中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (19): 3108-3116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2077
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇
细胞标记与体内追踪成像:在动物和人类中应用的最新进展
徐梦欣1,李一佳2,刘志博1,3
- 1北京大学化学与分子工程学院,北京市 100871;2浙江清华长三角研究院细胞药物转化公共服务平台,浙江省嘉兴市 314000;3北京大学北大-清华生命科学联合中心,北京市 100871
-
收稿日期:2019-08-26修回日期:2019-08-27接受日期:2019-10-15出版日期:2020-07-08发布日期:2020-04-09 -
通讯作者:刘志博,博士,研究员,北京大学化学与分子工程学院,北京市 100871;北京大学北大-清华生命科学联合中心,北京市 100871 -
作者简介:徐梦欣,女,1993年生,山东省汶上县人,汉族,北京大学化学与分子工程学院在读博士,主要从事生物大分子标记与成像的研究工作。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(U186720011)
Cell labeling and tracking imaging in vivo: newest advance in animals and humans
Xu Mengxin1, Li Yijia2, Liu Zhibo1, 3
- 1College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China; 2Cell Drug Transformation Public Service Platform of Yangtze Delta Region Institute of Tsinghua University, Jiaxing 314000, Zhejiang Province, China; 3Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
-
Received:2019-08-26Revised:2019-08-27Accepted:2019-10-15Online:2020-07-08Published:2020-04-09 -
Contact:Liu Zhibo, PhD, Researcher, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China; Peking-Tsinghua Center for Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China -
About author:Xu Mengxin, Doctoral candidate, College of Chemistry and Molecular Engineering, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. U186720011
摘要:
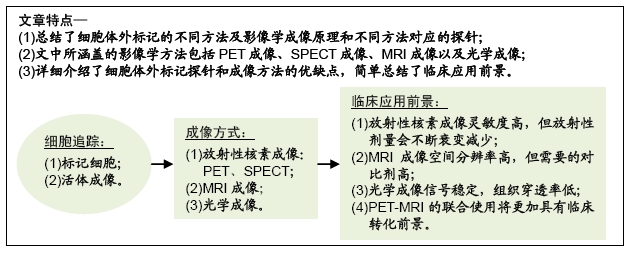
文题释义:
细胞治疗:采用生物工程方法获取细胞,再通过体外扩增、特殊培养等处理后,使这些细胞具有增强免疫、杀死病原体和肿瘤细胞、促进组织器官再生和机体康复等治疗功效,从而达到治疗疾病的目的。
分子影像学:运用影像学对活体状态下的生物过程进行细胞和分子水平的定性和定量研究。以药物分子作为探针进行成像,能够得到药物的药代动力学、生物分布、靶向性、毒性等众多信息,从而帮助缩短药物研发周期、降低失败风险。
背景:随着国内外多个细胞治疗产品获得临床试验批准,细胞治疗例如干细胞治疗、肿瘤过继免疫疗法得到广泛关注。体内细胞实时观察与成像可以直观显示细胞的分布,追踪细胞的活动,监测细胞的活性,观察细胞的迁移和生长。目前的许多成像技术可以使体内细胞可视化,例如超声、光学、磁共振成像以及核成像技术,这些方法均需对应不同的标记和检测策略,每种策略都有其固有的优点和缺点。
目的:结合最新的研究动态,将对不同细胞追踪方法的原理、发展和这些方法在动物和人类中应用的最新进展进行综述。
方法:第一作者以“cell tracking,in vivo cell tracking,PET imaging,MRI,optical imaging”为关键词在PubMed、Google Scholar、Web of Science、中国知网等数据库进行检索,重点关注过去5-10年的相关文章。文章内容主要描述不同细胞追踪方法的原理以及在动物模型和临床患者体内的细胞追踪应用。
结果与结论:在过去的二十几年中,细胞追踪已经发展成为一个多方面的学科,不仅在动物模型中建立了多种稳健的方法,并且在人类的一些研究中证明了临床转化的可行性。尤其是以PET、MRI成像技术为代表的无创检测,新型对比剂的研发,为细胞治疗在临床与科研的应用提供了强有力的支持。
ORCID: 0000-0002-3764-0154(徐梦欣)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
徐梦欣, 李一佳, 刘志博. 细胞标记与体内追踪成像:在动物和人类中应用的最新进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(19): 3108-3116.
Xu Mengxin, Li Yijia, Liu Zhibo. Cell labeling and tracking imaging in vivo: newest advance in animals and humans[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(19): 3108-3116.
2.1 PET成像 PET成像原理是利用其环形探测器对一对具有511 keV但方向相反飞出的γ光子进行信号捕捉、数据处理、图像重建。这对光子是由放射性核素发生β+衰变产生正电子,正电子进一步与电子发生湮灭产生的。较常使用发射正电子的核素有C-11、F-18、Cu-64、Ga-68、Zr-89、I-124。通过将核素标记在可用于生物体的分子上,根据其信号分布进行成像从而获得待测组织或器官的放射性药物分布,根据探针集聚情况提供测量生物变化的方法,例如代谢、细胞定位或肿瘤负荷[4-5]。在以下内容中将主要按照核素类型来介绍PET成像在细胞标记中的应用。探针分类见图1。

2.1.1 18F-FDG F-18是F-19的同位素,半衰期为 118 min。18F-FDG(氟代脱氧葡萄糖)是临床上最常用的PET显像剂[6],是2-脱氧葡萄糖的氟代衍生物,因此18F-FDG可以与葡萄糖一样被细胞摄取,参与代谢过程。葡萄糖分子的2位氧是参与糖酵解所必需的,但18F-FDG的2位氧被氟取代,因此糖酵解过程不能继续,生成的18F-FDG-6-磷酸将滞留在细胞内。18F-FDG的分布能很好地反映体内细胞对葡萄糖的摄取和磷酸化情况。由于癌细胞代谢旺盛,对葡萄糖等营养物质的需求比正常细胞要高得多,因此18F-FDG的PET成像可用于癌症的诊断、分期和治疗监测,尤其是对于霍奇金氏病、非霍奇金氏淋巴瘤、结直肠癌、乳腺癌、黑色素瘤以及肺癌有较好的诊断效果[7-9]。
随着嵌合抗原受体T细胞免疫治疗的兴起,移植到人体内的细胞分布、增长和增殖情况一直困扰着科研和医疗工作者。18F-FDG在临床中同样可以用于体外标记细胞,然后进行体内细胞追踪,主要用于体外标记干细胞、T细胞和癌细胞等[10-12]。
1997年,KOIKE等[13]使用18F-FDG对小鼠黑色素瘤细胞B16BL6和肝转移性RAW117大细胞淋巴瘤的2个亚系进行了体外标记和小鼠体内追踪。研究发现2种细胞注射后立即在肺中积累,其中肝转移性RAW117细胞比B16BL6黑素瘤细胞从肺中消除得更快。该研究表明,转移性肿瘤细胞的运输可以极大地影响癌症转移的器官特异性。
由于18F-FDG安全性较高,十分适合用于临床试验。KANG等[14]为了探究冠状动脉内注射外周血造血干细胞的归巢和组织分布,采用18F-FDG对外周血造血干细胞进行体外标记然后在人体冠状动脉内注射,其中17例心肌梗死患者作为冠状动脉内注射组(男14例,女3例),3例心肌梗死患者作为静脉注射组(均为男性),总量175-370 MBq(5-10 mCi)的18F-FDG在37 ℃下与外周血造血干细胞共孵育40 min,离心、洗涤、收集细胞后,测得平均标记效率为72%(46%-95%),通过冠状动脉内注射44.4-175 MBq(1.2-5.0 mCi)的18F-FDG标记的外周血造血干细胞。在冠状动脉内输注后2 h,使用三维采集模式获得PET/CT图像,有1.5%(0.2%-3.3%)外周血造血干细胞积聚在梗死心肌中,在脾、肝、膀胱和骨髓中显示出高的外周血造血干细胞积累,输注后20 h PET图像显示外周血造血干细胞仍然驻留在心肌中,而静脉注射组显示出高的初始肺摄取,没有心肌活动。实验证明,PET可用于评估和测量靶组织中18F-FDG标记的外周血造血干细胞的分布和数量。
2.1.2 18F-FHBG 18F-FHBG是报告基因显像中的一种报告探针[15]。报告基因表达成像又称转基因表达显像,报告基因表达PET显像是其中的一种,需具备PET报告基因和PET报告探针(显像剂)。报告基因表达PET显像又分为酶报告基因表达PET显像系统和受体报告基因表达PET显像系统,前者应用较为广泛。酶报告基因表达的蛋白质产物是一种酶,报告探针一般是酶的底物,其作用机制为底物在酶作用下,发生磷酸化或脱胺基反应[16]。
