中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5152-5157.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.012
• 肌肉肌腱韧带组织构建 tissue construction of the muscle, tendon and ligament • 上一篇 下一篇
振动结合负重刺激对下肢表面肌电均方根振幅的影响: 基于4种刺激下半蹲起提踵练习
罗莉斯,彭 莉,汪振环,裴希俊
- (西南大学体育学院,国家体育总局体质评价与运动机能监控重点实验室,重庆市 400715)
Effects of four patterns of vibration combined with load on the root mean square amplitude of surface electromyogram of the lower limbs during semi-squats with the heel lifting
Luo Li-si, Peng Li, Wang Zhen-huan, Pei Xi-jun
- (Sport Institute of Southwest University, Key Laboratory for Physical Evaluation and Sports Function Monitoring of General Administration of Sport of China, Chongqing 400715, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
振动结合负重刺激:是一种训练方法,它是针对抗阻力训练的弊端而新生的一种弥补性训练方法,也是振动训练和抗阻力运动的有机结合,这种训练方法多用于腿部肌肉力量的训练。
表面肌电均方根振幅:表面肌电是一种使用表面电极,相对安全、无创和操作简单的肌电图,它作为一种研究手段广泛应用于运动生物力学领域和研究如何科学化训练等问题中。因为它能记录肌肉收缩时产生的电位变化,从而产生肌电图和反映相关肌肉活动特征的参数。均方根振幅是表面肌电数据中用来反映肌电信号的幅值大小变化的指标,一般认为与运动单位的募集和兴奋节律的同步化有关,所以肌电信号的振幅值常用来描述肌肉激活程度。
文题释义:
振动结合负重刺激:是一种训练方法,它是针对抗阻力训练的弊端而新生的一种弥补性训练方法,也是振动训练和抗阻力运动的有机结合,这种训练方法多用于腿部肌肉力量的训练。
表面肌电均方根振幅:表面肌电是一种使用表面电极,相对安全、无创和操作简单的肌电图,它作为一种研究手段广泛应用于运动生物力学领域和研究如何科学化训练等问题中。因为它能记录肌肉收缩时产生的电位变化,从而产生肌电图和反映相关肌肉活动特征的参数。均方根振幅是表面肌电数据中用来反映肌电信号的幅值大小变化的指标,一般认为与运动单位的募集和兴奋节律的同步化有关,所以肌电信号的振幅值常用来描述肌肉激活程度。
.jpg) 文题释义:
振动结合负重刺激:是一种训练方法,它是针对抗阻力训练的弊端而新生的一种弥补性训练方法,也是振动训练和抗阻力运动的有机结合,这种训练方法多用于腿部肌肉力量的训练。
表面肌电均方根振幅:表面肌电是一种使用表面电极,相对安全、无创和操作简单的肌电图,它作为一种研究手段广泛应用于运动生物力学领域和研究如何科学化训练等问题中。因为它能记录肌肉收缩时产生的电位变化,从而产生肌电图和反映相关肌肉活动特征的参数。均方根振幅是表面肌电数据中用来反映肌电信号的幅值大小变化的指标,一般认为与运动单位的募集和兴奋节律的同步化有关,所以肌电信号的振幅值常用来描述肌肉激活程度。
文题释义:
