| [1] Stupp R,Tonn JC,Brada M,et al.High-grade malignant glioma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up.Ann Oncol.2010;21 Suppl 5:190-193.[2] 郑国沛,贾小婷,彭聪,等.miR-205通过靶向调控TBX18抑制神经胶质瘤细胞的侵袭能力[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015,31(7): 1219-1224.[3] Bao S,Wu Q,McLendon RE,et al.Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response.Nature.2006;444(7120):756-760.[4] Beier D,Rohrl S,Pillai DR,et al.Temozolomide preferentially depletes cancer stem cells in glioblastoma.Cancer Res. 2008;68(14):5706-5715.[5] Pek JW,Lim AK,Kai T.Drosophila maelstrom ensures proper germline stem cell lineage differentiation by repressing microRNA-7.Dev Cell.2009;17(3):417-424.[6] Rani SB,Rathod SS,Karthik S,et al. MiR-145 functions as a tumor-suppressive RNA by targeting Sox9 and adducin 3 in human glioma cells.Neuro Oncol.2013;15(10):1302-1316.[7] Jia J,Tian Q,Ling S,et al.miR-145 suppresses osteogenic differentiation by targeting Sp7.FEBS Lett. 2013;587(18): 3027-3031.[8] Wang F,Xue X,Wei J,et al.hsa-miR-520h downregulates ABCG2 in pancreatic cancer cells to inhibit migration, invasion, and side populations.Br J Cancer.2010;103(4): 567-574.[9] Xu ZY,Wang K,Li XQ,et al.The ABCG2 transporter is a key molecular determinant of the efficacy of sonodynamic therapy with Photofrin in glioma stem-like cells.Ultrasonics. 2013; 53(1):232-238.[10] Shibata S,Ochi A,Yamashita H,et al.Ultrastructure of capillary permeability in human brain tumor: primary meningeal malignant melanoma.No Shinkei Geka.1990;18(6):527-531.[11] 张华,郭文涛.miR-21通过靶向 FasL 基因对脑胶质瘤细胞生长的影响[J].中国病理生理杂志,2015, 31(8):1495-1499.[12] Bhatia P,Bernier M,Sanghvi M,et al.Breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) localises to the nucleus in glioblastoma multiforme cells.Xenobiotica.2012; 42(8):748- 755.[13] Xia H,Cheung WK,Ng SS,et al.Loss of brain-enriched miR-124 microRNA enhances stem-like traits and invasiveness of glioma cells.J Biol Chem.2012;287(13): 9962-9971.[14] Xiang L,Su P,Xia S,et al.ABCG2 is associated with HER-2 expression, lymph node metastasis and clinical stage in breast invasive ductal carcinoma.Diagn Pathol.2011; 6(90): 1596-1690.[15] Mohan A,Kandalam M,Ramkumar HL,et al.Stem cell markers: ABCG2 and MCM2 expression in retinoblastoma.Br J Ophthalmol.2006;90(7):889-893.[16] Ho MM,Ng AV,Lam S,et al.Side population in human lung cancer cell lines and tumors is enriched with stem-like cancer cells.Cancer Res.2007;67(10):4827-4833.[17] Chiou SH,Yu CC,Huang CY,et al.Positive correlations of Oct-4 and Nanog in oral cancer stem-like cells and high-grade oral squamous cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res.2008;14(13): 4085-4095.[18] Ye XZ,Xu SL,Xin YH,et al.Tumor-associated microglia/ macrophages enhance the invasion of glioma stem-like cells via TGF-beta1 signaling pathway.J Immunol. 2012;189(1): 444-453.[19] Shi L,Wan Y,Sun G,et al.Functional differences of miR-125b on the invasion of primary glioblastoma CD133-negative cells and CD133-positive cells.Neuromolecular Med.2012;14(4): 303-316.[20] Jin Y,Bin ZQ,Qiang H,et al.ABCG2 is related with the grade of glioma and resistance to mitoxantone, a chemotherapeutic drug for glioma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.2009;135(10): 1369-1376.[21] Omran OM.The prognostic value of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRB/ABCG2) expression in breast carcinomas.J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol.2012;31(4):367-376. |
.jpg)
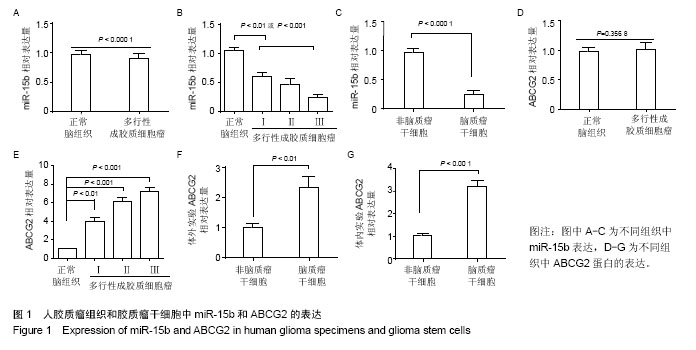
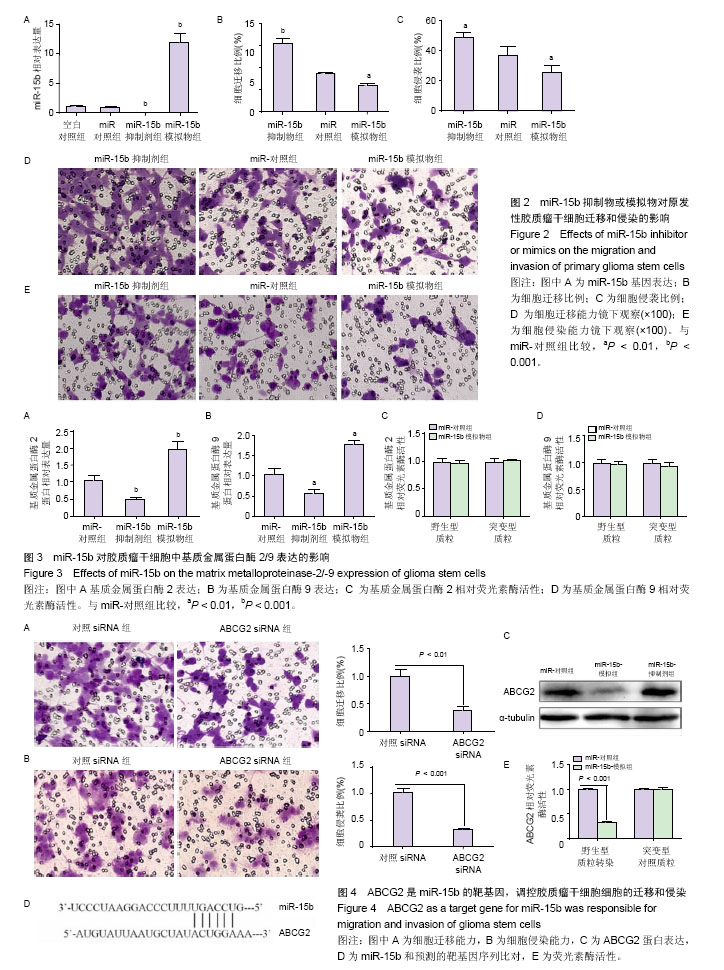

.jpg)