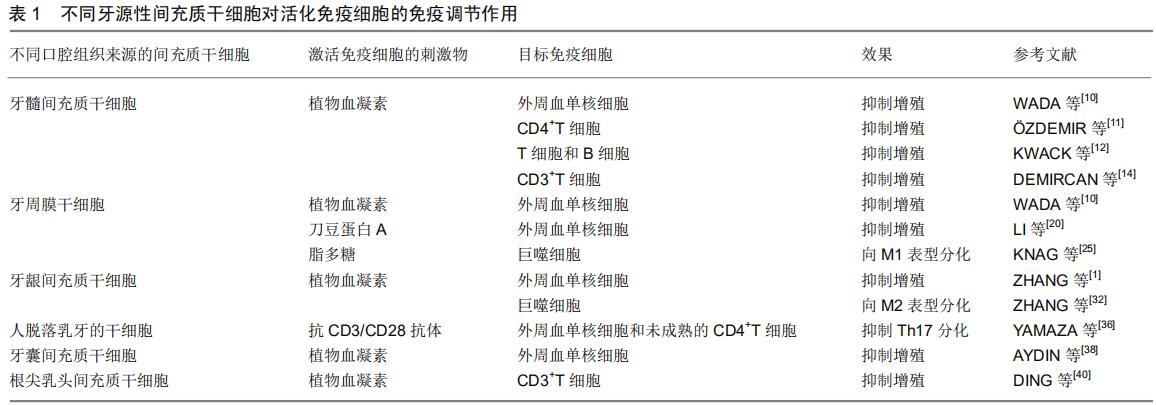
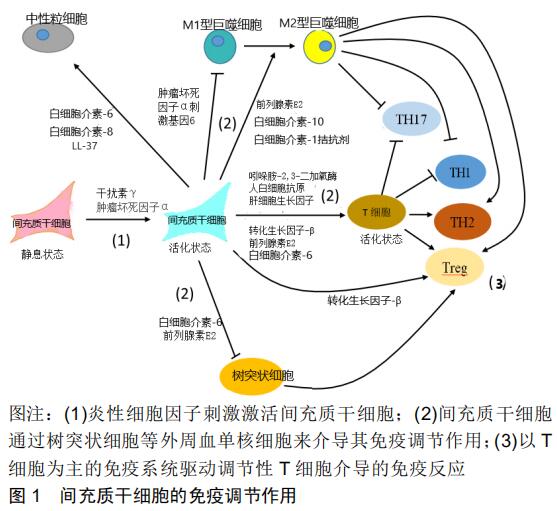
|
[1] ZHANG Q, SHI S, LIU Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from human gingiva are capable of immunomodulatory functions and ameliorate inflammation-related tissue destruction in experimental colitis. J Immunol. 2009;183(12):7787-7798.
[2] YANG R, YU T, ZHOU Y. Interplay between craniofacial stem cells and immune stimulus. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):147.
[3] MA OK, CHAN KH. Immunomodulation by mesenchymal stem cells: Interplay between mesenchymal stem cells and regulatory lymphocytes. World J Stem Cells. 2016;8(9):268-278.
[4] MUNN DH, MELLOR AL. Indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase and metabolic control of immune responses. Trends Immunol. 2013;34(3):137-143.
[5] FONTAINE MJ, SHIH H, SCHÄFER R, et al. Unraveling the Mesenchymal Stromal Cells' Paracrine Immunomodulatory Effects. Transfus Med Rev. 2016;30(1):37-43.
[6] KALINSKI P. Regulation of immune responses by prostaglandin E2. J Immunol. 2012;188(1):21-28.
[7] NEMETH K,KEANE-MYERS A, BROWN JM, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells use TGF-beta to suppress allergic responses in a mouse model of ragweed-induced asthma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107(12):5652-5657.
[8] DOMINICI M, LE BLANC K, MUELLER I, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006; 8(4):315-317.
[9] GRONTHOS S, MANKANI M, BRAHIM J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[10] WADA N, MENICANIN D, SHI S, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of human periodontal ligament stem cells. J Cell Physiol. 2009;219(3): 667-676.
[11] ÖZDEMIR AT, ÖZGÜL ÖZDEMIR RB, KIRMAZ C, et al. The paracrine immunomodulatory interactions between the human dental pulp derived mesenchymal stem cells and CD4 T cell subsets. Cell Immunol. 2016;310:108-115.
[12] KWACK KH, LEE JM, PARK SH, et al. Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Suppress Alloantigen-induced Immunity by Stimulating T Cells to Release Transforming Growth Factor Beta. J Endod. 2017;43(1): 100-108.
[13] ZHAO Y, WANG L, JIN Y, et al. Fas ligand regulates the immunomodulatory properties of dental pulp stem cells. J Dent Res. 2012;91(10):948-954.