目前,研究最多的PET酶报告基因是细胞感染1型单纯疱疹病毒胸苷激酶(herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase,HSV1-tk),该基因能表达胸苷激酶,酶能催化胸苷磷酸化和一系列核苷类似物磷酸化,例如鸟嘌呤的类似物无环鸟苷(acyclovir,ACV)、丙氧鸟苷(ganciclovir,GCV)以及胸腺嘧啶的类似物等。放射性核素标记的核苷类似物进入HSV1-tk基因转染的细胞后,被该基因编码的酶磷酸化成5-磷酸核苷,不能通过细胞膜滞留在被转染细胞内[17]。因而将HSV1-tk基因转录到需要观察细胞内,细胞则可以在体内和体外表达该基因,使用放射性探针便可以追踪目标细胞的位置分布、活性等信息。
常用的HSV1-tk基因报告探针有2类:无环鸟苷衍生物和尿嘧啶核苷衍生物。第一类有18F-ACV、18F-GCV、18F-PCV、18F-FHPG和18F-FHBG,第二类有124I-FIAU、14C-FMAU、18F-FEAU等[18]。研究最多的是18F-FHBG。
18F-FHBG的全称是9-(4-18F-3-羟基甲基丁基)鸟嘌呤。ALAUDDIN和CONTI于1998年首先合成了18F-FHBG,并且在体外实验中验证了在转染基因HT-29结肠癌细胞中的摄取是非转染细胞的18.2倍,非转染细胞中几乎没有摄取[19]。SHIUE等[20]于2001年最早报道了一步合成18F-FHBG,2002年PENUELAS等[21]提出了全自动一步法合成,并对该技术进行了临床前放化纯度及生产率的研究,结果显示放化纯度大于99%,操作简便,节省时间,为临床应用打下了基础。
2001年,GAMBHIR团队首先探究了该探针在动物体内的PET成像,PET图像显示18F-FHBG探针可以追踪HSV1-sr39TK的生物分布,建立了定量的从PET图像中量化治疗基因表达水平的方法,在成像的不同时间点也观察到良好的相关性。通过PET报告基因和PET报告探针成像追踪治疗基因的生物分布、大小和持续时间[22];同年,GAMBHIR团队在健康志愿者体内测定了18F-FHBG的药代动力学、生物分布、稳定性、剂量和安全性,结果显示该探针血液清除速度很快,主要由肾和肝胆途径代谢,其清除快、背景信号低、生物安全、剂量在机体接受范围内等特点表明该探针具有良好的应用前景[23]。此外,该探针不能通过正常的血脑屏障,因此除了像神经胶质母细胞瘤类似的血脑屏障已经被破坏的疾病之外,一般不用于脑部中枢神经系统[24]。
随着嵌合抗原受体T细胞免疫疗法的研究与发展,T细胞在体内的分布和活动越来越受到关注。GAMBHIR团队将HSV1-sr39TK基因转录到T细胞内,利用18F-FHBG做PET成像观测T细胞的抗肿瘤效应。结果显示该探针在肿瘤处有大量的富集,而对体内原始T细胞无成像效应,说明免疫T细胞在肿瘤处有大量富集[25-26],说明利用PET报告基因探针显像可以监测T细胞活性,为肿瘤免疫治疗和其他免疫疾病诊断提供新的方法。
2005年,FDA批准GAMBHIR团队申请的临床一期试验——Assessing the Suitability of an Imaging Probe for Use in Clinical Cell and Gene Therapy Trials in Cancer and Rheumatoid Arthritis。在这项研究中18F-FHBG被FDA的Investigational New Drug(IND)批准用作PET显像剂(IND #61880)。1例接受细胞基因免疫治疗的晚期脑胶质瘤患者在经过治疗之后使用18F-FHBG成像显示在脑胶质瘤部位有高放射性富集,可以认为是T细胞在此部位有大量积聚,在身体其他部位与健康志愿者无差别[27]。此次临床研究于2017年结束,共招募了4例男性患者和3例女性患者,证实了18F-FHBG成像是安全的,并且能够对PET报告基因稳定转染的T细胞进行纵向成像。这种用于监测体内细胞运输的成像方法应该极大地有益于各种基于细胞的癌症治疗。
2.1.3 18F-HFB 直接标记细胞膜进行细胞放射性标记是一种简单直接的方式,KIRU等[28]报道了一种简单的用F-18标记细胞的方法。亲脂性长链酯作为前体,其标记原理与目前用的细胞膜荧光染料相似,可以快速有效的被细胞膜吸收。
十六烷基-4-[18F]氟苯甲酸酯(18F-HFB)是一种长链氟化苯甲酸酯,通过氟离子在十六烷基-4-(N,N,N-三甲基铵)苯甲酸甲酯上的芳香亲核取代一步合成制备,获得高产率(52%)和高纯度(97%)的放射性产物。18F-HFB通过与大鼠间充质干细胞直接孵育标记到细胞膜上,静脉注射到大鼠体内,PET成像在0-60 min内显示肺中放射性逐渐积累,在100 min时主要积累在肝脏中。18F-HFB易于制备和标记等特点适用于细胞的短期分布研究。
2.1.4 64Cu-PTSM F-18的半衰期是110 min,C-11半衰期只有20 min,核素的短半衰期使得细胞追踪研究限于6 h或更短。而Cu-64的半衰期为12.7 h,可以在更长时间尺度上追踪细胞进行各项研究[29]。
ADONAI等[30]利用亲脂性的氧化还原活性载体分子丙酮醛-双(N4-甲基氨基硫脲)(PTSM)递送到细胞中。PTSM对二价铜具有高结合亲和力,Cu(II)-PTSM复合物非常稳定(Ka=1018,pH=7.4)。Cu(II)-PTSM充当Cu(II)离子的亲脂性氧化还原活性转运蛋白,能被动扩散穿过细胞膜将铜递送到细胞中[31-32]。
为了评估用64Cu-PTSM标记细胞的可行性,作者首先评估了细胞摄取和外排以及细胞活力和标记后的增殖能力。研究发现64Cu-PTSM能迅速扩散到C6大鼠胶质瘤(C6)细胞中,标记产率能够达到70%-85%。与FDG相比,64Cu-PTSM具有更高的细胞标记效率。64Cu-PTSM标记的细胞活力和增殖率没有受到影响。细胞流出实验则发现64Cu-PTSM和FDG具有相同的从细胞中流出的趋势,24 h之后细胞的滞留量为22%。
小鼠尾静脉注射标记的C6细胞进行PET成像, 0.45 h显示在肺中有大量放射性积聚,3.33 h可清楚地检测到在脾脏有放射性积聚,肝脏也是64Cu-PTSM尾静脉给药后示踪剂定位的主要器官。此外,在进行长达20.3 h的成像中,可以连续观察细胞的代谢过程。这些结果表明,用64Cu-PTSM标记的细胞可以进行细胞运输的体内成像。
2.1.5 64Cu-PEI 聚乙烯亚胺(PEI)是一种向细胞中递送基因的阳离子聚合物,因其在许多不同类型细胞中的转染效率和转染的一致性而成为最常用的阳离子基因载体之一。LI等[33]提出利用Cu-64标记PEI,用于标记细胞和对肿瘤的追踪成像。他们分别用64Cu-PEI和64Cu-PTSM标记U87MG细胞,进行细胞摄取、外排、细胞毒性检测,并通过PET成像跟踪它们在小鼠体内的分布。64Cu-PEI和64Cu-PEI-PEG均以高标记产率获得,无需大环螯合剂。64Cu-PEI显示出比64Cu-PTSM更低的细胞标记效率。小鼠的PET图像表明尾静脉注射的64Cu-PTSM或64Cu-PEIU87MG标记细胞均在肺和肝脏有大量积聚。在皮下U87MG异种移植模型中,64Cu-PEI比64Cu-PTSM[24 h为(12.4±1.7)%ID/g]具有更高的肿瘤摄取[24 h为(18.7±2.2)%ID/g],证明64Cu-PEI可用于标记细胞和图像肿瘤。与64Cu-PTSM相比,64Cu-PEI显示出相当的细胞运输能力和改善的肿瘤成像能力。与64Cu-PEI相比,64Cu-PEI-PEG也显示出U87MG异种移植物中的高肿瘤摄取和良好的肿瘤与背景对比。
2.1.6 89Zr-DBN 随着近年来细胞疗法和放射性标记细胞产物研究的增多,能够更长时间用于体内追踪活细胞的细胞标记、成像方法得到关注。FERRIS等[34]在研究中描述了用同位素Zr-89标记细胞的新方法。89Zr具有高空间分辨率和78.4 h的半衰期,可以监测给药细胞长达2至3周。
他们首先合成了一种新型的细胞标记试剂89Zr-desferrioxamine-NCS(89Zr-DBN)。在3种细胞类型中评估了这种标记策略:小鼠黑素瘤细胞(mMC)、人间充质干细胞(hMSC)和小鼠树突细胞(mDC)。89Zr-DBN经由NCS基团和存在于细胞伯胺基团表面膜蛋白共价连接在细胞膜表面。通过硅胶iTLC测量,89Zr-DBN的放射化学产率为(55±5)%。根据细胞类型,标记30 min后的细胞标记效率为30%-50%,实现了高达0.5 MBq/106个标记细胞的放射性浓度,而对细胞活力没有负面影响。细胞外排研究表明放射性标记的稳定性高达7 d。通过细胞增殖、锥虫蓝和细胞毒性/细胞凋亡来测试标记后对细胞活力的影响。连续PET扫描小鼠模型,研究 Zr-89标记的人类间充质干细胞的生物分布。心肌递送的89Zr标记的人间充质干细胞在心肌中保留,以及重新分布到肺、肝和骨。静脉注射89Zr标记的人间充质干细胞也主要分布于肺、肝和骨,而静脉注射89Zr(HPO4)2主要分布于肝脏和骨骼,肺部无活动。因此,证明了放射性标记的人间充质干细胞在体内的稳定性。
2.2 SPECT SPECT探测器直接捕捉放射性探针发射的伽马光子,与传统的伽马照相机的成像原理相似,且能够经过数字化技术提供3D信息。PET成像能够提供比SPECT(约1 cm分辨率)更高的空间分辨率图像,但是SPECT扫描比PET扫描更加便宜,一部分原因是它们能够使用寿命更长、更容易获得且相对便宜的放射性同位素,例如mTc-99、In-111、I-125。通过SPECT成像进行细胞跟踪已经在核医学中使用了30多年,广泛用于追踪自体白细胞以检测感染或炎症部位。最常用的放射性标记方法是In-111的非特异同化的亲脂性亚稳态复合物(oxine,tropolone 或其他双齿螯合剂),以及后来的99mTc的非特异性同化复合物[35]。
2.2.1 99mTc-HMPAO mTc-99是锝-99的核同质异能素,半衰期为6.12 h。锝-99m-六甲基-丙烯胺肟(99mTc-HMPAO)是一种亲脂性复合物[36],被细胞捕获之后通过谷胱甘肽依赖性机制被还原成亲水性复合物,并且和细胞内蛋白结合,因此在细胞内可以较为稳定存在。它为体内细胞追踪提供了稳定的标记,目前许多细胞类型已经用99mTc-HMPAO标记,可以研究长达24 h的细胞生物分布[37-38]。
