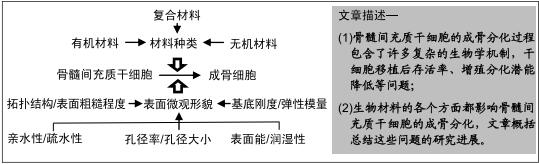
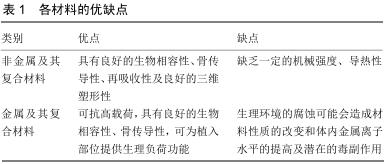
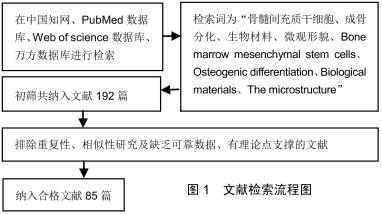
|
[1] MOHAMMAD MH, AL SHAMMARI AM, AL JUBOORY AA, et al. Characterization of neural stemness status through the neurogenesis process for bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Stem Cells Cloning.2016;9:1-15.
[2] 韩振霞,时庆,汪大琨.骨髓源与脐带源间充干细胞的基本生物学特征的比较[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2013,21(5):1248-1255.
[3] ZHAN XS, EL-ASHRAM S, LUO DZ, et al. A Comparative Study of Biological Characteristics and Transcriptome Profiles of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Different Canine Tissues.Int J Mol Sci.2019;20(6):1485.
[4] MUTLU L, HUFNAGEL D, TAYLOR HS. The endometrium as a source of mesenchymal stem cells for regenerative medicine. Biol Reprod.2015;92(6):138.
[5] IGE O, UMORU L, ARIBO S. Natural products:a minefield of biomaterials.ISRN Mater Sci.2012;2012:1-20.
[6] MORN N, KAPUSETTI G. Piezoelectric material-A promising approachfor bone and cartilage regeneration.Med Hypotheses. 2017;108(10):10-16.
[7] 杨雄峰,姜慧娇,王小义,等.体外负压培养对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖能力和血管内皮生长因子分泌水平的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(1):33-39.
[8] 邹维艳,赵洁,李仪,等.体外培养SD大鼠与BALB/c小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特性比较[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2018, 34(12):1099-1104.
[9] 叶含钊,安荣泽,王兆杰.不同代次骨髓间充质干细胞的生物学特性[J].贵州医药,2015,39(1):83-86.
[10] NEUHUBER B, SWANGER SA, HOWARD L, et al. Effects of plating density and culture time on bone marrow stromal cell characteristics.Exp Hematol.2008;36(9):1176-1185.
[11] LI X, ZHANG Y, QI G. Evaluation of isolation methods and culture conditions for rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells.Cytotechnology.2013;65(3):323.
[12] 刘贤华,仝青英,白晓东.人骨髓间充质干细胞体外不同分离与培养方法的比较[J].武警医学,2012,23(10):836-839.
[13] MAYLE A, LUO M, JEONG M, et al. Flow cytometry analysis of murine hematopoietic stem cells.ytometry Part A. 2013; 83(1):27-37.
[14] HALL SR, JIANG Y, LEARY E, et al. Identification and isolation of small CD44 negative mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells from human bone marrow using elutriation and polychromatic flow cytometry.Stem Cells Transl Med.2013;2(8):567-578.
[15] SONG K, HUANG M, SHI Q, et al. Cultivation and identification of rat bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mole Med Rep.2014;10(2):755.
[16] JANG NK, LEE SE, CHA SR, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cell in silk fibroin scaffold.Int J Tissue Reg. 2015;6:56-63.
[17] BARBA A, DIEZ-ESCUDERO A, MAAZOUZ Y, et al. Osteoinduction by foamed and 3D-printed calcium phosphate scaffolds:effect of nanostructure and pore architecture.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2017;9(48):41722-41736.
[18] XIA Y, CHEN H, ZHANG F, et al. Gold nanoparticles in injectable calcium phosphate cement enhance osteogenic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells.Nanomedicine. 2018;14(1):35-45.
[19] XIE H, CHUA M, ISLAM I, et al. CVD-grown monolayer graphene induces osteogenic but not odontoblastic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells. Dent Mater. 2017; 33:e13-e21.
[20] XIE H, CAO T, GOMES JV, et al. Two and three-dimensional graphene substrates to magnify osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells. Carbon.2015;93:266-275.