[14] DEMIRCAN PC, SARIBOYACI AE, UNAL ZS, et al. Immunoregulatory effects of human dental pulp-derived stem cells on T cells: comparison of transwell co-culture and mixed lymphocyte reaction systems. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(10):1205-1220.
[15] OMI M, HATA M, NAKAMURA N, et al. Transplantation of dental pulp stem cells suppressed inflammation in sciatic nerves by promoting macrophage polarization towards anti-inflammation phenotypes and ameliorated diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7(4): 485-496.
[16] LEE S, ZHANG QZ, KARABUCAK B, et al. DPSCs from Inflamed Pulp Modulate Macrophage Function via the TNF-α/IDO Axis. J Dent Res. 2016;95(11):1274-1281.
[17] RUFAS P, JEANNEAU C, ROMBOUTS C, et al. Complement C3a Mobilizes Dental Pulp Stem Cells and Specifically Guides Pulp Fibroblast Recruitment. J Endod. 2016;42(9):1377-1384.
[18] SEO BM, MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, et al. Investigation of multipotent postnatal stem cells from human periodontal ligament. Lancet. 2004; 364(9429):149-155.
[19] LIU D, XU J, LIU O, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells derived from inflamed periodontal ligaments exhibit impaired immunomodulation. J Clin Periodontol. 2012;39(12):1174-1182.
[20] LI C, WANG X, TAN J, et al. The immunomodulatory properties of periodontal ligament stem cells isolated from inflamed periodontal granulation. Cells Tissues Organs. 2014;199(4):256-265.
[21] TANG HN, XIA Y, YU Y, et al. Stem cells derived from "inflamed" and healthy periodontal ligament tissues and their sheet functionalities: a patient-matched comparison. J Clin Periodontol. 2016;43(1):72-84.
[22] SHIN C, KIM M, HAN JA, et al. Human periodontal ligament stem cells suppress T-cell proliferation via down-regulation of non-classical major histocompatibility complex-like glycoprotein CD1b on dendritic cells. J Periodontal Res. 2017;52(1):135-146.
[23] LIU O, XU J, DING G, et al. Periodontal ligament stem cells regulate B lymphocyte function via programmed cell death protein 1. Stem Cells. 2013;31(7):1371-1382.
[24] NAGATA M, IWASAKI K, AKAZAWA K, et al. Conditioned Medium from Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Enhances Periodontal Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017;23(9-10):367-377.
[25] KANG H, LEE MJ, PARK SJ, et al. Lipopolysaccharide-Preconditioned Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Induce M1 Polarization of Macrophages through Extracellular Vesicles. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19(12): E3843.
[26] SILVÉRIO KG, RODRIGUES TL, COLETTA RD, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell properties of periodontal ligament cells from deciduous and permanent teeth. J Periodontol. 2010;81(8):1207-1215.
[27] TZACH-NAHMAN R, NASHEF R, FLEISSIG O, et al. Oral fibroblasts modulate the macrophage response to bacterial challenge. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):11516.
[28] WANG Q, DING G, XU X. Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Regulate Apoptosis of Neutrophils. Open Med (Wars). 2017;12:19-23.
[29] KUKOLJ T, TRIVANOVIĆ D, DJORDJEVIĆ IO, et al. Lipopolysaccharide can modify differentiation and immunomodulatory potential of periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK1,2 signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(1):447-462.
[30] MISAWA MYO, SILVÉRIO RUIZ KG, NOCITI FH Jr, et al. Periodontal ligament-derived mesenchymal stem cells modulate neutrophil responses via paracrine mechanisms. J Periodontol. 2019;90(7): 747-755.
[31] GRAWISH ME. Gingival-derived mesenchymal stem cells: An endless resource for regenerative dentistry. World J Stem Cells. 2018;10(9): 116-118.
[32] ZHANG QZ, SU WR, SHI SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells elicit polarization of m2 macrophages and enhance cutaneous wound healing. Stem Cells. 2010;28(10): 1856-1868.
[33] ZHANG X, HUANG F, LI W, et al. Human Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Modulate Monocytes/Macrophages and Alleviate Atherosclerosis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:878.
[34] DU L, YANG P, GE S. Isolation and characterization of human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stem cells using limiting dilution method. J Dent Sci. 2016;11(3):304-314.
[35] MIURA M, GRONTHOS S, ZHAO M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003; 100(10):5807-5812.
[36] YAMAZA T, KENTARO A, CHEN C, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2010;1(1):5.
[37] GAO X, SHEN Z, GUAN M, et al. Immunomodulatory Role of Stem Cells from Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth on Periodontal Regeneration. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(17-18):1341-1353.
[38] AYDIN S, ŞAHIN F. Stem Cells Derived from Dental Tissues. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1144:123-132.
[39] HIEKE C, KRIEBEL K, ENGELMANN R, et al. Human dental stem cells suppress PMN activity after infection with the periodontopathogens Prevotella intermedia and Tannerella forsythia. Sci Rep. 2016;6:39096.
