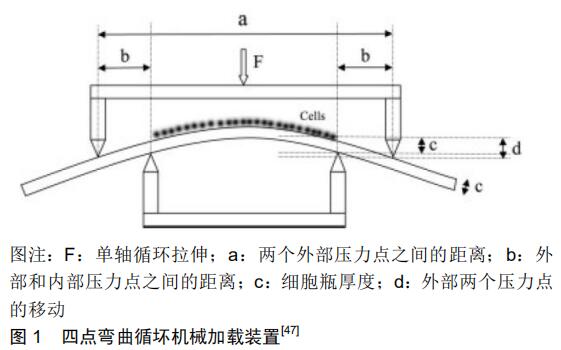
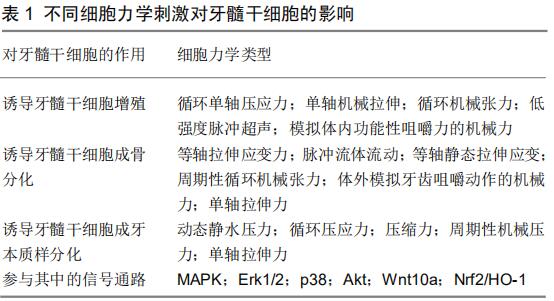
[1] et al. Role(s) of cytokines in pulpitis: Latest evidence and therapeutic approaches. Cytokine. 2020;126:154896.
[2] YU C, ABBOTT PV. An overview of the dental pulp: its functions and responses to injury. Aust Dent J. 2007;52 (1 Suppl):S4-16.
[3] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[4] ALMUSHAYT A, NARAYANAN K, ZAKI AE, et al. Dentin matrix protein 1 induces cytodifferentiation of dental pulp stem cells into odontoblasts. Gene Ther. 2006;13(7):611-620.
[5] D'AQUINO R, GRAZIANO A, SAMPAOLESI M, et al. Human postnatal dental pulp cells co-differentiate into osteoblasts and endotheliocytes: a pivotal synergy leading to adult bone tissue formation. Cell Death Differ. 2007;14(6):1162-1171.
[6] ARTHUR A, RYCHKOV G, SHI S, et al. Adult human dental pulp stem cells differentiate toward functionally active neurons under appropriate environmental cues. Stem Cells. 2008;26(7):1787-1795.
[7] MARCHIONNI C, BONSI L, ALVIANO F, et al. Angiogenic potential of human dental pulp stromal (stem) cells. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2009;22(3):699-706.
[8] YANG R, CHEN M, LEE CH, et al. Clones of ectopic stem cells in the regeneration of muscle defects in vivo. PLoS One. 2010;5(10):e13547.
[9] PATIL R, KUMAR BM, LEE WJ, et al. Multilineage potential and proteomic profiling of human dental stem cells derived from a single donor. Exp Cell Res. 2014;320(1):92-107.
[10] MARRELLI M, PADUANO F, TATULLO M. Human periapical cyst-mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into neuronal cells. J Dent Res. 2015;94(6):843-852.
[11] YU J, HE H, TANG C, et al. Differentiation potential of STRO-1+ dental pulp stem cells changes during cell passaging. BMC Cell Biol. 2010;11:32.
[12] XUAN K, LI B, GUO H, et al. Deciduous autologous tooth stem cells regenerate dental pulp after implantation into injured teeth. Sci Transl Med. 2018;10(455): eaaf3227.
[13] LIZIER NF, KERKIS A, GOMES CM, et al. Scaling-up of dental pulp stem cells isolated from multiple niches. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39885.
[14] MITSIADIS TA, BARRANDON O, ROCHAT A, et al. Stem cell niches in mammals. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313(16):3377-3385.
[15] MITSIADIS TA, FEKI A, PAPACCIO G, et al. Dental pulp stem cells, niches, and notch signaling in tooth injury. Adv Dent Res. 2011;23(3):275-279.
[16] HOFFMAN BD, GRASHOFF C, SCHWARTZ MA. Dynamic molecular processes mediate cellular mechanotransduction. Nature. 2011;475(7356):316-323.
[17] STEWARD AJ, KELLY DJ. Mechanical regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J Anat. 2015;227(6): 717-731.
[18] SHAH N, MORSI Y, MANASSEH R. From mechanical stimulation to biological pathways in the regulation of stem cell fate. Cell Biochem Funct. 2014;32(4):309-325.
[19] KEARNEY EM, FARRELL E, PRENDERGAST PJ, et al. Tensile strain as a regulator of mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis. Ann Biomed Eng. 2010;38(5):1767-1779.
[20] LEONG WS, WU SC, PAL M, et al. Cyclic tensile loading regulates human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation into neuron-like phenotype. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6 Suppl 3:s68-s79.
[21] CUI D, XIAO J, ZHOU Y, et al. Epiregulin enhances odontoblastic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells via activating MAPK signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(6): e12680.
[22] FAROOQ A, ZHOU MM. Structure and regulation of MAPK phosphatases. Cell Signal. 2004;16(7):769-779.
[23] YU Y, MU J, FAN Z, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 enhances the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK and JNK MAPK pathways. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012;137(4):513-525.
[24] KESHET Y, SEGER R. The MAP kinase signaling cascades: a system of hundreds of components regulates a diverse array of physiological functions. Methods Mol Biol. 2010;661: 3-38.
[25] WAGNER EF, NEBREDA AR. Signal integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009;9(8):537-549.
