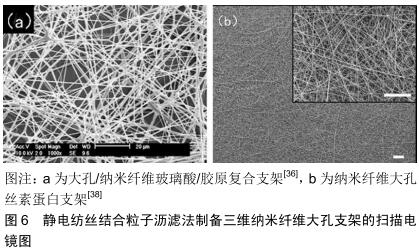
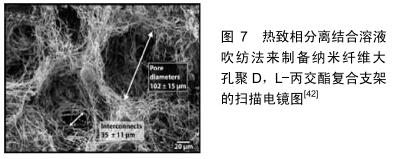
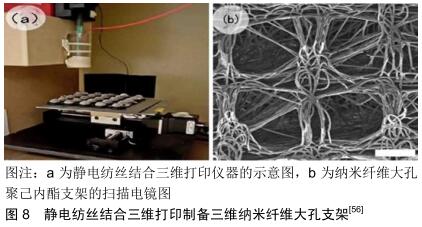
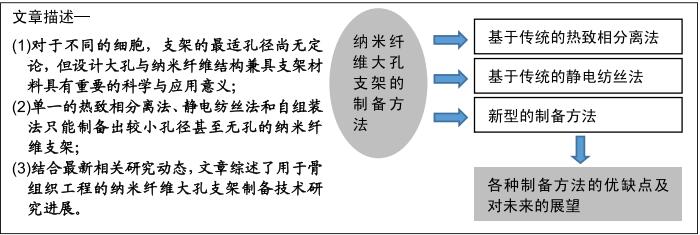
|
[1] 曹谊林,刘伟,张文杰,等.组织工程研究进展[J].上海交通大学学报(医学版), 2012,32(9):1241-1250.
[2] CHUENJITKUNTAWORN B, OSATHANON T, NOWWAROTE N, et al. The efficacy of polycaprolactone/hydroxyapatite scaffold in combination with mesenchymal stem cells for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(1):264-271.
[3] 贺钧,李自良,谢志刚.骨替代材料的骨诱导性能研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(2):124-127.
[4] LANGER R, VACANTI JP. Tissue engineering. Sci. 1993;260 (5110):920-926.
[5] 曹谊林.组织工程学的研究进展[J].中国美容医学, 2005,14(2): 134-135.
[6] 张淦,程迅生.骨组织工程的研究进展[J].安徽医学, 2016,37(8): 1057-1061.
[7] DIECKMANN C, RENNER R, MILKOVA L, et al. Regenerative medicine in dermatology: biomaterials, tissue engineering, stem cells, gene transfer and beyond.Exp Dermatol.2010;19(8):697-706.
[8] MA PX. Scaffolds for tissue fabrication.Mater Today.2004;7(5): 30-40.
[9] MITCHELL GR, TOJEIRA A. Role of anisotropy in tissue engineering. Procedia Eng.2013;59(2):117-125.
[10] 黄霞,陈家昌,申长雨.骨组织工程支架材料研究进展[J].化工新型材料, 2010,38(9):65-68.
[11] KWON IK, MATSUDA T. Co-electrospun nanofiber fabrics of poly(L-lactide-co-epsilon-caprolactone) with type I collagen or heparin.Biomacromolecules.2005;6(4):2096-2105.
[12] BENIASH E, HARTGERINK JD, STORRIE H, et al. Self-assembling peptide amphiphile nanofiber matrices for cell entrapment.Acta Biomater.2005;1(4):387-397.
[13] HSU FY, WENG RC, LIN HM, et al. A biomimetic extracellular matrix composed of mesoporous bioactive glass as a bone graft material. Microporous Mesoporous Mater.2015;212:56-65.
[14] LIU Y, SUN Q, WANG S, et al. Preparation of SF/PLGA scaffold with microporous-nano/microfibrous architecture by thermal induced phase separation.Sci Adv Mater.2015;7(11):2380-2387.
[15] OH SH, PARK IK, KIM JM, et al. In vitro and in vivo characteristics of PCL scaffolds with pore size gradient fabricated by a centrifugation method.Biomaterials.2007;28(9):1664-1671.
[16] 吴林波,丁建东.组织工程三维多孔支架的制备方法和技术进展[J].功能高分子学报,2003,16(1):91-96.
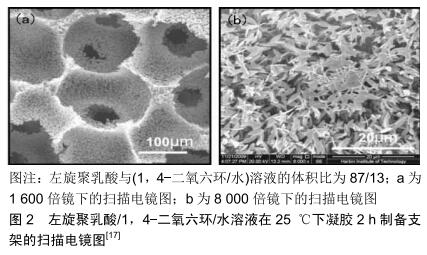
[17] 郑雄飞,翟文杰.单一热致相分离法制备聚乳酸纳米纤维大孔支架[J].功能材料,2010,41 (S1):184-188.
[18] CHEN S, ZHAO X, DU C. Macroporous poly (L-lactic acid)/chitosan nanofibrous scaffolds through cloud point thermally induced phase separation for enhanced bone regeneration.Eur Polym J. 2018;109: 303-316.
[19] WANG W, MIAO Y, ZHOU X, et al. Local delivery of BMP-2 from poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) microspheres incorporated into porous nanofibrous scaffold for bone tissue regeneration.J Biomed Nanotechno. 2017;13(11):1446-1456.
[20] HAN W, ZHAO J, TU M, et al. Preparation and characterization of nanohydroxyapatite strengthening nanofibrous poly(L-lactide) scaffold for bone tissue engineering.J Appl Polym Sci.2013;128(3): 1332-1338.
[21] LIU X, MA PX. Phase separation,pore structure, and properties of nanofibrous gelatin scaffolds.Biomaterials.2009;30(25): 4094-4103.
[22] LIU S, HE Z, XU G, et al. Fabrication of polycaprolactone nanofibrous scaffolds by facile phase separation approach.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2014;44:201-208.
[23] SALERNO A, MAR FERNÁNDEZ-GUTIÉRREZ, BARRIO JSRD, et al. Macroporous and nanometre scale fibrous PLA and PLA-HA composite scaffolds fabricated by a bio safe strategy.RSC Adv. 2014; 4(106):61491-61502.
[24] WEI G, JIN Q, GIANNOBILE WV, et al. The enhancement of osteogenesis by nano-fibrous scaffolds incorporating rhBMP-7 nanospheres.Biomaterials.2007;28(12):2087-2096.
[25] WEI G, JIN Q, GIANNOBILE WV, et al. Nano-fibrous scaffold for controlled delivery of recombinant hµman PDGF-BB.J Control Release. 2006;112(1):103-110.
[26] GUPTE MJ, SWANSON WB, HU J, et al. Pore size directs bone marrow stromal cell fate and tissue regeneration in nanofibrous macroporous scaffolds by mediating vascularization.Acta Biomater.2018;82:1-11.
[27] CHEN VJ, MA PX. Nano-fibrous poly(L-lactic acid) scaffolds with interconnected spherical macropores.Biomaterials. 2004;25(11): 2065-2073.
[28] ZHANG R, MA PX. Synthetic nano-fibrillar extracellular matrices with predesigned macroporous architectures.J Biomed Mater Res. 2000; 52(2):430-438.
[29] SAKINA R, ALI M. An appraisal of the efficacy and effectiveness of nanoscaffolds developed by different techniques for bone tissue engineering applications: electrospinning a paradigm shift.Adv Polym Technol.2014;33(4).DOI:10.1002/adv.21429
[30] CAI YZ, ZHANG GR, WANG LL, et al. Novel biodegradable three-dimensional macroporous scaffold using aligned electrospun nanofibrous yarns for bone tissue engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(5):1187-1194.
[31] MAJIDI SS, SLEMMING-ADAMSEN P, HANIF M, et al. Wet electrospun alginate/gelatin hydrogel nanofibers for 3D cell culture.Int J Biol Macromol.2018;118(PtB):1648-1654.
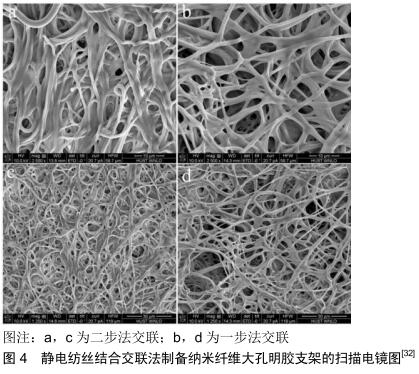
[32] TENG F, DING H, HUANG Y, et al. Fabrication of three- dimensional nanofibrous gelatin scaffolds using one-step crosslink technique.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2018;29(15):1859-1875.
[33] KIM HW, SONG JH, KIM HE. Bioactive glass nanofiber-collagen nanocomposite as a novel bone regeneration matrix.J Biomed Mater Res A.2010;79(3):698-705.
[34] JOSHI MK, PANT HR, TIWARI AP, et al. Multi-layered macroporous three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold via a novel gas foaming technique. Chem Eng J.2015;275:79-88.
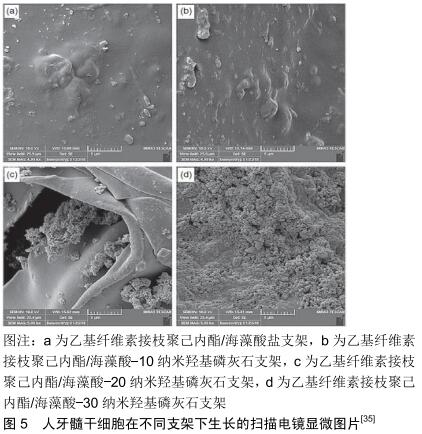
[35] HOKMABAD VR, DAVARAN S, AGHAZADEH M, et al. Fabrication and characterization of novel ethyl cellulose-grafted- poly(ɛ-caprolactone)/ alginate nanofibrous/ macroporous scaffolds incorporated with nano-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering.J Biomater Appl. 2019;33(8):1128-1144.
[36] KIM TG, CHUNG HJ, PARK TG. Macroporous and nanofibrous hyaluronic acid/collagen hybrid scaffold fabricated by concurrent electrospinning and deposition/leaching of salt particles.Acta Biomater. 2008;4(6):1611-1619.
[37] KIM SH, KWON JH, CHUNG MS, et al. Fabrication of a new tubular fibrous PLCL scaffold for vascular tissue engineering.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2006;17(12):1359-1374.
[38] WANG K, XU M, ZHU M, et al. Creation of macropores in electrospun silk fibroin scaffolds using sacrificial PEO-microparticles to enhance cellular infiltration.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(12):3474-3481.
[39] HSU FY, HSU HW, CHANG YH, et al. Macroporous microbeads containing apatite-modified mesoporous bioactive glass nanofibres for bone tissue engineering applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;89:346-354.
[40] GHOSH LD, JAIN A, SUNDERASAN NR, et al. Elucidating molecular events underlying topography mediated cardiomyogenesis of stem cells on 3D nanofibrous scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;88:104-114.
[41] LEE JB, JEONG SI, BAE MS, et al. Poly(L-lactic acid) nanocylinders as nanofibrous structures for macroporous gelatin scaffolds.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2011;11(7):6371-6376.
[42] MEDEIROS ELG, BRAZ AL, PORTO IJ, et al. Porous bioactive nanofibers via cryogenic solution blow spinning and their formation into 3D macroporous scaffolds.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2016;2(9): 1442-1449.
[43] WINDER J, BIBB R. Medical rapid prototyping technologies: state of the art and current Limitations for application in oral and maxillofacial surgery.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2005;63(7):1006-1015.
[44] LIN L, JU S, CEN L, et al. Fabrication of porous β-TCP scaffolds by combination of rapid prototyping and freeze drying technology. In 7th Asian-Pacific Conference on Medical and Biological Engineering. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.2008:88-91.
[45] WOODFIELD TB, GUGGENHEIM M, VON RECHENBERG B, et al. Rapid prototyping of anatomically shaped, tissue-engineered implants for restoring congruent articulating surfaces in small joints. Cell Prolif. 2010;42(4):485-497.
[46] YU D, LI Q, MU X, et al. Bone regeneration of critical calvarial defect in goat model by PLGA/TCP/rhBMP-2 scaffolds prepared by low-temperature rapid-prototyping technology.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;37(10):929-934.
[47] KHALIL S, SUN W. Bioprinting endothelial cells with alginate for 3D tissue constructs.J Biomech Eng.2009;131(11):111002.
[48] MIRONOV V, KASYANOV V, DRAKE C, et al. Organ printing: promises and challenges.Regen Med.2008;3(1):93-103.
[49] KAI H, WANG X, MADHUKAR KS, et al. Fabrication of a two-level tµmor bone repair biomaterial based on a rapid prototyping technique. Biofabrication.2009;1(2):025003.
[50] YANG S, LEONG KF, DU Z, et al. The design of scaffolds for use in tissue engineering. Part II.Rapid prototyping techniques.Tissue Eng. 2002;8(1):1-11.
[51] BAKER CT, BOCHAROV GA, PAUL CA, et al. Modelling and analysis of time-lags in some basic patterns of cell proliferation.J math biol. 1998;37(4):341-371.
[52] LAM CXF, MO XM, TEOH SH, et al. Scaffold development using 3D printing with a starch-based polymer.Mater Sci Eng C. 2002; 20(1-2): 49-56.
[53] PATTANAYAK DK,FUKUDA A,MATSUSHITA T,et al.Bioactive Ti metal analogous to hµman cancellous bone:fabrication by selective laser melting and chemical treatments.Acta Biomater. 2011;7(3):1398-1406.
[54] SUGAVANESWARAN M, ARµmAIKKANNU G. Analytical and experimental investigation on elastic modulus of reinforced additive manufactured structure.Mater Des(1980-2015).2015;66: 29-36.
[55] KALITA SJ, BOSE S, HOSICK HL, et al. Development of controlled porosity polymer-ceramic composite scaffolds via fused deposition modeling.Mater Sci Eng C. 2003;23(5):611-620.
[56] BROWN TD, EDIN F, DETTA N, et al. Melt electrospinning of poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds:phenomenological observations associated with collection and direct writing.Mater Sci Eng C. 2014; 45:698-708.
[57] FULLER KP, GASPAR D, DELGADO LM, et al. Development macro-porous electro-spun meshes with clinically relevant mechanical properties-A technical note.Biomed Mater.2019; 14(2):024103.
[58] NIVEDHITHA SUNDARAM M, DEEPTHI S, MONY U, et al. Chitosan hydrogel scaffold reinforced with twisted poly (l lactic acid) aligned microfibrous bundle to mimic tendon extracellular matrix.Int J Biol Macro.2019;122:37-44.
|