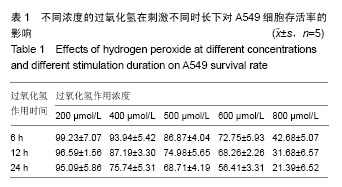
| [1] 凌亚豪,魏金锋,王爱平,等.急性肺损伤和急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制的研究进展[J].癌变•畸变•突变,2017,29(2):151-154.[2] Hayes M, Curley G, Ansari B, et al. Clinical review: stem cell therapies for acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome-hope or hype? J Crit Care. 2012;16(205):1-14.[3] Han F, Luo Y, Li Y, et al. Seawater induces apoptosis in alveolar epithelial cells via the Fas/FasL-mediated pathway. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2012;182(2-3):71-80.[4] Al-Biltagi M, Elezz AA, Elshafiey RM, et al. The predictive value of soluble endothelial selectin plasma levels in children with acute lung injury. J Crit Care. 2016; 32:31-35.[5] Lima Trajano ET, Sternberg C, da Silva MC, et al. Endotoxin-induced acute lung injury is dependent upon oxidative response . Inhal Toxicol. 2011;23(14): 918-926.[6] Poljsak B, Šuput D, Milisav I. Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013; 2013:956792.[7] 杨玲,许速.氧化应激与疾病发生的相关性[J].西南国防医药,2012,22(11): 1268-1270.[8] Gallorini M, Petzel C, Bolay C, et al. Activation of the Nrf2-regulated antioxidant cell response inhibits HEMA-induced oxidative stress and supports cell viability. Biomaterials. 2015; 56:114-128.[9] 王宁,马慧萍,漆欣筑,等. Nrf2-ARE 信号通路在机体氧化应激损伤防护中的研究进展[J].解放军医药杂志,2015, 27(12):21-27.[10] 董渠龙,王华,侯海燕,等. Nrf2-ARE信号通路功能的研究进展[J].国际妇产科学杂志,2015,4:425-428.[11] Shalaby SM, El-Shal AS, Abd-Allah SH, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell injection protects against oxidative stress in Escherichia coli-induced acute lung injury in mice. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(6): 764-775.[12] Wilson JG, Liu KD, Zhuo H, et al. Mesenchymal stem (stromal) cells for treatment of ARDS: a phase 1 clinical trial. Lancet Respir Med. 2015;3(1):24-32.[13] Zhang G, Zou X, Huang Y, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles protect against acute kidney injury through anti-oxidation by enhancing Nrf2/ARE activation in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2016;41(2): 119-128.[14] 付雪,张玉洁,严秀蕊,等.人胎盘胎儿侧间充质干细胞无血清培养上清的抗氧化活性分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(5):773-779.[15] Ware LB, Matthay MA. The acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342(18):1334-1349.[16] Keum YS, Choi BY. Molecular and chemical regulation of the Keap1-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Molecules. 2014;19(7): 10074-10089.[17] 刘冲,彭御冰,王忠.Keap1-Nrf2-ARE信号通路在多器官疾病中的研究进展[J].中国临床医学,2015, 22(2):239-243.[18] Zhao R, Su Z, Wu J, et al. Serious adverse events of cell therapy for respiratory diseases:a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(18): 30511-30523.[19] Liu X, Zheng P, Wang X, et al. A preliminary evaluation of efficacy and safety of Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Stem Cell Res. 2014; 5(2):57.[20] Jang YO, Kim YJ, Baik SK et al. Histological improvement following administration of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells for alcoholic cirrhosis: a pilot study. Liver Int. 2014; 34(1): 33-41.[21] Hare JM, Fishman JE, Gerstenblith G, et al. Comparison of allogeneic vs autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells delivered by transendocardial injection in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy: the POSEIDON randomized trial. JAMA. 2012; 308(22):2369-2379.[22] Ni S, Wang D, Qiu X. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rat by activating Nrf2 signaling. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(7):7752-7761.[23] Chang YS, Ahn SY, Yoo HS, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for bronchopulmonary dysplasia: phase 1 dose-escalation clinical trial. J Pediatr. 2014;164(5):966-972.[24] 吴海青,李涛平,黄丽.骨髓间充质干细胞对急性肺损伤大鼠氧化应激的影响[J].临床肺科杂志,2012, 17(4):593-596.[25] Matthay MA. Extracellular vesicle transfer from mesenchymal stromal cells modulates macrophage function in acute lung injury: basic science and clinical implications. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017.[26] Morrison TJ, Jackson MV, Cunningham EK, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells modulate macrophages in clinically relevant lung injury models by extracellular vesicle mitochondrial transfer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017.[27] Martinet L, Fleury-Cappellesso S, Gadelorge M, et al. A regulatory cross-talk between Vgamma9Vdelta2 T lymphocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Eur J Immunol. 2009; 39(3):752-762.[28] Tasso R, Augello A, Carida M, et al. Development of sarcomas in mice implanted with mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto bioscaffolds. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30(1):150-157.[29] Chen W, Huang Y, Han J, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stromal cells-derived exosome. Immunol Res. 2016, 64(4):831-840.[30] Sabin K, Kikyo N. Microvesicles as mediators of tissue regeneration. Transl Res. 2014;163(4):286-295.[31] Sdrimas K, Kourembanas S. MSC microvesicles for the treatment of lung disease: a new paradigm for cell-free therapy. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014; 21(13):1905-1915.[32] 董曦,孙桂波,罗云,等.间充质干细胞条件培养基激活Nrf2-ARE通路对抗 H2O2致H9c2 细胞的氧化应激损伤[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015,31(6): 961-966.[33] 金明,王玉娇,金梅花,等.两种细胞建立肝细胞氧化损伤模型比较[J].中国公共卫生,2015,31(3): 324-326. |
.jpg)
.jpg)