[21] XIE H, CAO T, RODRÍGUEZ-LOZANO FJ, et al. Graphene for the development of the next-generation of biocomposites for dental and medical applications.Dent Mater.2017;33:765-774.
[22] XIE H, CAO T, FRANCO-OBREGÓN A, et al. Graphene-Induced Osteogenic Differentiation Is Mediated by the Integrin/FAK Axis.Int J Mol Sci.2019;20(3):547.
[23] JIA PP, SUN T, JUNAID M, et al. Pei Nanotoxicity of different sizes of graphene (G) and graphene oxide (GO) in vitro and in vivo.Environ Pollut.2019;247:595-606.
[24] HE Y, LI Y, CHEN G, et al. Concentration-dependent cellular behavior and osteogenic differentiation effect induced in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells treated with magnetic graphene oxide.J Biomed Mater Res A.2020;108(1):50-60.
[25] HAN P, WU C, XIAO Y. The effect of silicate ions on proliferation, osteogenic differentiation and cell signalling pathways (WNT and SHH) of bone marrow stromal cells. Biomater Sci. 2013;1:379-392.
[26] SHIE MY, DING SJ, CHANG HC. The role of silicon in osteoblast-like cell proliferation and apoptosis.Acta Biomater. 2011;7(6):2604-2614.
[27] LI J, WEI L, SUN J, et al. Effect of ionic products of dicalcium silicate coating on osteoblast differentiation and collagen production via TGF-β1 pathway.J Biomater Appl. 2013;27(5): 595-604.
[28] YANG X, LI Y, LIU X, et al. The stimulatory effect of silica nanoparticles on osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells.Biomed Mater.2016;12(1):015001.
[29] BELLUCCI D, VERONESI E, STRUSI V, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Combined with a New Strontium- Enriched Bioactive Glass: An ex-vivo Model for Bone Regeneration.Materials (Basel).2019;12(21):3633.
[30] KAZEMI M, DEHGHAN MM, AZAMI M. Biological evaluation of porous nanocomposite scaffolds based on strontium substituted beta-TCP and bioactive glass: An in vitro and in vivo study.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2019;105:110071.
[31] 孙朋.聚乳酸基生物医用复合材料制备与性能研究[D].长春:长春工业大学,2019.
[32] 程利,王鑫,赵雄燕.聚乳酸基复合材料的研究进展[J].应用化工, 2019,28(5):1181-1185.
[33] MI HY, SALICK MR, JING X, et al. Characterization of thermoplastic polyurethane/polylactic acid (TPU/PLA) tissue engineering scaffolds fabricated by microcellular injection molding.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2013;33(8):4767-4776.
[34] MI HY, PALUMBO S, JING X, et al. Thermoplastic polyurethane/ hydroxyapatite electrospun scaffolds for bone tissue engineering: effects of polymer properties and particle size.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2014;102(7):1434-1444.
[35] 闫峰,张越林,岳伟,等.体外构建纯化骨髓间充质干细胞与壳聚糖生物支架复合体的实验研究[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2014, 14(11):1000-1006.
[36] 王莉莉,严佳,李东升,等.两种新型胶原膜引导骨组织再生的体内外性能研究[J].口腔医学,2019,39(6):481-487.
[37] BI X, MATURAVONGSADIT P, TAN Y, et al. Polyamidoamine dendrimer-PEG hydrogel and its mechanical property on differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells.Biomed Mater Eng. 2019;30(1):111-123.
[38] KOOK YJ, LEE DH, SONG JE, et al. Osteogenesis evaluation of duck's feet-derived collagen/hydroxyapatite sponges immersed in dexamethasone.Biomater Res. 2017;21(2): 561-756.
[39] LIS-BARTOS A, SMIESZEK A, FRAŃCZYK K, et al. Fabrication, Characterization, and Cytotoxicity of Thermoplastic Polyurethane/Poly(lactic acid) Material Using Human Adipose Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Stem Cells (hASCs).Polymers (Basel).2018;10(10):1073.
[40] 陈娇,舒莉萍,李轩泽,等.聚乳酸-羟基乙酸共聚物负载人骨髓间充质干细胞构建组织工程骨[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(26):4109-4114.
[41] ABAZARI MF, NEJATI F, NASIRI N, et al. Platelet-rich plasma incorporated electrospun PVA-chitosan-HA nanofibers accelerates osteogenic differentiation and bone reconstruction. Gene.2019;720:144096.
[42] ZENG H, CAO JJ, COMBS GF JR. Selenium in bone health: roles in antioxidant protection and cell proliferation.Nutrients. 2013;5(1):97-110.