99mTc-HMPAO最早用来标记白细胞,早在1988年99mTc-HMPAO试剂盒就已经商业化[39],使用试剂盒可以简单方便快捷的完成细胞标记。放射性白细胞成像是评估感染和炎症的金标准,是炎症显像技术的重要里程碑。当机体发生炎症反应,白细胞可在炎症细胞因子的趋化作用下穿透毛细血管壁,迁徙并聚集在病灶部位,吞噬和清除病原体及机体自身的坏死组织。在静脉注射放射性核素标记的自体白细胞后,这些标记的白细胞在趋化因子的作用下进入炎症病灶部位,因此放射性摄取增加。临床适应证包括不明原因发热、炎性肠病、骨髓炎、血管和瓣膜移植物术后随访、人工关节感染与松动鉴别等;在中枢神经系统中标记白细胞还可用于区分感染与肿瘤,术后其有利于区别感染与正常术后改变。
近些年来99mTc-HMPAO用于标记人体T细胞或间充质干细胞[40],标记间充质干细胞显示出较高的标记产率(约为26%)和稳定的标记效果(4 h后有96%放射性驻留)。在初始间充质干细胞肺积累后,在2-20 h肺活动减少。脾脏是活动增加的唯一器官。静脉注射的间充质干细胞被瞬时捕获在肺中,可以在脾中隔离,并且主要通过肾脏消除,20 h后在缺血性病变中发现的间充质干细胞多于未受损的脑组织。静脉注射间充质干细胞可能是耐受性临床试验的最初途径。
2.2.2 111In-oxine In-111是铟(In)的一个放射性同位素。它通过电子捕获衰变为镉-111,半衰期为2.8 d。111In-oxine是俄歇电子发射体,能够非特异性内化到正常细胞和恶性细胞中[41-42]。111In(通常为111In-oxinate3)是人体中进行细胞追踪最早且适用广泛的方法,被称为放射性标记细胞的金标准,与99mTc-HMPAO相似经常用于白细胞标记,鉴别炎症部位[43-44]。
2.3 MRI MRI是利用原子核在强磁场内发生共振产生的信号经图像重建的一种成像技术。MRI成像技术可以直接作出横断面、矢状面、冠状面和各种斜面的体层图像;无电离辐射,对机体没有不良影响[45]。用于MRI的信号来自内源性移动水质子(1H)或氟化分子(19F)。当患者被置于大的静磁场中时,与1H或19F相关的磁矩倾向于沿磁场方向对齐,1H或19F通过脉冲射频辐射使原子核产生扰动。在去除射频辐射之后,核恢复到平衡并在接收器天线中引起瞬态电压;该瞬态电压构成核磁共振(NMR)信号。特定组织的物理特性,例如核密度、核自旋晶格弛豫时间(T1)和自旋-自旋弛豫时间(T2),通常决定可用信号的量。原子核沿磁场方向的排列不是瞬时的,而是在由时间常数T1参数化的周期内逐渐发生。T2是特征时间常数,反映了瞬态核磁共振信号的持续时间。基于MRI的细胞追踪涉及检测表现出差异信号的细胞[46-47],可以通过4种方式控制MRI信号,如下所述。
2.3.1 含有顺磁性金属的正对比剂 顺磁对比剂主要影响T1。大多数情况下,T1对比剂含有三价钆,其与低分子量分子螯合以限制毒性[48-49]。周围的水质子与复合物迅速交换,这导致T1加权磁共振图像上的Gd3+标记细胞的T1减少和信号强度增加成正比。顺磁对比剂是最广泛使用的临床MRI对比剂之一。钆(III)螯合物例如钆喷酸二葡甲胺,由于它们的不成对电子而成为有效的对比 剂[50]。这些电子赋予磁矩增加磁性化合物的弛豫,缩短纵向弛豫率(T1),因此通过在T1加权MRI序列上创建“正对比度”来增加信号。为了能够有效地将钆螯合物摄取到细胞中,可以使用转染剂[49],或者将对比剂与膜易位肽偶联[51]。最近,含有锰的纳米颗粒在细胞成像方面具有广泛的应用前景[52]。
2.3.2 含有超顺磁性氧化铁的负对比剂 超顺磁性氧化铁(SPIO)对比剂主要通过其氧化铁晶体影响T2,其具有强磁矩[53-54]。顺磁性试剂的存在通过引起局部磁场中的不均匀性和自旋-自旋相移导致T2加权序列中的负对比,这缩短了T1/T2弛豫时间。这些试剂通常由涂有葡聚糖的亚铁和氧化铁(FeO-Fe2O3)的小结晶颗粒组 成[55-56],这些微粒强烈扰动它们接近的磁场。周围的水分子随后经历高度不均匀的磁场,导致T2加权磁共振图像上的超顺磁性氧化铁标记细胞的局部信号损失(负对比度)。相比于顺磁剂需要足够的量才能引起MRI信号的变化,超顺磁性氧化铁颗粒具有高的灵敏度,因此在MRI的细胞追踪领域占主导地位[57]。这些颗粒通常被做成核壳结构,由嵌入葡聚糖、硅氧烷、柠檬酸盐或聚合物组成壳,由氧化铁组成核。核心通常含有数千个铁原子,增加了局部铁浓度,使研究人员能够检测到比使用顺磁剂更低浓度的细胞。超小超顺磁性氧化铁(USPIO)粒径范围为10-50 nm,超顺磁性氧化铁(SPIO)粒径范围为50-100 nm和微米级氧化铁(MPIO)粒径范围高达> 1 μm。未经修饰的超小超顺磁性氧化铁,例如单晶硅氧化铁纳米粒子(MIONs),已经用于体外标记细胞和成像,包括神经胶质瘤细胞、单核细胞、T细胞[58-61],但是细胞内颗粒浓度仍然相当小,因此需要细胞的量比较大,更适合在体外观测,而具有吞噬活性的大细胞,例如树突细胞或胰岛细胞,可累积足够量的纳米颗粒以允许其在患者中检测[62-64]。磁性线圈设计的改进提高了MRI的灵敏度,并且在检测少量细胞方面取得了有希望的初步结果[65-66]。
2.3.3 分子探针诱导化学交换饱和转移 在特定化学位点松散结合的某些质子,例如酰胺质子,具有与水质子略微不同的共振频率,从而始终收集MRI信号。当这些不稳定的非水质子以其特定的非共振频率用饱和脉冲照射时,质子失去产生MRI信号的能力。饱和的不稳定非水质子与水质子交换位置,导致化学交换饱和转移(CEST)图像上标记细胞的MRI信号丢失[67-69]。
2.3.4 含有19F的分子探针 19F MRI和1H的成像原理是相同的[70-71]。与基于金属离子的磁共振对比剂(通过它们对周围水质子的间接影响进行检测)不同,19F探针可以直接作为示踪剂起作用。19F有几个特性使其适合用作MRI示踪剂:①相对灵敏度高,为1H的83%;②100%天然丰度;③其共振与1H的共振仅相差6%,允许在现有的1H成像硬件上进行19F MRI成像;④极其广泛的化学位移和T1对氧气张力敏感,允许其用作体内传感器;⑤不是天然存在于生物组织中,因此对背景信号没有贡献(骨骼和牙齿中的氟化物具有极短的T2值,因此不会增加背景);⑥全氟化碳(PFCs)作为血液替代品已被广泛研究[72-74]。
2.4 光学成像 光学细胞追踪的方法可以分为基于荧光的方法和基于生物发光的方法[75-76]。与MRI或PET方法相比,光学方法的优点在于所需设备小且相对便宜。活体显微镜使细胞-细胞甚至细胞-蛋白质相互作用的可视化成为可能,并有助于提供免疫学和细胞生物学信息。光学成像的缺点是光的组织穿透率低,近红外光(波长650-900 nm)的穿透能力较深,可以改善信号的组织穿透,同时能减少组织的自发荧光[77]。
2.4.1 生物发光 生物发光成像基于荧光素酶介导的荧光素氧化发光(发射光:400-620 nm)。萤光素酶是由luc基因决定的一种发光蛋白,在ATP和氧气存在下,在底物(如荧光素)氧化过程中发出光子[78-81]。与基于荧光的光学成像相反,在静脉内施用荧光素后产生光发射的化学过程不需要激发光来产生光子。光子的产生仅发生在荧光素酶表达的位点,因此靶-背景信号比是非常高的[82]。生物发光成像的主要优点是细胞能稳定表达萤光素酶基因,理论上可以被跟踪无限的时间段,不会有信号稀释或消失,除非细胞死亡。例如,植入一个大脑半球的神经祖细胞可以在小鼠脑内持续跟踪观察3 周[83-85]。生物发光信号仅维持在活细胞中,因此生物发光成像能够提供体内细胞活力的准确图像。除了生物发光,也可以转染细胞表达绿色荧光蛋白、红色荧光蛋白、Katushka蛋白或mCherry蛋白[86-88]。与生物发光类似,荧光蛋白的稳定表达使细胞能够被长期跟踪。
2.4.2 荧光染料 基于荧光染料的细胞追踪研究包括用光学染料在体外标记细胞,将它们引入生物体,用限定波长的光激发荧光探针,使用高精准相机捕获激发的光子。有机荧光染料具有毒性小、价格合适的特征,但观察期较长时,容易发生光漂白。常规荧光染料的替代物是量子点[89-91],这些纳米级晶体具有高度光稳定性,可精确调节其发射波长。但由于大多数量子点含有镉,因此在人体中安全应用是一个主要问题。

| [1] NEELAPU SS, TUMMALA S, KEBRIAEI P, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy - assessment and management of toxicities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2018;15(1):47-62. [2] LEVINE BL, MISKIN J, WONNACOTT K, et al. Global Manufacturing of CAR T Cell Therapy. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2016;4:92-101. [3] SCHITO L, REY S. Hypoxic pathobiology of breast cancer metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017;1868(1): 239-245. [4] XU M, HAN Y, LIU G, et al. Preclinical Study of a Fully Human Anti-PD-L1 Antibody as a Theranostic Agent for Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol Pharm. 