[26] DOAN TKP, PARK KS, KIM HK,et al. Inhibition of JNK and ERK Pathways by SP600125-and U0126-Enhanced Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine.2012;9: 283-294.
[27] KRAFT DC, BINDSLEV DA, MELSEN B, et al. Human dental pulp cells exhibit bone cell-like responsiveness to fluid shear stress. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(2):214-226.
[28] YANG H, SHU YX, WANG LY, et al. Effect of cyclic uniaxial compressive stress on human dental pulp cells in vitro. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(3):255-262.
[29] HATA M, NARUSE K, OZAWA S, et al. Mechanical stretch increases the proliferation while inhibiting the osteogenic differentiation in dental pulp stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2013;19(5-6):625-633.
[30] PAPHANGKORAKIT J, OSBORN JW. The effect of normal occlusal forces on fluid movement through human dentine in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 2000;45(12):1033-1041.
[31] YASHIRO K, YAMAUCHI T, FUJII M, et al. Smoothness of human jaw movement during chewing. J Dent Res. 1999; 78(10):1662-1668.
[32] HAN MJ, SEO YK, YOON HH, et al. Effect of mechanical tension on the human dental pulp cells. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering.2008;13(4):410-417.
[33] GAO Q, WALMSLEY AD, COOPER PR, et al. Ultrasound Stimulation of Different Dental Stem Cell Populations: Role of Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase Signaling. J Endod. 2016; 42(3):425-431.
[34] CUI JH, PARK K, PARK SR, et al. Effects of low-intensity ultrasound on chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells embedded in polyglycolic acid: an in vivo study. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(1):75-82.
[35] LEE HJ, CHOI BH, MIN BH, et al. Low-intensity ultrasound stimulation enhances chondrogenic differentiation in alginate culture of mesenchymal stem cells. Artif Organs. 2006;30(9): 707-715.
[36] WANG YK, CHEN CS. Cell adhesion and mechanical stimulation in the regulation of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(7):823-832.
[37] HU B, ZHANG Y, ZHOU J, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound stimulation facilitates osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(4): e95168.
[38] MARVEL S, OKRASINSKI S, BERNACKI SH, et al. The development and validation of a LIPUS system with preliminary observations of ultrasonic effects on human adult stem cells. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2010;57(9):1977-1984.
[39] GAO Q, COOPER PR, WALMSLEY AD, et al. Role of Piezo Channels in Ultrasound-stimulated Dental Stem Cells. J Endod. 2017;43(7):1130-1136.
[40] YU V, DAMEK-POPRAWA M, NICOLL SB, et al. Dynamic hydrostatic pressure promotes differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;386(4): 661-665.
[41] GRAZIANO A, D'AQUINO R, LAINO G, et al. Dental pulp stem cells: a promising tool for bone regeneration. Stem Cell Rev. 2008;4(1):21-26.
[42] CHEN X, GUO J, YUAN Y, et al. Cyclic compression stimulates osteoblast differentiation via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15(5): 2890-2896.
[43] JI J, SUN W, WANG W, et al. The effect of mechanical loading on osteogenesis of human dental pulp stromal cells in a novel in vitro model. Cell Tissue Res. 2014;358(1):123-133.
[44] TABATABAEI FS, JAZAYERI M, GHAHARI P, et al. Effects of equiaxial strain on the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells without using biochemical reagents. Mol Cell Biomech. 2014; 11(3):209-220.
[45] KRAFT DC, BINDSLEV DA, MELSEN B, et al. Mechanosensitivity of dental pulp stem cells is related to their osteogenic maturity. Eur J Oral Sci. 2010;118(1):29-38.
[46] HAN MJ, SEO YK, YOON HH, et al. Upregulation of bone-like extracellular matrix expression in human dental pulp stem cells by mechanical strain. Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering. 2010;15(4):572-579.
[47] CAI X, ZHANG Y, YANG X, et al. Uniaxial cyclic tensile stretch inhibits osteogenic and odontogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(5): 347-353.
[48] SHIBUTANI N, HOSOMICHI J, ISHIDA Y, et al. Influence of occlusal stimuli on the microvasculature in rat dental pulp. Angle Orthod. 2010;80(2):316-321.
[49] MIYASHITA S, AHMED NE, MURAKAMI M, et al. Mechanical forces induce odontoblastic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on three-dimensional biomimetic scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017;11(2):434-446.
[50] 肖敏,陈博,李明伟,等.机械压应力刺激对人牙髓干细胞体外增殖矿化的影响[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25(4):187-192.
[51] DADO D, SAGI M, LEVENBERG S, et al. Mechanical control of stem cell differentiation. Regen Med. 2012;7(1):101-116.
[52] YAMASHIRO T, ZHENG L, SHITAKU Y, et al. Wnt10a regulates dentin sialophosphoprotein mRNA expression and possibly links odontoblast differentiation and tooth morphogenesis. Differentiation. 2007;75(5):452-462.
[53] 何梅,吴家媛.Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对牙根发育的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(28):4556-4562.
[54] ZHANG H, LIU S, ZHOU Y, et al. Natural mineralized scaffolds promote the dentinogenic potential of dental pulp stem cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(7-8):677-691.
[55] SHI S, ROBEY PG, GRONTHOS S. Comparison of human dental pulp and bone marrow stromal stem cells by cDNA microarray analysis. Bone. 2001;29(6):532-539.
[56] LEE SK, LEE CY, KOOK YA, et al. Mechanical stress promotes odontoblastic differentiation via the heme oxygenase-1 pathway in human dental pulp cell line. Life Sci. 2010;86(3-4):107-114.