振动结合负重刺激:是一种训练方法,它是针对抗阻力训练的弊端而新生的一种弥补性训练方法,也是振动训练和抗阻力运动的有机结合,这种训练方法多用于腿部肌肉力量的训练。
表面肌电均方根振幅:表面肌电是一种使用表面电极,相对安全、无创和操作简单的肌电图,它作为一种研究手段广泛应用于运动生物力学领域和研究如何科学化训练等问题中。因为它能记录肌肉收缩时产生的电位变化,从而产生肌电图和反映相关肌肉活动特征的参数。均方根振幅是表面肌电数据中用来反映肌电信号的幅值大小变化的指标,一般认为与运动单位的募集和兴奋节律的同步化有关,所以肌电信号的振幅值常用来描述肌肉激活程度。摘要
背景:肌电图能通过反映记录肌肉活动特征参数来评价锻炼效果,振动练习是传统负重训练的最佳补充,近年来研究单纯性振动训练对下肢表面肌电影响的文献较多,但振动结合负重练习对下肢表面肌电影响的研究较少。
目的:通过表面肌电从肌肉工作原理的微观层面来探讨振动结合负重刺激对下肢肌肉的影响。
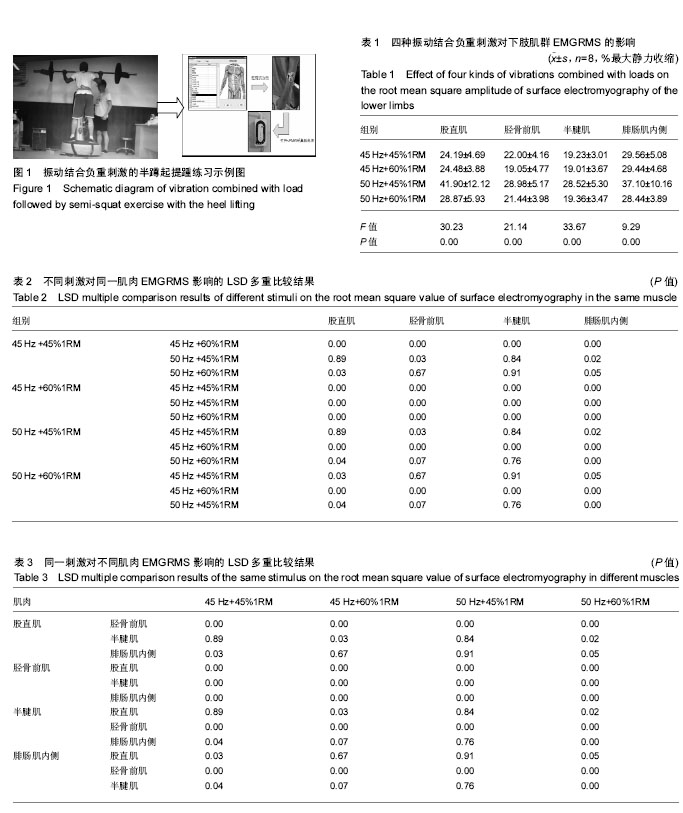
方法:以8名健康大学生为研究对象,分别附加4种不同刺激:频率45 Hz振动结合45%最大力量负重、频率45 Hz振动结合60%最大力量负重、频率50 Hz振动结合45%最大力量负重和频率50 Hz振动结合60%最大力量负重,完成每组1 min的10次半蹲起提踵练习,共3组,间隔2 h以上。
结果与结论:不同振动结合负重刺激对被测肌肉表面肌电均方根振幅的影响非常有显著性意义(P < 0.01)。与其他3种刺激比,频率50 Hz振动结合45%最大力量负重刺激作用下的肌肉表面肌电均方根振幅的均值最大,尤其是腓肠肌内侧。除了半腱肌外,4种刺激对股直肌、胫骨前肌和腓肠肌内侧肌肉表面肌电均方根振幅的影响效果差异有显著性意义(P ≤0.05);除频率50 Hz振动结合45%最大力量负重刺激外,其他3种刺激对股直肌、胫骨前肌、半腱肌和腓肠肌内侧肌肉表面肌电均方根振幅的影响效果差异有显著性意义(P ≤0.05)。与其他3种刺激相比,频率50 Hz振动结合45%最大力量负重刺激对被测肌肉激活程度的效果更好。不同振动结合负重刺激对同一肌肉运动单位的激活效果是不同的,适宜的刺激可能产生更好激活效果;同一刺激针对不同部位的肌肉运动单位的激活效果是不同的,可能是因为要求刺激与肌肉本身的特质相匹配。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-5013-3520(罗莉斯)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
振动结合负重刺激:是一种训练方法,它是针对抗阻力训练的弊端而新生的一种弥补性训练方法,也是振动训练和抗阻力运动的有机结合,这种训练方法多用于腿部肌肉力量的训练。
表面肌电均方根振幅:表面肌电是一种使用表面电极,相对安全、无创和操作简单的肌电图,它作为一种研究手段广泛应用于运动生物力学领域和研究如何科学化训练等问题中。因为它能记录肌肉收缩时产生的电位变化,从而产生肌电图和反映相关肌肉活动特征的参数。均方根振幅是表面肌电数据中用来反映肌电信号的幅值大小变化的指标,一般认为与运动单位的募集和兴奋节律的同步化有关,所以肌电信号的振幅值常用来描述肌肉激活程度。
文题释义:
振动结合负重刺激:是一种训练方法,它是针对抗阻力训练的弊端而新生的一种弥补性训练方法,也是振动训练和抗阻力运动的有机结合,这种训练方法多用于腿部肌肉力量的训练。
表面肌电均方根振幅:表面肌电是一种使用表面电极,相对安全、无创和操作简单的肌电图,它作为一种研究手段广泛应用于运动生物力学领域和研究如何科学化训练等问题中。因为它能记录肌肉收缩时产生的电位变化,从而产生肌电图和反映相关肌肉活动特征的参数。均方根振幅是表面肌电数据中用来反映肌电信号的幅值大小变化的指标,一般认为与运动单位的募集和兴奋节律的同步化有关,所以肌电信号的振幅值常用来描述肌肉激活程度。