2018;15(10):4426-4433. [5] HONG H, YANG Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Non-invasive cell tracking in cancer and cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010;10(12): 1237-1248. [6] CHATTERJEE S, LESNIAK WG, MILLER MS, et al. Rapid PD-L1 detection in tumors with PET using a highly specific peptide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;483(1):258-263. [7] CAVO M, TERPOS E, NANNI C, et al. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the diagnosis and management of multiple myeloma and other plasma cell disorders: a consensus statement by the International Myeloma Working Group. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(4):e206-e217. [8] ZHANG XY, ZHANG PY. Positron Emission Tomography in Neuroimaging - An Update. Current Medical Imaging Reviews. 2017;13(2): 108-112. [9] LOVINFOSSE P, POLUS M, VAN DAELE D, et al. FDG PET/CT radiomics for predicting the outcome of locally advanced rectal cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018;45(3):365-375. [10] SOOD V, MITTAL BR, BHANSALI A, et al. Biodistribution of 18F-FDG-Labeled Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Exploring Targeted and Intravenous Routes of Delivery. Clin Nucl Med. 2015;40(9): 697-700. [11] FAIVRE L, CHAUSSARD M, VERCELLINO L, et al. 18F-FDG labelling of hematopoietic stem cells: Dynamic study of bone marrow homing by PET-CT imaging and impact on cell functionality. Curr Res Transl Med. 2016;64(3):141-148. [12] KAWAI T, YASUCHIKA K, SEO S, et al. Identification of Keratin 19-Positive Cancer Stem Cells Associating Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(6):1450-1460. [13] KOIKE C, WATANABE M, OKU N, et al. Tumor cells with organ-specific metastatic ability show distinctive trafficking in vivo: analyses by positron emission tomography and bioimaging. Cancer Res. 1997;57(16):3612-3619. [14] KANG WJ, KANG HJ, KIM HS, et al. Tissue distribution of 18F-FDG-labeled peripheral hematopoietic stem cells after intracoronary administration in patients with myocardial infarction. J Nucl Med. 2006;47(8):1295-1301. [15] KEU KV, WITNEY TH, YAGHOUBI S, et al. Reporter gene imaging of targeted T cell immunotherapy in recurrent glioma. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9(373): eaag2196. [16] EISSENBERG LG, RETTIG MP, RITCHEY JK, et al. [(18)F]FHBG PET/CT Imaging of CD34-TK75 Transduced Donor T Cells in Relapsed Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Patients: Safety and Feasibility. Mol Ther. 2015;23(6):1110-1122. [17] SALABERT AS, VAYSSE L, BEAURAIN M, et al. Imaging grafted cells with [18F]FHBG using an optimized HSV1-TK mammalian expression vector in a brain injury rodent model. PLoS One. 2017; 12(9):e0184630. [18] LI M, WANG Y, LIU M, et al. Multimodality reporter gene imaging: Construction strategies and application. Theranostics. 2018;8(11): 2954-2973. [19] ALAUDDIN MM, CONTI PS. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of 9-(4-[18F]-fluoro-3-hydroxymethylbutyl)guanine ([18F]FHBG): a new potential imaging agent for viral infection and gene therapy using PET. Nucl Med Biol. 1998;25(3):175-180. [20] SHIUE GG, SHIUE CY, LEE RL, et al. A simplified one-pot synthesis of 9-[(3-[18F]fluoro-1-hydroxy-2-propoxy) methyl] guanine([18F]FHPG) and 9-(4-[18F]fluoro-3-hydroxymethylbutyl) guanine ([18F]FHBG) for gene therapy. Nucl Med Biol. 2001;28(7): 875-883. [21] PEÑUELAS I, BOÁN JF, MARTÍ-CLIMENT JM, et al. A fully automated one pot synthesis of 9-(4-[18F]fluoro-3- hydroxymethylbutyl)guanine for gene therapy studies. Mol Imaging Biol. 2002;4(6):415-424. [22] YAGHOUBI SS, WU L, LIANG Q, et al. Direct correlation between positron emission tomographic images of two reporter genes delivered by two distinct adenoviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2001; 8(14):1072-1080. [23] YAGHOUBI S, BARRIO JR, DAHLBOM M, et al. Human pharmacokinetic and dosimetry studies of [(18)F]FHBG: a reporter probe for imaging herpes simplex virus type-1 thymidine kinase reporter gene expression. J Nucl Med. 2001;42(8): 1225-1234. [24] VAN DER VEEN EL, BENSCH F, GLAUDEMANS AWJM, et al. Molecular imaging to enlighten cancer immunotherapies and underlying involved processes. Cancer Treat Rev. 2018;70: 232-244. [25] KREBS S, PONOMAREV V, SLOVIN S, et al. Imaging of CAR T-Cells in Cancer Patients: Paving the Way to Treatment Monitoring and Outcome Prediction. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(7): 879-881. [26] GAMBHIR SS. Imaging of T cells in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Translational Cancer Research. 