接剂的耐久性。
背景:当用旋转式或手动器械处理牙表面时,在牙釉质和牙本质上由切割和磨损产生的碎片形成了玷污层。玷污层是影响牙和修复材料之间粘接的重要因素,明确玷污层对不同种类粘接剂的影响对口腔医生的临床选择与正确使用具有重要的临床意义。
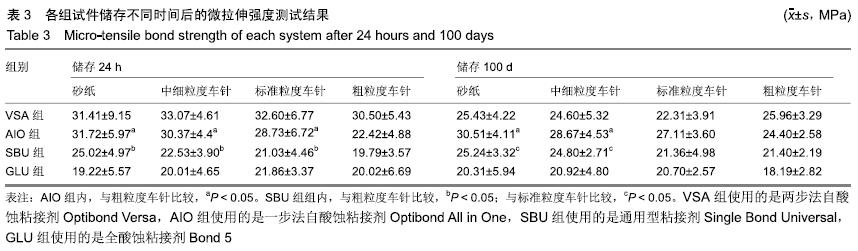
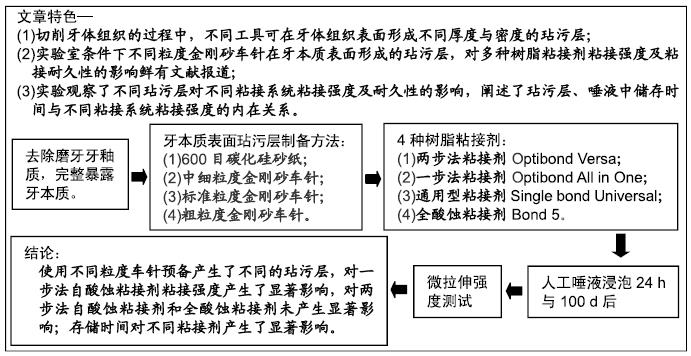
目的:评价使用不同金刚砂车针预备的试件在人工唾液中存储24 h与100 d后,对4种粘接剂与牙本质粘接强度的影响。
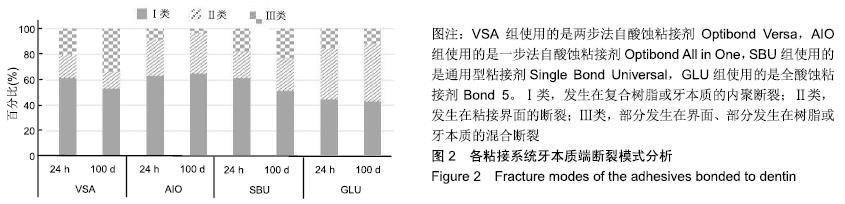
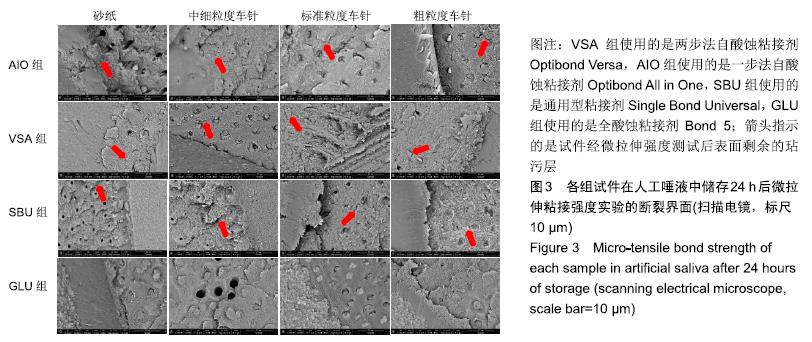
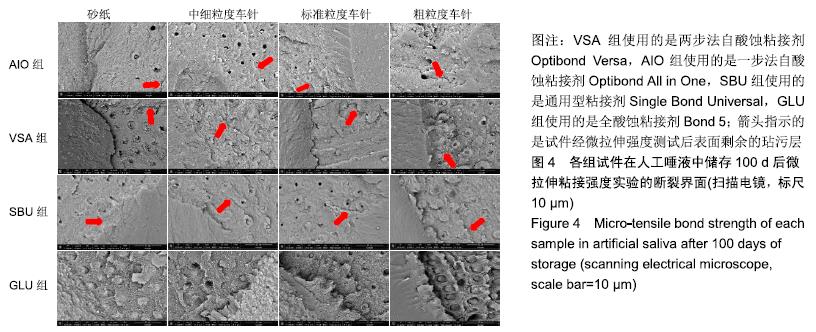
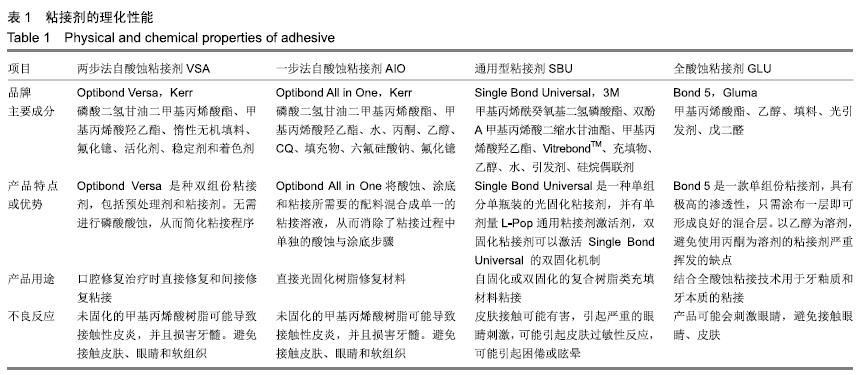
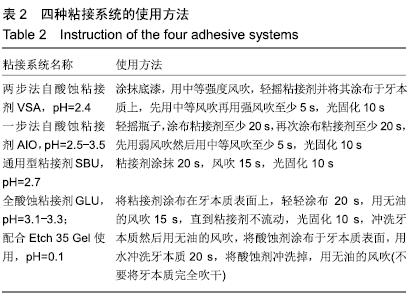
方法:获取离体人磨牙80颗,分别进行600号碳化硅砂纸(对照)、中细粒度金刚砂车针、标准粒度金刚砂车针、粗粒度金刚砂车针4种牙本质表面处理,每种处理20颗;每种处理方法内分4个亚组,分别以两步法自酸蚀粘接剂Optibond Versa(VSA组)、一步法自酸蚀粘接剂Optibond All in One(AIO组)、通用型粘接剂Single Bond Universal(SBU组)及全酸蚀粘接剂Bond 5(GLU组)进行树脂粘接。粘接完成后,将试件置于人工唾液中37 ℃储存24 h及100 d,随后进行微拉伸强度测试,使用扫描电镜观察牙本质端断裂面,并对断裂模式进行分析。
结果与结论:①储存24 h:使用两步法粘接剂或全酸蚀粘接剂的情况下,不同表面处理组间的粘接强度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);使用一步法粘接剂或通用型粘接剂的情况下,仅粗粒度车针组粘接强度低于砂纸组(P < 0.05)。