中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (32): 5085-5090.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.32.001
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 下一篇
强直性脊柱炎患者外周血DKK-1、骨硬化素以及血管内皮生长因子A 表达及与疾病的相关性
卢仲琳,官 众
- (青海大学附属医院创伤骨科,青海省西宁市 810001)
Serum levels of Dickkopf-1, sclerostin and vascular endothelial growth factor A and their correlation with ankylosing spondylitis progression
Lu Zhong-lin, Guan Zhong
- (Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Qinghai University, Xining 810001, Qinghai Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
DKK-1:从全身角度而言,DKK-1不仅在扁骨中骨细胞表达,也在管状骨中出现表达,DKK-1水平与脊椎骨密度Z值呈负相关表现,高DKK-1水平可能提示椎体骨折风险相关,DKK-1与炎性因子相互作用参与上述结果形成。强直性脊柱炎患者也发现有不同程度的骨质疏松。因此,血清DKK-1的浓度不仅与局部韧带骨赘形成有关,也参与系统性炎症和全身性骨量丢失的病理过程(通过对成骨细胞抑制以及破骨细胞激活)。
骨硬化素:是经典型Wnt通路的抑制剂,有韧带骨赘形成的强直性脊柱炎患者其骨硬化素水平较低,而强直性脊柱炎患者和健康对照组的骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义。部分研究提示,骨硬化素水平在强直性脊柱炎患者中显著较低,在影像学提示严重病变的强直性脊柱炎患者中也有降低。
文题释义:
DKK-1:从全身角度而言,DKK-1不仅在扁骨中骨细胞表达,也在管状骨中出现表达,DKK-1水平与脊椎骨密度Z值呈负相关表现,高DKK-1水平可能提示椎体骨折风险相关,DKK-1与炎性因子相互作用参与上述结果形成。强直性脊柱炎患者也发现有不同程度的骨质疏松。因此,血清DKK-1的浓度不仅与局部韧带骨赘形成有关,也参与系统性炎症和全身性骨量丢失的病理过程(通过对成骨细胞抑制以及破骨细胞激活)。
骨硬化素:是经典型Wnt通路的抑制剂,有韧带骨赘形成的强直性脊柱炎患者其骨硬化素水平较低,而强直性脊柱炎患者和健康对照组的骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义。部分研究提示,骨硬化素水平在强直性脊柱炎患者中显著较低,在影像学提示严重病变的强直性脊柱炎患者中也有降低。
.jpg) 文题释义:
DKK-1:从全身角度而言,DKK-1不仅在扁骨中骨细胞表达,也在管状骨中出现表达,DKK-1水平与脊椎骨密度Z值呈负相关表现,高DKK-1水平可能提示椎体骨折风险相关,DKK-1与炎性因子相互作用参与上述结果形成。强直性脊柱炎患者也发现有不同程度的骨质疏松。因此,血清DKK-1的浓度不仅与局部韧带骨赘形成有关,也参与系统性炎症和全身性骨量丢失的病理过程(通过对成骨细胞抑制以及破骨细胞激活)。
骨硬化素:是经典型Wnt通路的抑制剂,有韧带骨赘形成的强直性脊柱炎患者其骨硬化素水平较低,而强直性脊柱炎患者和健康对照组的骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义。部分研究提示,骨硬化素水平在强直性脊柱炎患者中显著较低,在影像学提示严重病变的强直性脊柱炎患者中也有降低。
文题释义:
DKK-1:从全身角度而言,DKK-1不仅在扁骨中骨细胞表达,也在管状骨中出现表达,DKK-1水平与脊椎骨密度Z值呈负相关表现,高DKK-1水平可能提示椎体骨折风险相关,DKK-1与炎性因子相互作用参与上述结果形成。强直性脊柱炎患者也发现有不同程度的骨质疏松。因此,血清DKK-1的浓度不仅与局部韧带骨赘形成有关,也参与系统性炎症和全身性骨量丢失的病理过程(通过对成骨细胞抑制以及破骨细胞激活)。
