中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (30): 4775-4780.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.30.004
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
低强度脉冲超声联合关节腔内注射玻璃酸钠修复关节软骨缺损
郝德峰,张鲁青,刘玉栋
- 潍坊医学院附属益都中心医院、潍坊市益都中心医院,山东省潍坊市 262500
Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound combined with intra-articular injection of sodium hyaluronate in the repair of articular cartilage defects
Hao De-feng, Zhang Lu-qing, Liu Yu-dong
- Department of Ultrasound, Weifang Yidu Central Hospital, Weifang 262500, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
玻璃酸钠:又名透明质酸钠,是由N-乙酰葡萄糖醛酸反复交替而形成的一种高分子多糖体生物材料。玻璃酸钠为广泛存在于动物和人体内的生理活性物质,在人皮肤、关节滑膜液、脐带、房水、眼玻璃体中均有分布。玻璃酸钠具有高度的黏弹性、可塑性以及良好的生物相容性,在预防粘连和修复软组织方面有明显作用。临床上用于多种皮肤损伤,促进伤口愈合,对于擦伤及撕裂伤,腿部的溃疡,糖尿病性溃疡,压迫性溃疡,以及清创术、静脉淤滞性溃疡等均有效;玻璃酸钠为关节滑液的主要成分,是软骨基质的成分之一,在关节腔内起润滑作用,可覆盖和保护关节软骨,改善关节挛缩,抑制软骨变性变化表面,改善病理性关节液。可用于变形膝关节病和肩关节周围炎的辅助治疗 。
低强度脉冲超声波(Low intensity pulsed ultrasound,LIPU):是一种加速骨折修复、促进骨折愈合的物理疗法。低强度脉冲超声波是一种非侵入性机械能,经皮传递后可在生物器官内产生高频率的声波。1952年意大利学者首先报道了低强度脉冲超声波可加速兔桡骨骨折愈合,随后Heckman和Kristiansen等学者关于低强度脉冲超声波促进人胫骨和桡骨远端骨折的报道不仅促使美国FDA批准低强度脉冲超声波的临床应用,同时带来低强度脉冲超声波在骨折愈合修复领域应用和研究的热潮。
背景:文献报道将低强度脉冲超声联合关节腔内注射玻璃酸钠运用于家兔关节软骨缺损修复中效果理想,能促进缺损部位愈合,但是该结论尚未得到进一步证实。
目的:进一步验证低强度脉冲超声联合关节腔内注射玻璃钠在家兔关节软骨缺损中的修复效果。
方法:60只家兔采用4 mL/kg浓度为20%乌拉坦溶液注射麻醉,在股骨踝部作直径为3 mm、深为3 mm的关节软骨缺损模型,根据处理方法分为模型对照组、玻璃酸钠组和观察组。模型对照组建模成功后不采取任何措施处理,玻璃酸钠组关节腔内注射玻璃酸钠修复,观察组在玻璃酸钠组基础上联合低强度脉冲超声修复。大体观察关节兔软骨缺损部位的形态;比较3组家兔修复后苏木精-伊红染色、番红O染色及Wakitani组织学评分。
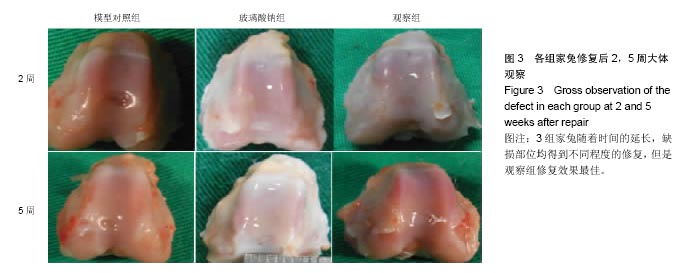
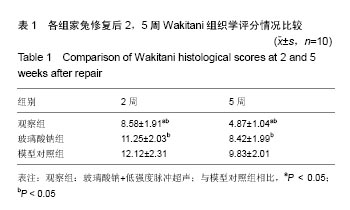
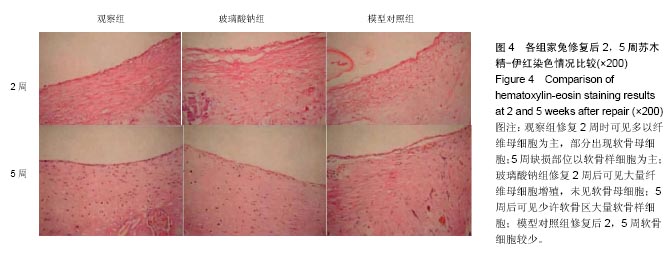
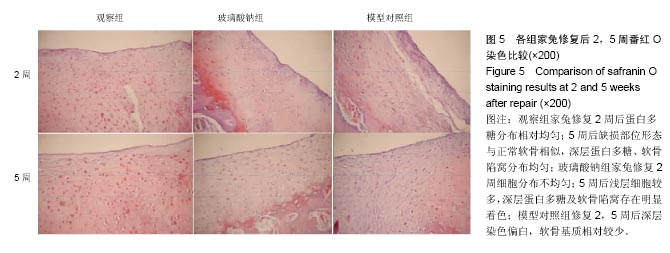
结果与结论:①大体观察:模型对照组修复5周后缺损直径缩小,表面不平整且低于周围组织;玻璃酸钠组修复5后缺损部位与正常软骨组织边界清晰;观察组修复5周后缺损部位完全修复;②观察组家兔修复后2,5周Wakitani组织学评分,低于玻璃酸钠组和模型对照组(P < 0.05);③观察组修复5周缺损部位细胞排列整齐;玻璃酸钠组修复5周后可见少许软骨区大量软骨样细胞;模型对照组修复后2,5周可见毛细心血管分布,排列不均匀;④观察组修复5周后缺损部位形态与正常软骨相似;玻璃酸钠组修复5周后深层蛋白多糖及软骨陷窝存在明显着色;模型对照组修复2,5周后深层染色偏白;⑤结果提示:低强度脉冲超声联合关节腔内注射玻璃钠在家兔关节软骨缺损中能取得理想修复效果。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)