| [1] World Health Organisation Scientific Group. The Burden of Musculoskeletal Conditions at the Start of the New Millennium. Geneva: World Health Organization,2003.[2] Hunter DJ. Pharmacologic therapy for osteoarthritis--the era of disease modification. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7(1):13-22.[3] Lohmander LS, Roos EM. Clinical update: treating osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2007;370(9605):2082-2084.[4] Matricali GA, Dereymaeker GP, Luyten FP. Donor site morbidity after articular cartilage repair procedures: a review. Acta Orthop Belg. 2010;76(5):669-674.[5] Kretlow JD, Jin YQ, Liu W, et al. Donor age and cell passage affects differentiation potential of murine bone marrow-derived stem cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2008;9:60.[6] Hubbard JJ, Sullivan SK, Mills JA, et al. Efficient iPS cell generation from blood using episomes and HDAC inhibitors. J Vis Exp. 2014;(92):e52009.[7] Trokovic R, Weltner J, Nishimura K, et al. Advanced feeder-free generation of induced pluripotent stem cells directly from blood cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2014;3(12): 1402-1409.[8] Saito T, Yano F, Mori D, et al. Generation of Col2a1-EGFP iPS cells for monitoring chondrogenic differentiation. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74137.[9] Liu Z, Tang Y, Lü S, et al. The tumourigenicity of iPS cells and their differentiated derivates. J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(6): 782-791.[10] Teramura T, Onodera Y, Mihara T, et al. Induction of mesenchymal progenitor cells with chondrogenic property from mouse-induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell Reprogram. 2010;12(3):249-261.[11] Kim MJ, Son MJ, Son MY, et al. Generation of human induced pluripotent stem cells from osteoarthritis patient-derived synovial cells.Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(10):3010-3021.[12] Koyama N, Miura M, Nakao K, et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cells differentiated into chondrogenic lineage via generation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(1):102-113.[13] Giuliani N, Lisignoli G, Magnani M, et al. New insights into osteogenic and chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and their potential clinical applications for bone regeneration in pediatric orthopaedics. Stem Cells Int. 2013;2013:312501.[14] Illich DJ, Demir N, Stojkovi? M, et al. Concise review: induced pluripotent stem cells and lineage reprogramming: prospects for bone regeneration. Stem Cells. 2011;29(4):555-563.[15] Giovannini S, Diaz-Romero J, Aigner T, et al. Micromass co-culture of human articular chondrocytes and human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to investigate stable neocartilage tissue formation in vitro. Eur Cell Mater. 2010;20:245-259.[16] Diecke S, Jung SM, Lee J, et al. Recent technological updates and clinical applications of induced pluripotent stem cells. Korean J Intern Med. 2014;29(5):547-557.[17] Csobonyeiova M, Polak S, Koller J, et al. Induced pluripotent stem cells and their implication for regenerative medicine. Cell Tissue Bank. 2015;16(2):171-180.