[43] KOROWASH SI, BURDZINSKA A, PĘDZISZ P. Selenium- Substituted Hydroxyapatite Nanoparticles and their in Vitro Interaction on Human Bone Marrow- and Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Interceram- International Ceramic Review. 2017;66(6):244-252.
[44] CAO JJ, GREGOIRE BR, ZENG H. Selenium defificiency decreases antioxidative capacity and is detrimental to bone microarchitecture in mice.J Nutr.2012;142(8):1526-1531.
[45] LI C, WANG Q, GU X, et al. Porous Se@SiO2 nanocomposite promotes migration and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell to accelerate bone fracture healing in a rat model.Int J Nanomedicine.2019;14:3845-3860.
[46] SRIVASTAVA N, MUKHOPADHYAY M. Green synthesis and structural characterization of selenium nanoparticles and assessment of their antimicrobial property.Bioprocess Biosyst Eng. 2015;38(9):1723-1730.
[47] ESTEVEZ H, GARCIA-LIDON JC, LUQUE-GARCIA JL, et al. Effects of chitosan-stabilized selenium nanoparticles on cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle pattern in HepG2 cells: comparison with other selenospecies.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2014;122:184-193.
[48] AL-NAWAS B, BRÄGGER U, MEIJER HJ, et al. A double-blind randomized controlled trial (RCT) of titanium-13zirconium versus titanium grade IV small-diameter bone level implants in edentulous mandibles—results from a 1-year observation period.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2012;14 (6):896-904.
[49] WEN B, ZHU F, LI Z, et al. The osseointegration behavior of titanium-zirconium implants in ovariectomized rabbits.Clin Oral Implants Res.2014;25(7):819-825.
[50] BOLAT G, IZQUIERDO J, SANTANA JJ, et al. Electrochemical characterization of ZrTi alloys for biomedical applications. Electrochim Acta.2013;88(2):447-456.
[51] JIN Z, YAN X, SHEN K, et al. TiO2 nanotubes promote osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via regulation of lncRNA CCL3-AS.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019:181:416-425.
[52] JONITZ A, LOCHNER K, LINDNER T, et al. Oxygen consumption, acidification and migration capacity of human primary osteoblasts within a three-dimensional tantalum scaffold.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2011;22(9):2089-2095.
[53] LIU G, WANG J, YANG S, et al. Effect of a porous tantalum rod on early and intermediate stages of necrosis of the femoral head.Biomed Mater.2010;5(6):65-68.
[54] LACHIEWICZ PF, SOILEAU ES. Tantalum components in diffificult acetabular revisions.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2010; 468:454-458.
[55] SMITH JO, SENGERS BG, AARVOLD A, et al. Tantalum trabecular metal - addition of human skeletal cells to enhance bone implant interface strength and clinical application.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2014;8(4):304-313.
[56] 谢辉,马志杰,王建川,等.新型多孔钽金属支架材料的生物学评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(18):2839-2845.
[57] HEIDEN M, HUANG S, NAUMAN E, et al. Nanoporous metals for biodegradable implants: Initial bone mesenchymal stem cell adhesion and degradation behavior.J Biomed Mater Res A.2016;104(7):1747-1758.
[58] BOSTANCIOGLU RB, GURBUZ M, AKYUREKLI AG, et al. Adhesion profile and differentiation capacity of human adipose tissue derived mesenchymal stem cells grown on metal ion (Zn, Ag and Cu) doped hydroxyapatite nano-coated surfaces.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2017;155:415-428.
[59] XIA Y, ZHAO Y, ZHANG F, et al. Iron oxide nanoparticles in liquid or powder form enhanced osteogenesis via stem cells on injectable calcium phosphate scaffold.Nanomedicine. 2019;21:102069.
[60] MYLLYMAA S, KAIVOSOJA E, MYLLYMAA K, et al. Adhesion, spreading and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on micropatterned amorphous diamond, titanium, tantalum and chromium coatings on silicon.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2010;21(1):329-341.
[61] QUERIDO W, ROSSI AL, FARINA M. The effffects of strontium on bone mineral: A review of current knowledge and microanalytical approaches.Micron.2016;80:122-134.
[62] MOGHANIAN A, FIROOZI S, TAHRIRI M. Characterization, in vitro bioactivity and biological studies of sol-gel synthesized SrO substituted 58S bioactive glass.Ceram Int. 2017;43: 4880-4890.