2017;6(S7): S1291-S1292. [27] YAGHOUBI SS, JENSEN MC, SATYAMURTHY N, et al. Noninvasive detection of therapeutic cytolytic T cells with 18F-FHBG PET in a patient with glioma. Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2009;6(1):53-58. [28] KIRU L, KIM TJ, SHEN B, et al. Single-Cell Imaging Using Radioluminescence Microscopy Reveals Unexpected Binding Target for [18F]HFB. Mol Imaging Biol. 2018;20(3):378-387. [29] KIM MH, WOO SK, KIM KI, et al. Simple Methods for Tracking Stem Cells with (64)Cu-Labeled DOTA-hexadecyl-benzoate. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2015;6(5):528-530. [30] ADONAI N, ADONAI N, NGUYEN KN, et al. Ex vivo cell labeling with 64Cu-pyruvaldehyde-bis(N4-methylthiosemicarbazone) for imaging cell trafficking in mice with positron-emission tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(5):3030-3035. [31] RENE S, SHONER S, YAGLE K, et al. Copper ATSM/PTSM Mechanism in Cells without Mitochondria. Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 2017; 58:905. [32] PRICE TW, GREENMAN J, STASIUK GJ. Current advances in ligand design for inorganic positron emission tomography tracers 68Ga, 64Cu, 89Zr and 44Sc. Dalton Trans. 2016;45(40): 15702-15724. [33] LI ZB, CHEN K, WU Z, et al. 64Cu-labeled PEGylated polyethylenimine for cell trafficking and tumor imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 2009;11(6):415-423. [34] FERRIS TJ, CHAROENPHUN P, MESZAROS LK, et al. Synthesis and characterisation of zirconium complexes for cell tracking with Zr-89 by positron emission tomography. Dalton Trans. 2014;43(39):14851-14857. [35] KIRCHER MF, GAMBHIR SS, GRIMM J. Noninvasive cell-tracking methods. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2011;8(11):677-688. [36] ANDERSEN AR. 99mTc-D,L-hexamethylene-propyleneamine oxime (99mTc-HMPAO): basic kinetic studies of a tracer of cerebral blood flow. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev. 1989; 1(4): 288-318. [37] MALHERBE C, DUPONT AC, MAIA S, et al. Estimation of the added value of 99mTc-HMPAO labelled white blood cells scintigraphy for the diagnosis of infectious foci. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2017 May 3. doi: 10.23736/S1824-4785.17.02964-8. [Epub ahead of print] [38] UCCELLI L, MARTINI P, PASQUALI M, et al. Radiochemical purity and stability of Tc-99m-HMPAO in routine preparations. Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry. 2017;314(2): 1177-1181. [39] DEVILLERS A, MOISAN A, JEAN S, et al. Technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime leucocyte scintigraphy for the diagnosis of bone and joint infections: a retrospective study in 116 patients. Eur J Nucl Med. 1995;22(4):302-307. [40] MESEGUER-OLMO L, MONTELLANO AJ, MARTÍNEZ T, et al. Intraarticular and intravenous administration of 99MTc-HMPAO-labeled human mesenchymal stem cells (99MTC-AH-MSCS): In vivo imaging and biodistribution. Nucl Med Biol. 2017;46:36-42. [41] MALVIYA G, NAYAK T, GERDES C, et al. Isolation and (111)In-Oxine Labeling of Murine NK Cells for Assessment of Cell Trafficking in Orthotopic Lung Tumor Model. Mol Pharm. 2016; 13(4):1329-1338. [42] ELGAZZAR AH, DANNOON S, SARIKAYA I, et al. Scintigraphic Patterns of Indium-111 Oxine-Labeled White Blood Cell Imaging of Gram-Negative versus Gram-Positive Vertebral Osteomyelitis. Med Princ Pract. 2017;26(5):415-420. [43] MUSELAERS CH, BOERMAN OC, OOSTERWIJK E, et al. Indium-111-labeled girentuximab immunoSPECT as a diagnostic tool in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol. 2013;63(6): 1101-1106. [44] ROCA M, DE VRIES EF, JAMAR F, et al. Guidelines for the labelling of leucocytes with (111)In-oxine. Inflammation/Infection Taskgroup of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(4):835-841. [45] SMITH-BINDMAN R, MIGLIORETTI DL, JOHNSON E, et al. Use of diagnostic imaging studies and associated radiation exposure for patients enrolled in large integrated health care systems, 1996-2010. JAMA. 2012;307(22):2400-2409. [46] VESANEN PT, NIEMINEN JO, ZEVENHOVEN KC, et al. Hybrid ultra-low-field MRI and magnetoencephalography system based on a commercial whole-head neuromagnetometer. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69(6):1795-1804. [47] SHIN TH, CHOI Y, KIM S, et al. Recent advances in magnetic nanoparticle-based multi-modal imaging. Chem Soc Rev. 2015; 44(14):4501-4516. [48] RUDELIUS M, DALDRUP-LINK HE, HEINZMANN U, et al. Highly efficient paramagnetic labelling of embryonic and neuronal stem cells. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003;30(7):1038-1044. [49] ROGOSNITZKY M, BRANCH S. Gadolinium-based contrast agent toxicity: a review of known and proposed mechanisms. Biometals. 2016;29(3):365-376. [50] VERWILST P, PARK S, YOON B, et al. Recent advances in Gd-chelate based bimodal optical/MRI contrast agents. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(7):1791-1806. [51] LOHRKE J, FRENZEL T, ENDRIKAT J, et al. 25 Years of Contrast-Enhanced MRI: Developments, Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Adv Ther. 2016;33(1):1-28. [52] ZHANG M, XING L, KE H, et al. MnO2-Based Nanoplatform Serves as Drug Vehicle and MRI Contrast Agent for Cancer Theranostics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(13): 11337-11344. [53] WANG Z, QIAO R, TANG N, et al. Active targeting theranostic iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI and magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound ablation of lung cancer. Biomaterials. 2017; 127:25-35. [54] YU EY, BISHOP M, ZHENG B, et al. Magnetic Particle Imaging: A Novel in Vivo Imaging Platform for Cancer Detection. Nano Lett. 2017;17(3):1648-1654. [55] SMIRNOV P, LAVERGNE E, GAZEAU F, et al. In vivo cellular imaging of lymphocyte trafficking by MRI: a tumor model approach to cell-based anticancer therapy. Magn Reson Med. 2006;56(3):498-508. [56] LUCIANI A, WILHELM C, BRUNEVAL P, et al. Magnetic targeting of iron-oxide-labeled fluorescent hepatoma cells to the liver. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(5):1087-1096. [57] YUAN Y, DING Z, QIAN J, et al. Casp3/7-Instructed Intracellular Aggregation of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles Enhances T2 MR Imaging of Tumor Apoptosis. Nano Lett. 2016;16(4):2686-2691. [58] TANG Y, ZHANG C, WANG J, et al. MRI/SPECT/Fluorescent Tri-Modal Probe for Evaluating the Homing and Therapeutic Efficacy of Transplanted Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Rat Ischemic Stroke Model. Adv Funct Mater. 2015;25(7):1024-1034. [59] OTTOBRINI L, MARTELLI C, TRABATTONI DL, et al. In vivo imaging of immune cell trafficking in cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2011;38(5):949-968. [60] CORREIA CARREIRA S, ARMSTRONG JP, SEDDON AM, et al. Ultra-fast stem cell labelling using cationised magnetoferritin. Nanoscale. 2016;8(14):747474-83. [61] SANZ-ORTEGA L, ROJAS JM, MARCOS A, et al. T cells loaded with magnetic nanoparticles are retained in peripheral lymph nodes by the application of a magnetic field. J Nanobiotechnology. 2019;17(1):14. [62] SAUDEK F, JIRÁK D, GIRMAN P, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of pancreatic islets transplanted into the liver in humans. Transplantation. 2010;90(12):1602-1606. [63] CAO Q, YAN X, CHEN K, et al. Macrophages as a potential tumor-microenvironment target for noninvasive imaging of early response to anticancer therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;152:63-76. [64] SANZ-ORTEGA L, ROJAS JM, PORTILLA Y, et al. Magnetic Nanoparticles Attached to the NK Cell Surface for Tumor Targeting in Adoptive Transfer Therapies Does Not Affect Cellular Effector Functions. Front Immunol. 2019;10:2073. [65] SMIRNOV P, POIRIER-QUINOT M, WILHELM C, et al. In vivo single cell detection of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes with a clinical 1.5 Tesla MRI system. Magn Reson Med. 2008;60(6): 1292-1297. [66] ZEINALI SEHRIG F, MAJIDI S, ASVADI S, et al. An update on clinical applications of magnetic nanoparticles for increasing the resolution of magnetic resonance imaging. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44(7):1583-1588. [67] CAI K, SINGH A, POPTANI H, et al. CEST signal at 2ppm (CEST@2ppm) from Z-spectral fitting correlates with creatine distribution in brain tumor. NMR Biomed. 2015;28(1):1-8. [68] VINOGRADOV E, SHERRY AD, LENKINSKI RE. CEST: from basic principles to applications, challenges and opportunities. J Magn Reson. 2013;229:155-172. [69] SCHEIDEGGER R, VINOGRADOV E, ALSOP DC. Amide proton transfer imaging with improved robustness to magnetic field inhomogeneity and magnetization transfer asymmetry using saturation with frequency alternating RF irradiation. Magn Reson Med. 2011;66(5):1275-1285. [70] OLIVA J, BARDAG-GORCE F, WOOD A, et al. Direct labeling of 19F-perfluorocarbon onto multilayered cell sheet for MRI-based non-invasive cell tracking. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. 2015;12(5): 371-378. [71] ZHONG J, MILLS PH, HITCHENS TK, et al. Accelerated fluorine-19 MRI cell tracking using compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med. 2013;69(6):1683-1690. [72] WAICZIES S, ROSENBERG JT, KUEHNE A, et al. Fluorine-19 MRI at 21.1 T: enhanced spin-lattice relaxation of perfluoro-15-crown-5-ether and sensitivity as demonstrated in ex vivo murine neuroinflammation. MAGMA. 2019;32(1):37-49. [73] CHIRIZZI C, DE BATTISTA D, TIROTTA I, et al. Multispectral MRI with Dual Fluorinated Probes to Track Mononuclear Cell Activity in Mice. Radiology. 2019;291(2):351-357. [74] COLOTTI R, BASTIAANSEN JAM, WILSON A, et al. Characterization of perfluorocarbon relaxation times and their influence on the optimization of fluorine-19 MRI at 3 tesla. Magn Reson Med. 2017;77(6):2263-2271. [75] MEMPEL TR, PITTET MJ, KHAZAIE K, et al. Regulatory T cells reversibly suppress cytotoxic T cell function independent of effector differentiation. Immunity. 2006;25(1):129-141. [76] MCARDLE S, MIKULSKI Z, LEY K. Live cell imaging to understand monocyte, macrophage, and dendritic cell function in atherosclerosis. J Exp Med. 2016;213(7):1117-1131. [77] ZHU H, FAN J, WANG B, et al. Fluorescent, MRI, and colorimetric chemical sensors for the first-row d-block metal ions. Chem Soc Rev. 2015;44(13):4337-4366. [78] SHAH K, WEISSLEDER R. Molecular optical imaging: applications leading to the development of present day therapeutics. NeuroRx. 2005;2(2):215-225. [79] SHARKEY J, SCARFE L, SANTERAMO I, et al. Imaging technologies for monitoring the safety, efficacy and mechanisms of action of cell-based regenerative medicine therapies in models of kidney disease. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016;790:74-82. [80] DING J, ZHAO Z, WANG C, et al. Bioluminescence imaging of transplanted human endothelial colony-forming cells in an ischemic mouse model. Brain Res. 2016;1642:209-218. [81] KIM JE, KALIMUTHU S, AHN BC. In vivo cell tracking with bioluminescence imaging. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015;49(1): 3-10. [82] CONTAG PR, OLOMU IN, STEVENSON DK, et al. Bioluminescent indicators in living mammals. Nat Med. 1998;4(2): 245-247. [83] SHARIFIAN S, HOMAEI A, HEMMATI R, et al. Light emission miracle in the sea and preeminent applications of bioluminescence in recent new biotechnology. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;172:115-128. [84] FREEMAN BT, KOURIS NA, OGLE BM. Tracking fusion of human mesenchymal stem cells after transplantation to the heart. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(6):685-694. [85] DANIEL C, POIRET S, DENNIN V, et al. Dual-Color Bioluminescence Imaging for Simultaneous Monitoring of the Intestinal Persistence of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactococcus lactis in Living Mice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81(16): 5344-5349. [86] IWANO S, SUGIYAMA M, HAMA H, et al. Single-cell bioluminescence imaging of deep tissue in freely moving animals. Science. 2018;359(6378):935-939. [87] CHEHADE M, SRIVASTAVA AK, BULTE JW. Co-Registration of Bioluminescence Tomography, Computed Tomography, and Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Multimodal In Vivo Stem Cell Tracking. Tomography. 2016;2(2):159-165. [88] LI Z, HU X, MAO J, et al. Optimization of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) delivery dose and route in mice with acute liver injury by bioluminescence imaging. Mol Imaging Biol. 2015;17(2):185-194. [89] MICHALET X, PINAUD FF, BENTOLILA LA, et al. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science. 2005; 307(5709):538-544. [90] JU D, LIU X, ZHU Z, et al. Solution processed membrane-based wearable ZnO/graphene Schottky UV photodetectors with imaging application. Nanotechnology. 2019;30(37):375701. [91] HUA XW, BAO YW, ZENG J, et al. Nucleolus-Targeted Red Emissive Carbon Dots with Polarity-Sensitive and Excitation-Independent Fluorescence Emission: High-Resolution Cell Imaging and in Vivo Tracking. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(36):32647-32658. |
| [1] | 余浪波, 卿明松, 赵春涛, 彭笳宸. 动态对比增强MRI在骨科临床应用中的热点问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 449-455. |
| [2] | 田 洋, 唐 超, 廖烨晖, 唐 强, 马 飞, 钟德君. CT和MRI在腰椎管狭窄症中测量椎管面积的一致性和可重复性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3882-3887. |
| [3] | 周元博, 王晋东. 股骨滑车发育不良的病因及治疗:是先天基因还是后天髌骨应力刺激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3908-3913. |
| [4] | 江丽红, 吴晓锋, 欧阳林, 罗爱芳, 黄 丽. 基于代谢组学腰椎间盘退变的计算机辅助诊断[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3796-3803. |
| [5] | 钟远鸣, 罗 满, 唐福波, 唐 成. 骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折MRI STIR黑色线性信号与外力程度的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(9): 1400-1404. |
| [6] | 张聿达, 王昌耀, 王向宇. 微创全髋关节置换后的影像学评估 [J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(33): 5379-5384. |
| [7] | 刘君艳, 潘诗农. 儿童发育性髋关节发育不良解剖学改变与影像学表现[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(30): 4875-4881. |
| [8] | 李旭祥, 张惠康, 魏 波, 姚庆强, 徐 燕, 唐 成, 王黎明. 基于MRI和三维CT个性化截骨导板在内轴型膝关节假体置换中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(30): 4835-4840. |
| [9] | 黄雪洁, 常晓丹, 赵德伟. 动态增强MRI在骨关节中的热点研究[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(15): 2418-2424. |
| [10] | 徐浩翔, 文王强, 张泽佩, 苗 军. 腰椎间盘生物力学体内外研究的新进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(15): 2425-2432. |
| [11] | 莫 凌, 梁 德, 黄锦菁, 江晓兵, 杨志东, 叶林强, 崔健超, 张顺聪, 姚珍松, 晋大祥. 基于CT多平面重建及MRI分析新鲜骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折椎体内骨折区域形态类型及分布规律[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(11): 1647-1653. |
| [12] | 韩明利,吕鹏威,钱学珂,杨 雪,杨云卿,谷元廷. 微小RNA-10b调控乳腺癌MCF-7细胞中乳腺癌干细胞标记物乙醛脱氢酶1 mRNA和蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(9): 1349-1353. |
| [13] | 谢雨晨,陈文栋,马 莉. 困难气道患者三维有限元模型解剖差异的分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(4): 562-566. |
| [14] | 戎飞龙,尹若峰,冯蒙蒙,张伯寅,刘 艺,赵宝林. 退变性腰椎滑脱症和腰椎管狭窄症与椎体周围肌容量的相关性:CT和MRI影像资料分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(24): 3840-3845. |
| [15] | 马钧峰,汪 伟,王紫括,江泽华,龙明星,袁建军,朱如森,胡 炜,张学利. 腰椎MRI评价椎间小关节积液与退变性腰椎滑脱稳定性的相关性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(24): 3845-3851. |
无论是发展细胞疗法还是阐明肿瘤学研究中的生物学机制,有效追踪生物活性细胞在体内的分布和迁移都是非常重要的。细胞治疗是目前癌症免疫疗法中非常有前途的方法,通常使用的细胞有天然T细胞、基因工程T细胞、树突细胞或干细胞[1-2]。然而开发和使用细胞疗法的主要障碍是难以评估其治疗功效。迄今为止,使用细胞疗法的应答者和无应答者主要通过肿瘤大小或治疗后一段时间内的肿瘤标志物来间接评估而不能直接进行评估。体内细胞追踪能够非侵入性地实时监测细胞在靶肿瘤或身体其他部位的分布、数量和活力;此外,体内细胞追踪方法还可以用于评估细胞的迁移特性[3]。因此,细胞体内追踪在基础研究、新免疫疗法的临床前评估以及临床试验设计到最终的临床监测中都具有巨大的作用。在该综述中,作者将对目前应用于动物模型或人体的细胞成像方法以及这些技术的成像原理进行概述。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1 资料来源 第一作者在2019年3至8月进行检索,以“cell tracking,in vivo cell tracking,PET imaging,MRI,optical imaging”为关键词,在PubMed、google scholar、web of science、中国知网等数据库检索相关文献,重点关注过去5-10年的相关文章,主要描述不同细胞追踪方法的原理以及在动物模型和临床患者体内的细胞追踪应用。
1.2 入选标准 ①与细胞体外标记有关,使用的方法为正电子发射断层扫描技术(positron emission computed tomography,PET)、单光子发射型计算机断层显像仪(single-photon emission computed tomography,SPECT)、磁共振成像(MRI)、光学标记中的任意一种;②将标记细胞注入动物体内进行活体成像或者临床成像;③相同领域选择权威期刊发表、引用率高、近期新成果的文献。
1.3 质量评估及数据的提取 计算机初检得到2 064篇文献,经资料收集者互相评估纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选;排除中英文文献重复性研究,以及内容不相关的文献,最后纳入91篇文献进行综述。
在过去的二十几年中,细胞追踪已经发展成为一个多学科交叉的领域。不仅在动物模型中建立了多种稳健的方法,并且在人体的一些研究中证明了临床转化的可行性。
基于核素成像的SPECT和PET成像方式灵敏度都极高,可以检测出皮摩尔甚至更低浓度的放射性示踪剂。高灵敏度成像允许使用微量探针进行直接或间接标记,而不会引起生物反应。例如,放射性标记的配体浓度远低于其受体浓度,不可能通过阻断内源性配体的生物学功能或放射性核素发射的放射性,来改变细胞功能和生存能力。但是,直接用放射性同位素标记细胞的明显缺点是可能发生大量外排和标记丢失,如111 In-oxine、64Cu-PTSM、18F-FDG等标记物均在24 h内显示有大量核素外排。另一个限制是核素的半衰期导致无法在整个细胞生命周期中都起到监测作用。探针类型的限制主要体现在不同探针类型在生物体内的代谢特性,例如核苷类似物无法穿透血脑屏障,从而阻碍了全身注射示踪剂对脑细胞的追踪。
光学成像的基本缺点是光的组织穿透率低。由于吸收和散射,由荧光发射的可见光谱中的光仅具有数百微米的有限组织穿透。这个问题限制了大多数光学方法在小型动物或人类表面结构研究中的应用。
MRI的关键优势是其卓越的空间分辨率。用MRI进行细胞追踪使研究人员能够观察到间隔很近的淋巴结之间的细胞迁移。但是MRI的灵敏度相对较低,需要的对比剂剂量大,造成细胞标记方面困难。
PET的灵敏度非常高,但空间分辨率有限,可以通过与CT或MRI结合得到部分补偿。与MRI相比,PET成像选择合适的核素,能够做到长时间检测细胞并且能够评估它们的生存能力。MRI和PET可以高度互补,临床MRI-PET扫描器最近已成为现实。PET-MRI为将来人体细胞分布、靶向递送、活力和治疗功效的组合成像提供了强大的多模式方法。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程

文题释义:
细胞治疗:采用生物工程方法获取细胞,再通过体外扩增、特殊培养等处理后,使这些细胞具有增强免疫、杀死病原体和肿瘤细胞、促进组织器官再生和机体康复等治疗功效,从而达到治疗疾病的目的。
分子影像学:运用影像学对活体状态下的生物过程进行细胞和分子水平的定性和定量研究。以药物分子作为探针进行成像,能够得到药物的药代动力学、生物分布、靶向性、毒性等众多信息,从而帮助缩短药物研发周期、降低失败风险。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
非侵入性细胞成像技术可以追踪移植的细胞并监测其体内迁移路径和规律,对追踪癌细胞和治疗性干细胞有很大的潜在应用价值。目前可以通过2种方法进行细胞跟踪:直接标记(用标签标记细胞)和间接标记(用报告基因转染细胞,并在施用报告探针后可视化)。用于体内检测移植细胞的技术包括光学成像、核医学成像、磁共振成像、microCT成像和超声成像。理想的成像方式具有高灵敏度、高分辨率和低毒性。所有可用的成像方法都基于不同的原理,具有不同的属性和不同的局限性,因此可以认为其中几种是互补的。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||