[18] Bigdeli N, Karlsson C, Strehl R, et al. Coculture of human embryonic stem cells and human articular chondrocytes results in significantly altered phenotype and improved chondrogenic differentiation. Stem Cells. 2009;27(8):1812-1821.[19] Craft AM, Ahmed N, Rockel JS, et al. Specification of chondrocytes and cartilage tissues from embryonic stem cells. Development. 2013;140(12):2597-2610.[20] Vinatier C, Mrugala D, Jorgensen C, et al. Cartilage engineering: a crucial combination of cells, biomaterials and biofactors. Trends Biotechnol. 2009;27(5):307-314.[21] Olee T, Grogan SP, Lotz MK, et al. Repair of cartilage defects in arthritic tissue with differentiated human embryonic stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014;20(3-4):683-692.[22] Hino K, Saito A, Kido M, et al. Master regulator for chondrogenesis, Sox9, regulates transcriptional activation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress transducer BBF2H7/ CREB3L2 in chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2014;289(20): 13810-13820.[23] Huh JE, Koh PS, Seo BK, et al. Mangiferin reduces the inhibition of chondrogenic differentiation by IL-1β in mesenchymal stem cells from subchondral bone and targets multiple aspects of the Smad and SOX9 pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(9):16025-16042.[24] Yang W, Lee S, Jo YH, et al. Effects of natural cartilaginous extracellular matrix on chondrogenic potential for cartilage cell transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2014;46(4):1247-1250. [25] Medvedev SP, Grigor'eva EV, Shevchenko AI, et al. Human induced pluripotent stem cells derived from fetal neural stem cells successfully undergo directed differentiation into cartilage. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(6):1099-1112.[26] Im HJ, Kim JS, Li X, et al. Alteration of sensory neurons and spinal response to an experimental osteoarthritis pain model. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(10):2995-3005.[27] Ferreira-Gomes J, Adães S, Sousa RM, et al. Dose-dependent expression of neuronal injury markers during experimental osteoarthritis induced by monoiodoacetate in the rat. Mol Pain. 2012;8:50.[28] Moon SJ, Jeong JH, Jhun JY, et al. Ursodeoxycholic Acid ameliorates pain severity and cartilage degeneration in monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats. Immune Netw. 2014;14(1):45-53.[29] Lories RJ, Luyten FP. The bone-cartilage unit in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):43-49. [30] Li B, Aspden RM. Mechanical and material properties of the subchondral bone plate from the femoral head of patients with osteoarthritis or osteoporosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1997;56(4): 247-254.[31] Zhen G, Wen C, Jia X, et al. Inhibition of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 2013;19(6):704-712.[32] Hubka KM, Dahlin RL, Meretoja VV, et al. Enhancing chondrogenic phenotype for cartilage tissue engineering: monoculture and coculture of articular chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014;20(6): 641-654. |
.jpg)
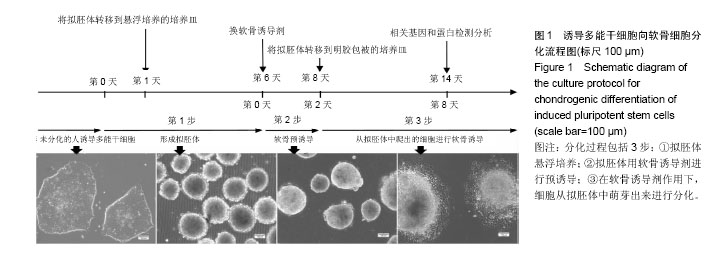
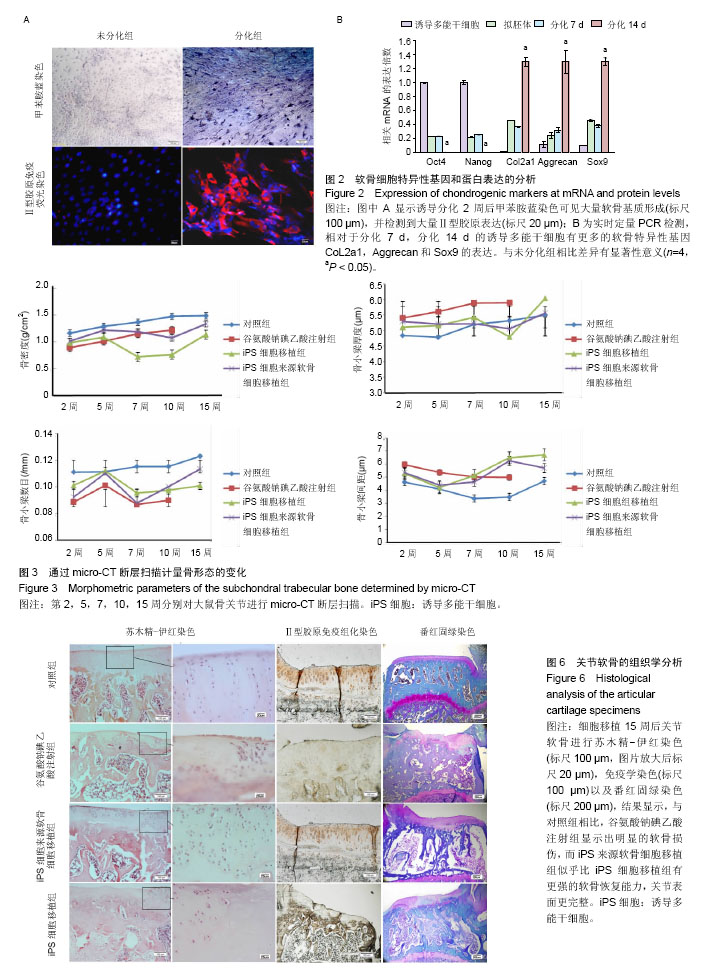
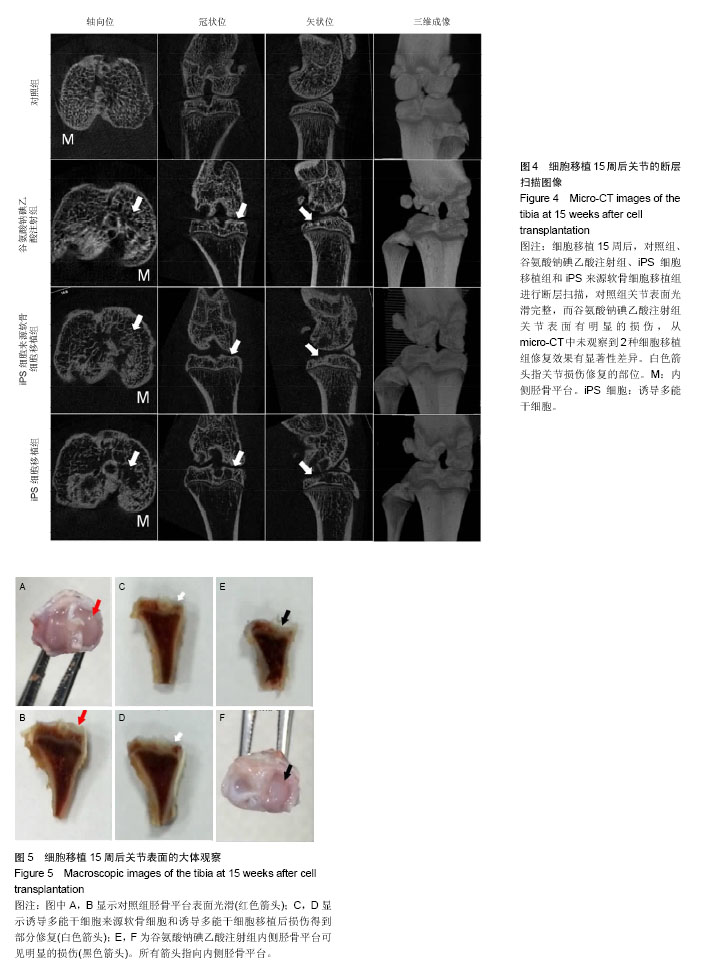
.jpg)
.jpg)