[63] DELAINE-SMITH RM, REILLY GC.The effects of mechanical loading on mesenchymal stem cell differentiation and matrix production.Vitam Horm.2011;87:417-480.
[64] DAVID BG, FUJITA H, YASUDA K, et al. Linking substrate and nucleus via actin cytoskeleton in pluripotency maintenance of mouse embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res.2019;41:101614.
[65] TEIXEIRA LN, CRIPPA GE, LEFEBVRE LP, et al. The influence of pore size on osteoblast phenotype expression in cultures grown on porous titanium.Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012;41(9):1097-1101.
[66] 王敏.人脂肪干细胞在PLGA支架上向肝细胞诱导分化的实验研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军军事医学科学院,2009.
[67] COVERDALE BDM, GOUGH JE, SAMPSON WW, et al. Use of lecithin to control fiber morphology in electrospun poly (ɛ-caprolactone) scaffolds for improved tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res A.2017;105(10): 2865-2874.
[68] YIN L, CHANG Y, YOU Y, et al. Biological responses of human bone mesenchymal stem cells to Ti and TiZr implant materials.Clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2019;21(4):550-564.
[69] YANG Y, WANG K, GU X, et al. Biophysical Regulation of Cell Behavior-Cross Talk between Substrate Stiffness and Nanotopography.Engineering (Beijing).2017;3(1):36-54
[70] 吕东媛,周吕文,龙勉.干细胞的生物力学研究[J].力学进展, 2017, 47(1):534-585.
[71] LI Z, GONG Y, SUN S, et al. Differential regulation of stiffness, topography, and dimension of substrates in rat mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials.2013;34(31):7616-7625.
[72] ZHENG G, GUAN B, HU P, et al. Topographical cues of direct metal laser sintering titanium surfaces facilitate osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through epigenetic regulation.Cell Prolif.2018;51(4):e12460.
[73] WITKOWSKA-ZIMNY M, WALENKO K, WROBEL E, et al. Effect of substrate stiffness on the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stem cells and bone-derived cells.Cell Biol Int.2013;37:608-616.
[74] WITKOWSKA-ZIMNY M, WROBEL E, MROWKA P. α2β1 integrin-mediated mechanical signals during osteodifferentiation of stem cells from the Wharton's jelly of the umbilical cord. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2014;52(4):297-307.
[75] SUN M, CHI G, XU J, et al. Extracellular matrix stiffness controls osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells mediated by integrin α5.Stem Cell Res Ther.2018;9(1):52.
[76] HU YL, LU S, SZETO KW, et al. FAK and paxillin dynamics at focal adhesions in the protrusions of migrating cells.Sci Rep. 2014;4:6024.
[77] ZHOU C, ZHANG D, ZOU J, et al. Substrate Compliance Directs the Osteogenic Lineages of Stem Cells from the Human Apical Papilla via the Processes of Mechanosensing and Mechanotransduction.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2019; 11(29):26448-26459.
[78] ZHANG D, ZHOU C, WANG Q, et al. Extracellular Matrix Elasticity Regulates Osteocyte Gap Junction Elongation: Involvement of Paxillin in Intracellular Signal Transduction. Cell Physiol Biochem.2018;51(3):1013-1026.
[79] ROWLANDS AS, GEORGE PA, COOPER-WHITE JJ. Directing osteogenic and myogenic differentiation of MSCs: interplay of stiffness and adhesive ligand presentation.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2008;295(4):C1037-1044.
[80] TIBBITT MW, ANSETH KS. Dynamic microenvironments: the fourth dimension.Sci Transl Med.2012;4(160):160ps24.
[81] KHETAN S, GUVENDIREN M, LEGANT WR, et al. Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels.Nat Mater. 2013;12(5):458-465.
[82] YANG C, TIBBITT MW, BASTA L, et al. Mechanical memory and dosing influence stem cell fate. Nat Mater. 2014;13(6): 645-652.
[83] KLOXIN AM, KASKO AM, SALINAS CN, et al. Photodegradable hydrogels for dynamic tuning of physical and chemical properties.Science.2009;324(5923):59-63.
[84] GU Y, ZHU J, XUE C, et al. Chitosan/silk fibroin-based, Schwann cell-derived extracellular matrix-modified scaffolds for bridging rat sciatic nerve gaps.Biomaterials. 2014;35(7): 2253-2263.
[85] LIU X, ZHANG F, WANG Q, et al. Platelet-inspired multiscaled cytophilic interfaces with high specificity and efficiency toward point-of-care cancer diagnosis.Small.2014;10(22):4677-4683.
|