| [1]Nan M,Yangmei C,Bangcheng Y.Magnesium metal--a potential biomaterial with antibone cancer properties.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(8):2644-2651. [2]Rad MP,Fattahi Masoum SH,Layegh P,et al.Primary Osteosarcoma of the Sternum: A case Report and Review of the Literature.Arch Bone J Surg.2014;2(4):272-275. [3]殷实.生物材料植入体内引发肿瘤的机制研究[J].科技信息, 2010, 24(3):384-385.[4]Schoen FJ,奚廷斐,王春仁.生物材料引起的感染、肿瘤和钙化[J].国外医学:生物医学工程分册, 1989,12(1):29-35.[5]Guo Y,Liu W,Ma S,et al.A preliminary study for novel use of two Mg alloys(WE43 and Mg3Gd).J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016; 27(5):82.[6]Li Z,Gu X,Lou S,et al.The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone. Biomaterials. 2008;29(10):1329-1344.[7]Zhang S,Zhang X,Zhao C,et al.Research on an Mg-Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial. Acta Biomater.2010;6(2):626-640.[8]Li Z,Gu X,Lou S,et al.The development of binary Mg-Ca alloys for use as biodegradable materials within bone.Biomaterials. 2008;29(10):1329-1344.[9]Gu XN,Xie XH,Li N,et al.In vitro and in vivo studies on a Mg-Sr binary alloy system developed as a new kind of biodegradable metal.Acta Biomater.2012;8(6):2360-2374.[10]Li Y,Liu L,Wan P,et al.Biodegradable Mg-Cu alloy implants with antibacterial activity for the treatment of osteomyelitis: In vitro and in vivo evaluations.Biomaterials.2016;106:250-263.[11]Tie D,Feyerabend F,Müller WD,et al.Antibacterial biodegradable Mg-Ag alloys.Eur Cell Mater.2013;25:284-298.[12]Neel, E.A., et al.Characterisation of antibacterial copper releasing degradable phosphate glass fibres.Biomaterials. 2005;26(15):2247-2254.[13]Chen Y, Xia J,Fan G,et al.Biodegradable Mg-6Zn Alloy Down-Regulation the NF- B Signaling Pathway of Intestinal Epithelial Cells.J Biomater Tissue Eng.2016;6(7):531-537.[14]Zhang S,Zhang X,Zhao C,et al.Research on an Mg–Zn alloy as a degradable biomaterial.Acta Biomaterialia.2010;6:626-640.[15]Chen Y,Yan J,Zhao C,et al.In vitro and in vivo assessment of the biocompatibility of an Mg-6Z(n) alloy in the bile.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2014;25(2):471-480.[16]Barahuie F,Hussein MZ,Abd Gani S,et al.Anticancer nanodelivery system with controlled release property based on protocatechuate–zinc layered hydroxide nanohybrid.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:3137-4319. [17]Song Y,Guan R,Lyu F,et al.In vitro cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles and zinc oxide nanoparticles to human epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma (Caco-2) cells.Mutat Res. 2014;769: 113-118.[18]Chyan W,Zhang DY,Lippard SJ,et al.Reaction-based fluorescent sensor for investigating mobile Zn2+ in mitochondria of healthy versus cancerous prostate cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(1):143-148. [19]Wandzilak A,Czyzycki M,Wrobel P,et al.The oxidation states and chemical environments of iron and zinc as potential indicators of brain tumour malignancy grade - preliminary results.Metallomics. 2013;5(11):1547-1553. [20]Bornapour M, Muja N,Shum-Tim D,et al.Biocompatibility and biodegradability of Mg-Sr alloys: the formation of Sr-substituted hydroxyapatite.Acta Biomater. 2013;9(2):5319-5330.[21]Ahamed M1,Akhtar MJ,Raja M,et al.ZnO nanorod-induced apoptosis in human alveolar adenocarcinoma cells via p53, survivin and bax/bcl-2 pathways: role of oxidative stress. Nanomedicine.2011;7(6):904-913.[22]Chiche J,Brahimi-Horn MC,Pouyssegur J.Tumour hypoxia induces a metabolic shift causing acidosis: a common feature in cancer.J Cell Mol Med.2010;14(4):771-794.[23]李文辉,张岩,陶海荣,等.镁锌合金在体外对MC3T3一E1细胞增殖、分化和矿化的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2010,26(6):819-822.[24]Herman-Antosiewicz A,Singh SV.Signal transduction pathways leading to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction in cancer cells by Allium vegetable-derived organosulfur compounds: a review. Mutat Res.2004;555(1-2):121-131.[25]Roth W,Reed JC.Apoptosis and cancer: when BAX is TRAILing away.Nat Med.2002;8(3):216-218.[26]Kang N,Zhang JH,Qiu F,et al.Inhibition of EGFR signaling augments oridonin-induced apoptosis in human laryngeal cancer cells via enhancing oxidative stress coincident with activation of both the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Cancer Lett.2010;294(2):147-158.[27]Pan JS,Hong MZ,Ren JL.Reactive oxygen species: A double-edged sword in oncogenesis.World J Gastroenterol. 2009;15(14):1702-1707.[28]Wang X,Liu JZ,Hu JX,et al.ROS-activated p38 MAPK/ERK-Akt cascade plays a central role in palmitic acid-stimulated hepatocyte proliferation.Free Radic Biol Med.2011;51(2):539-551.[29]Orzo?ek A,Wysocki P,Strze?ek J,et al.Superoxide dismutase (SOD) in boar spermatozoa: purification, biochemical properties and changes in activity during semen storage (16 degrees C) in different extenders.Reprod Biol. 2013;13(1):34-40. |
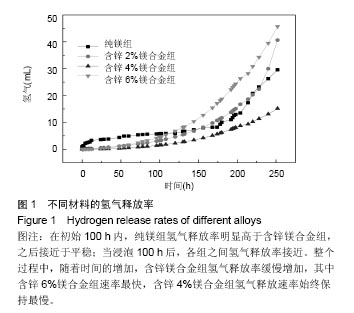
.jpg)
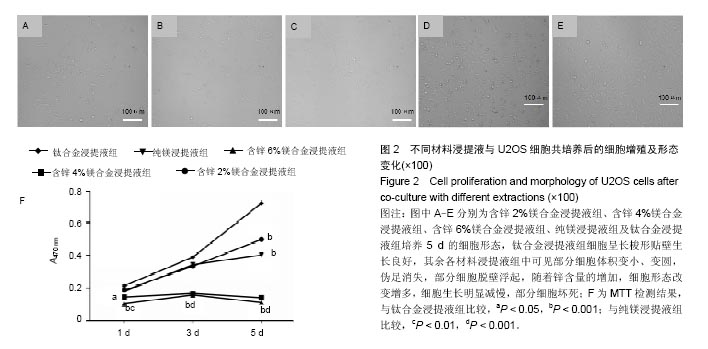
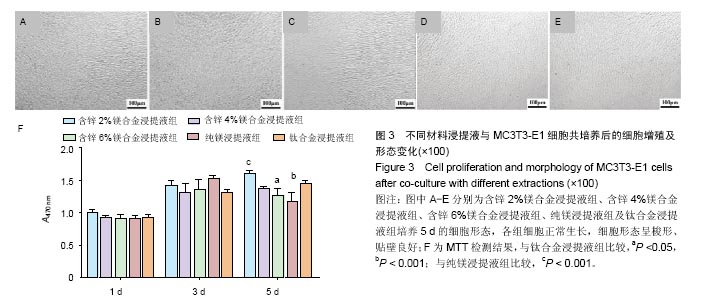
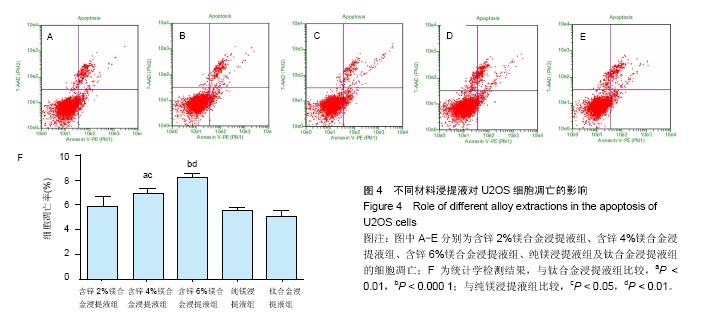
.jpg)