中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (26): 4101-4105.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.26.001
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 下一篇
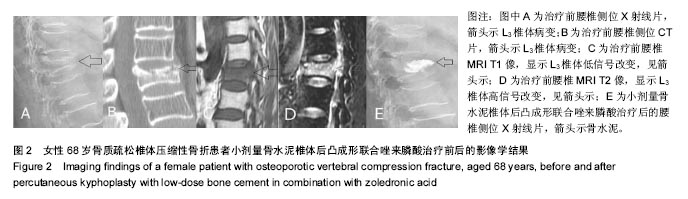
小剂量骨水泥椎体后凸成形联合唑来膦酸治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折
玄文虎,欧阳剑锋,王素伟
- 珠海市人民医院脊柱骨病科,广东省珠海市 519000
Percutaneous kyphoplasty with low-dose bone cement in combination with zoledronic acid for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures
Xuan Wen-hu, Ouyang Jian-feng, Wang Su-wei
- Department of Spinal Surgery, Zhuhai People’s Hospital, Zhuhai 519000, Guangdong Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
椎体后凸成形快速止痛机制:骨水泥的放热反应及骨水泥的细胞毒性作用可造成神经末梢坏死,减少对痛觉神经末梢的刺激,改善了疼痛;通过骨水泥的灌注固定椎体的微骨折,增加了伤椎强度,降低了伤椎塌陷后内部压力;骨水泥填充后恢复椎体高度及改善后凸畸形,恢复生物力学及脊柱稳定;血流阻断作用减少伤椎的炎性递质。
椎体后凸成形引发相邻椎体再骨折的机制:从生物力学角度分析,骨水泥注入可在短时间内导致骨折椎体局部生物力学特性发生改变,影响临近椎体的力学传导,导致术后邻近节段再发骨折风险增高。另外,椎体高度的恢复,椎体终板向外膨出与偏曲,也可使邻近椎体的应力和应变增加,不仅可导致相邻椎体压缩性骨折发生风险增加,同时可导致已治疗的椎体出现复发性疼痛,椎体内注入过多的骨水泥,相邻节段椎体的弹性保护丢失,失去了有效力学缓冲保护,相邻节段椎体更容易受到手术椎体刚性变化带来的力学载荷冲击,更易发生继发骨折。
背景:经皮椎体后凸成形治疗骨质疏松性压缩骨折的效果已获肯定,但仍旧存在骨水泥漏、再骨折等相关并发症,缺乏骨质疏松的后期治疗。
目的:探讨临床小剂量骨水泥椎体后凸成形联合唑来膦酸治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折后的骨密度、椎体高度及腰背痛疼痛改善情况。
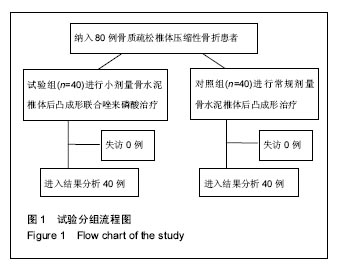
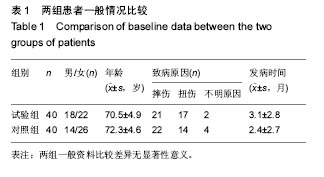
方法:将80例骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折患者随机分2组治疗,试验组(n=40)进行小剂量骨水泥椎体后凸成形联合唑来膦酸治疗,对照组(n=40)进行常规剂量骨水泥椎体后凸成形治疗,记录治疗前、治疗后3 d及末次随访的目测类比评分、椎体高度和Cobb角改善情况,治疗后1年复查骨密度及再发骨折情况。
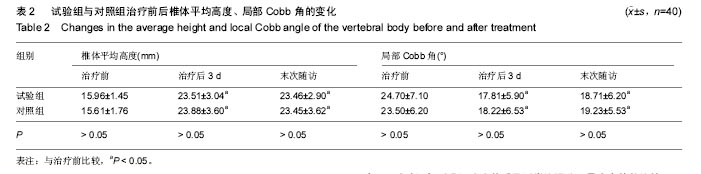
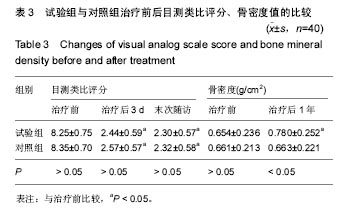
结果与结论:①目测类比评分:两组治疗3 d、末次随访的目测类比评分均显著低于治疗前(P < 0.05),两组间比较差异无显著性意义;②椎体高度和Cobb角:两组治疗3 d、末次随访的椎体高度和Cobb角均较治疗前明显改善(P < 0.05),两组间比较差异无显著性意义;③骨密度:试验组治疗后1年的骨密度明显高于治疗前(P < 0.05),对照组治疗前后无明显变化;④再发骨折情况:试验组1例出现邻近椎体骨折,对照组5例出现邻近椎体骨折;⑤结果表明:小剂量骨水泥椎体后凸成形联合唑来膦酸治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折在有效缓解疼痛、恢复椎体高度的同时可显著提高骨密度,减少相邻节段骨折的发生。
中图分类号:
.jpg)