[40] DING G, LIU Y, AN Y, et al. Suppression of T cell proliferation by root apical papilla stem cells in vitro. Cells Tissues Organs. 2010;191(5): 357-364.
[41] KRAMPERA M. Mesenchymal stromal cell 'licensing': a multistep process. Leukemia. 2011;25(9):1408-1414.
[42] MOONEN CGJ, ALDERS ST, BONTKES HJ, et al. Survival, Retention, and Selective Proliferation of Lymphocytes Is Mediated by Gingival Fibroblasts. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1725.
[43] HOSSEIN-KHANNAZER N, HASHEMI SM, NAMAKI S, et al. Study of the immunomodulatory effects of osteogenic differentiated human dental pulp stem cells. Life Sci. 2019;216:111-118.
[44] KIM JH, JO CH, KIM HR, et al. Comparison of Immunological Characteristics of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from the Periodontal Ligament, Umbilical Cord, and Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2018; 2018:8429042.
[45] SU WR, ZHANG QZ, SHI SH, et al. Human gingiva-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate contact hypersensitivity via prostaglandin E2-dependent mechanisms. Stem Cells. 2011;29(11): 1849-1860.
[46] 岳艳,屈艺,母得志.间充质干细胞源性外泌体在脑损伤治疗中的研究进展[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2017,19(12):1285-1290.
[47] ANDRUKHOV O, HONG JS, ANDRUKHOVA O, et al. Response of human periodontal ligament stem cells to IFN-γ and TLR-agonists. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):12856.
[48] ISSARANGGUN NA AYUTHAYA B, SATRAVAHA P, PAVASANT P. Interleukin-12 modulates the immunomodulatory properties of human periodontal ligament cells. J Periodontal Res. 2017;52(3):546-555.
[49] ZHANG J, WANG CM, ZHANG P, et al. Expression of programmed death 1 ligand 1 on periodontal tissue cells as a possible protective feedback mechanism against periodontal tissue destruction. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):2423-2430.
[50] KONERMANN A, BEYER M, DESCHNER J, et al. Human periodontal ligament cells facilitate leukocyte recruitment and are influenced in their immunomodulatory function by Th17 cytokine release. Cell Immunol. 2012;272(2):137-143.
[51] OLSEN I, LAMBRIS JD, HAJISHENGALLIS G. Porphyromonas gingivalis disturbs host-commensal homeostasis by changing complement function. J Oral Microbiol. 2017;9(1):1340085.
[52] 刘畅,王家凤,张志民.Toll样受体的免疫调节在口腔疾病中的研究进展[J].口腔生物医学, 2018,9(1):45-48.
[53] LIU Y, GAO Y, ZHAN X, et al. TLR4 activation by lipopolysaccharide and Streptococcus mutans induces differential regulation of proliferation and migration in human dental pulp stem cells. J Endod. 2014;40(9):1375-1381.
[54] 曹采方.牙周病学[M].4版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2013.
[55] 范芹,管晓燕,李小娜,等.茶多酚对脂多糖介导下人牙周膜成纤维细胞COX-2表达的影响[J].广东医学,2016,37(17):2566-2568.
[56] MEKHEMAR MK, ADAM-KLAGES S, KABELITZ D, et al. TLR-induced immunomodulatory cytokine expression by human gingival stem/progenitor cells. Cell Immunol. 2018;326:60-67.
[57] COCHET F, PERI F. The Role of Carbohydrates in the Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/Toll-Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Signalling. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11): E2318.
[58] MAHANONDA R, SA-ARD-IAM N, MONTREEKACHON P, et al. IL-8 and IDO expression by human gingival fibroblasts via TLRs. J Immunol. 2007;178(2):1151-1157.
[59] MOON JS, CHEONG NR, YANG SY, et al. Lipopolysaccharide- induced indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase expression in the periodontal ligament. J Periodontal Res. 2013;48(6):733-739.
[60] RASHEDI I, GÓMEZ-ARISTIZÁBAL A, WANG XH, et al. TLR3 or TLR4 Activation Enhances Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Mediated Treg Induction via Notch Signaling. Stem Cells. 2017;35(1):265-275.
[61] TOMIC S, DJOKIC J, VASILIJIC S, et al. Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp and dental follicle are susceptible to activation by toll-like receptor agonists. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(4):695-708.
[62] SONODA S, YAMAZA H, MA L, et al. Interferon-gamma improves impaired dentinogenic and immunosuppressive functions of irreversible pulpitis-derived human dental pulp stem cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19286.
[63] YANG H, APRECIO RM, ZHOU X, et al. Therapeutic effect of TSG-6 engineered iPSC-derived MSCs on experimental periodontitis in rats: a pilot study. PLoS One. 2014;9(6):e100285.
[64] MESTAS J, HUGHES CC. Of mice and not men: differences between mouse and human immunology. J Immunol. 2004;172(5):2731-2738.
|