骨硬化素:是经典型Wnt通路的抑制剂,有韧带骨赘形成的强直性脊柱炎患者其骨硬化素水平较低,而强直性脊柱炎患者和健康对照组的骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义。部分研究提示,骨硬化素水平在强直性脊柱炎患者中显著较低,在影像学提示严重病变的强直性脊柱炎患者中也有降低。摘要
背景:现阶段,强直性脊柱炎的发生率呈现逐年升高的趋势,极易导致患者出现残疾,因此需要重视强直性脊柱炎的合理治疗,深入分析疾病进展的相关因素,以此制定、实施相应的治疗方案。
目的:检测Wnt通路DKK-1蛋白(Dickkopf-1)、骨硬化素以及血管内皮生长因子A在强直性脊椎炎患者体内的表达水平,评估上述指标与病情进展的相关性。
方法:从强直性脊柱炎患者中招募研究对象,同时招募与其匹配的健康志愿者,收集上述研究对象基线资料及相关病史,采集外周血标本检测DKK-1蛋白、骨硬化素及血管内皮生长因子A的表达水平,利用Bath强直性脊柱炎疾病活动评分以及Bath强直性脊柱炎功能评分评估强直性脊柱炎病情进展,利用改良斯托克强直性脊柱炎脊柱评分评估影像学表现,常规检测C-反应蛋白表达水平,采用Spearman相关分析以及多重线性回归分析DKK-1蛋白、骨硬化素及血管内皮生长因子A与疾病进展、影像学表现及炎症反应等因素的相关性。
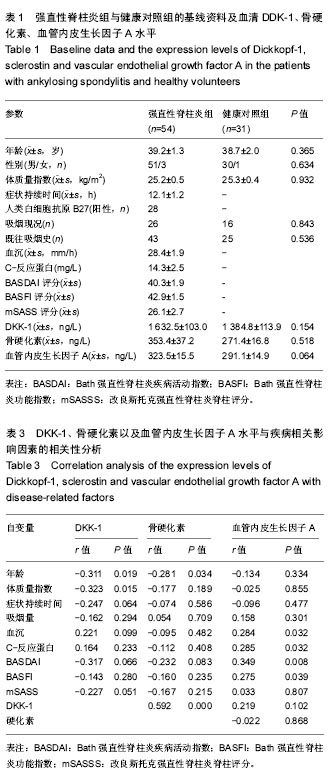
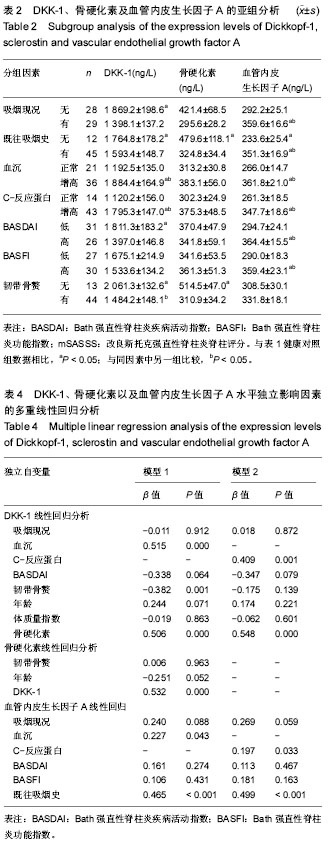
结果与结论:①2组DKK-1蛋白、血管内皮生长因子A以及骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义;②血沉、C-反应蛋白较高以及无韧带骨赘强直性脊柱炎患者的DKK-1蛋白水平显著增高(P < 0.05),与骨硬化素水平显著相关(r=0.592,P=0.000);③具有吸烟史、血沉及C-反应蛋白增高、Bath强直性脊柱炎疾病活动评分及Bath强直性脊柱炎功能评分较高的强直性脊柱炎患者其外周血血管内皮生长因子A水平较高;④多重线性回归分析提示,血沉、C-反应蛋白、韧带骨赘级骨硬化素水平是DKK-1蛋白增高的独立影响因素(P ≤ 0.001),吸烟史、血沉、C-反应蛋白是血管内皮生长因子A水平的独立影响因素(P < 0.05);⑤结果提示,强直性脊柱炎患者外周血清DKK-1蛋白水平与韧带骨赘形成相关,同时与全身炎症反应密切相关,而吸烟史主要影响血管内皮生长因子A水平,上述指标可作为临床诊断指标,提示强直性脊柱炎患者骨赘形成及全身骨质丢失情况。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0002-1264-1804(卢仲琳)
中图分类号:
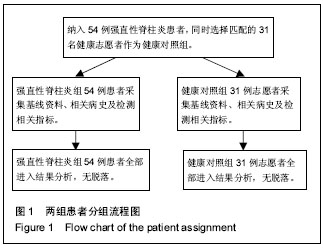
.jpg) 文题释义:
DKK-1:从全身角度而言,DKK-1不仅在扁骨中骨细胞表达,也在管状骨中出现表达,DKK-1水平与脊椎骨密度Z值呈负相关表现,高DKK-1水平可能提示椎体骨折风险相关,DKK-1与炎性因子相互作用参与上述结果形成。强直性脊柱炎患者也发现有不同程度的骨质疏松。因此,血清DKK-1的浓度不仅与局部韧带骨赘形成有关,也参与系统性炎症和全身性骨量丢失的病理过程(通过对成骨细胞抑制以及破骨细胞激活)。
骨硬化素:是经典型Wnt通路的抑制剂,有韧带骨赘形成的强直性脊柱炎患者其骨硬化素水平较低,而强直性脊柱炎患者和健康对照组的骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义。部分研究提示,骨硬化素水平在强直性脊柱炎患者中显著较低,在影像学提示严重病变的强直性脊柱炎患者中也有降低。
文题释义:
DKK-1:从全身角度而言,DKK-1不仅在扁骨中骨细胞表达,也在管状骨中出现表达,DKK-1水平与脊椎骨密度Z值呈负相关表现,高DKK-1水平可能提示椎体骨折风险相关,DKK-1与炎性因子相互作用参与上述结果形成。强直性脊柱炎患者也发现有不同程度的骨质疏松。因此,血清DKK-1的浓度不仅与局部韧带骨赘形成有关,也参与系统性炎症和全身性骨量丢失的病理过程(通过对成骨细胞抑制以及破骨细胞激活)。
骨硬化素:是经典型Wnt通路的抑制剂,有韧带骨赘形成的强直性脊柱炎患者其骨硬化素水平较低,而强直性脊柱炎患者和健康对照组的骨硬化素水平差异无显著性意义。部分研究提示,骨硬化素水平在强直性脊柱炎患者中显著较低,在影像学提示严重病变的强直性脊柱炎患者中也有降低。