使用砂纸或中细粒度车针的情况下,仅AIO组与VSA组粘接强度比较无差异;使用标准粒度车针的情况下,仅AIO组与VSA组、GLU组与SBU组粘接强度比较无差异(P > 0.05);使用粗粒度车针的情况下,VSA组与AIO组、GLU组、SBU组粘接强度比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05),其余组间比较无差异(P > 0.05);②储存100 d:使用两步法粘接剂或全酸蚀粘接剂的情况下,不同表面处理组间的粘接强度比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);使用一步法粘接剂的情况下,仅粗粒度车针组粘接强度低于砂纸组(P < 0.05);使用通用型粘接剂的情况下,仅标准粒度车针组、粗粒度车针组粘接强度低于砂纸组(P < 0.05)。使用砂纸或中细粒度车针的情况下,仅VSA组与SBU组粘接强度无差异(P > 0.05);使用标准粒度车针的情况下,仅SBU组与VSA组、GLU组与SBU组、GLU组与VSA组粘接强度无差异(P > 0.05);使用粗粒度车针的情况下,仅VSA组与AIO组粘接强度无差异(P > 0.05);③仅在使用两步法粘接剂的情况下,不同表面处理组100 d后的粘接强度与24 h比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④与浸泡24 h相比,VSA组、SBU组、GLU组浸泡100 d后的粘接界面断裂和混合断裂比例略有增加,其中VSA组变化最大;与其他组比较,GLU组浸泡24 h与100 d的粘接界面断裂和混合断裂模式比例均超过50%;⑤结果表明,使用不同粒度车针预备产生了不同的玷污层,对一步法自酸蚀粘接剂粘接强度产生了显著影响,对两步法自酸蚀粘接剂和全酸蚀粘接剂未产生显著影响;存储时间对不同粘接剂产生了显著影响。
ORCID: 0000-0002-1639-6498(郑适泽)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: