中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (4): 511-516.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2212
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
构建聚乳酸-羟基乙酸电纺丝-壳聚糖电喷微球牙周仿生膜
封小霞,侯玮玮,金晓婷,王心华
- 浙江大学医学院附属口腔医院,浙江省杭州市 310012
Construction of periodontal biomimetic membrane with electrospun poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanofibers and electrosprayed chitosan microspheres
Feng Xiaoxia, Hou Weiwei, Jin Xiaoting, Wang Xinhua
- Stomatology Hospital, Zhejiang University School of Medicine, Hangzhou 310012, Zhejiang Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
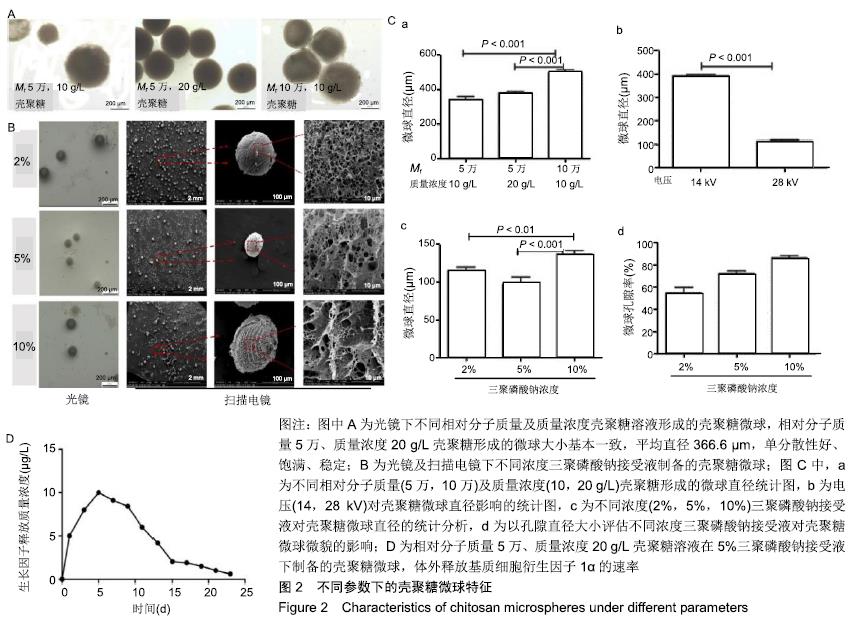
离子交联法制备壳聚糖微球:离子交联法利用酸性环境下壳聚糖呈阳离子性,向壳聚糖溶液中边搅拌边滴加三聚磷酸钠,带负电的磷酸根离子与壳聚糖分子链上带正电荷的氨基通过静电吸附,从而形成微球。
牙周膜:是连接牙齿和牙槽骨之间具有方向性的结缔组织,宽度为0.15-0.38 mm,其内含具有一定方向性胶原纤维束,其一端埋入牙骨质,另一端伸入牙槽骨内,具有固定牙根和缓解咀嚼时所产生压力的作用,又称牙周关节;牙周膜能形成牙槽骨及牙骨质,被破坏后能重建。由此可见,牙周膜不是普通的纤维结缔组织,它具有方向性、附着点、可再生牙周组织(牙骨质、牙周膜、牙槽骨)。
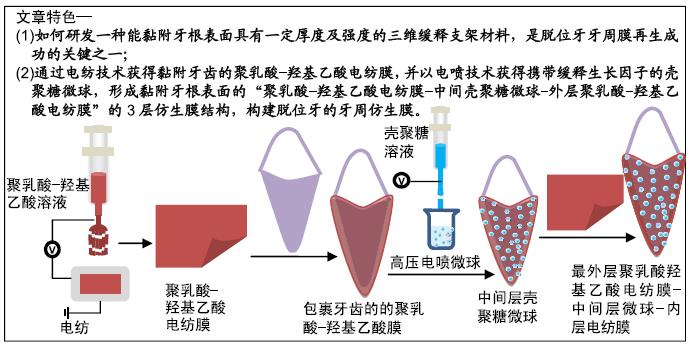
背景:当牙齿脱离牙槽窝后,牙周膜断裂,残留在脱位牙根表面的牙周膜由三维变成二维,丧失了支架膜的作用,导致脱位牙再植后根骨粘连。如何研发一种能黏附牙根表面具有一定厚度及强度的三维缓释支架材料,是脱位牙牙周膜再生成功的关键之一。
目的:构建可黏附脱位牙根表面的缓释生长因子的三维仿生膜。
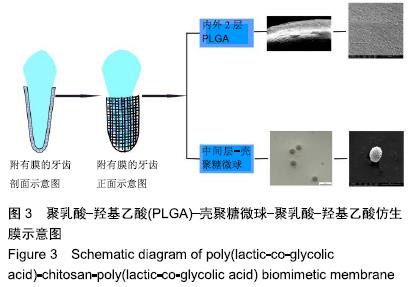
方法:采用静电纺丝技术制备聚乳酸-羟基乙酸电纺膜,研究电纺溶剂二氯甲烷与二甲基甲酰胺混合溶液、六氟异丙醇、三氯甲烷对电纺膜的影响,筛选最佳的电纺溶剂。采用电喷技术与离子交联法制备壳聚糖微球,研究壳聚糖相对分子质量(5万、10万)与质量浓度(10,20 g/L)、接受液三聚磷酸钠浓度(2%,5%,10%)、电压(14,28 kV)对壳聚糖微球的影响,筛选最佳的参数。构建含基质细胞衍生因子1壳聚糖微球(最优参数设计),检测其体外释放基质细胞衍生因子1α的速率。首先将聚乳酸-羟基乙酸电纺膜裹在牙齿根表面,然后在其表面滴加壳聚糖微球,在其外层裹一层薄薄的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸电纺膜,从而形成聚乳酸-羟基乙酸-壳聚糖微球-聚乳酸-羟基乙酸膜。
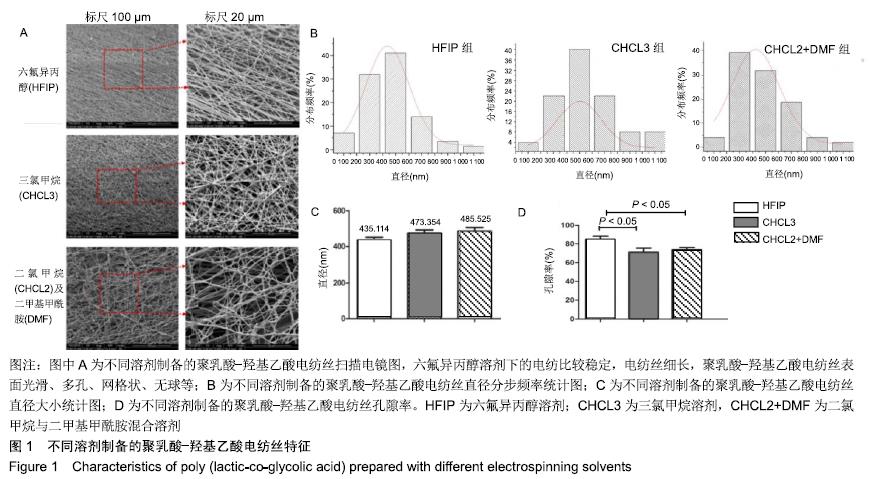
结果与结论:①利用电纺溶剂六氟异丙醇制备的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸电纺膜平均直径最小、空隙率最大;②当壳聚糖相对分子质量为5万、质量浓度为20 g/L时,微球的大小基本一致,平均直径366.6 μm,单分散性好、饱满、稳定;28 kV电压下形成的壳聚糖微球更符合脱位牙仿生膜的要求;利用5%三聚磷酸钠制备的壳聚糖微球表面微观结构孔径居中,最有利于临床牙周膜再生;壳聚糖微球可持续释放基质细胞衍生因子1α 1个月左右;③实验创建了一种黏附牙齿表面的具有缓释效能的聚乳酸-羟基乙酸-壳聚糖微球-聚乳酸-羟基乙酸三维仿生膜并筛选出构建此仿生膜的最佳参数,可在此模型基础上进一步研究组织工程手段对脱位牙再植的效果及机制。ORCID: 0000-0003-3957-3423(封小霞)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: