| [1] 宋占春,白静慧,张丽莉,等.替米沙坦对大鼠急性心肌梗死后炎症反应及纤维化的干预机制[J].中华医学杂志,2014,94(33): 2628-2633.[2] 梁晓辉,赵子粼,欧东波,等.人WJ-MHCs移植对心肌梗死后心力衰竭大鼠TNF-α及NT-proBNP的影响[J].重庆医学,2015,44(29): 4073-4076.[3] 金雅磊,黄从新,王腾,等.粒细胞集落刺激因子对兔心肌梗死后炎性因子的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(1):105-107.[4] 陈国钦,区彩文,张稳柱,等.糖尿病心肌梗死大鼠TGF-β1和CTGF表达变化及HGF的干预作用[J].广州医学院学报,2013, 41(2):1-4.[5] 贺忠梅,张红霞,杨敏,等.小鼠心肌梗死后补体系统激活与炎症反应的相关性研究[J].心肺血管病杂志,2014,33(1):98-102.[6] 蒋娜,匡希斌.急性ST段抬高心肌梗死患者再灌注损伤性心电图改变与炎症及氧化应激的关系[J].中南医学科学杂志,2014,3(2): 157-160.[7] Brenner C, Adrion C, Grabmaier U, et al. Sitagliptin plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients suffering from acute myocardial infarction: A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial of efficacy and safety (SITAGRAMI trial). Int J Cardiol. 2016;205:23-30.[8] Li X, Han D, Tian Z, et al. Activation of Cannabinoid Receptor Type II by AM1241 Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis via Nrf2-Mediated Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smad3 Pathway in Myocardial Infarction Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(4): 1521-1536.[9] Khan SA, Dong H, Joyce J, et al. Fibulin-2 is essential for angiotensin II-induced myocardial fibrosis mediated by transforming growth factor (TGF)-β. Lab Invest. 2016;96(7): 773-783.[10] Hou J, Wang L, Hou J, et al. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Promotes Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Express Connexin43 via the Inhibition of TGF-β1/Smads Signaling in a Rat Model of Myocardial Infarction. Stem Cell Rev. 2015;11(6):885-899.[11] 王艳丽,李金峰,王艳萍,等.脐血间充质干细胞移植对心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(14):2123-2128.[12] Jun Y, Chunju Y, Qi A, et al. The effects of compound danshen dripping pills and human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cell transplant after acute myocardial infarction. Exp Clin Transplant. 2014;12(2):123-128.[13] Santos Nascimento D, Mosqueira D, Sousa LM, et al. Human umbilical cord tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate remodeling after myocardial infarction by proangiogenic, antiapoptotic, and endogenous cell-activation mechanisms. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(1):5.[14] Li T, Ma Q, Ning M, et al. Cotransplantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord blood-derived CD34? cells in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;387(1-2): 91-100.[15] 陈立朋,郭天柱,郑韶欣,等.心肌干细胞和骨髓间充质干细胞改进心肌梗死大鼠室颤阈值和心电生理稳定性的对比研究[J].中华急诊医学杂志,2015,24(9):981-986.[16] 王娟,贾合磊,吉红亮,等.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植在心肌梗死后心室重建中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(50): 7487-7493.[17] 陈光涛,章岚,任文君,等.干细胞诱导心肌细胞增殖与运动促进心肌细胞再生的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,2(36): 5872-5877.[18] 高学东,胡科,魏虎,等.心脏干细胞对心肌细胞凋亡的保护机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(36):5405-5411.[19] Ma J, Zhao Y, Sun L, et al. Exosomes Derived from Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(1):51-59.[20] Ma J,Zhao Y,Sun L,et al.Exosomes Derived From Akt-Modified Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Cardiac Regeneration and Promote Angiogenesis via Activating Platelet-Derived Growth Factor D.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016;22(4):85-88.[21] Sun L, Xu R, Sun X, et al. Safety evaluation of exosomes derived from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cell. Cytotherapy. 2016;18(3):413-422.[22] Kim SW, Jin HL, Kang SM, et al. Therapeutic effects of late outgrowth endothelial progenitor cells or mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical cord blood on infarct repair. Int J Cardiol. 2016;203:498-507.[23] Musialek P, Mazurek A, Jarocha D, et al. Myocardial regeneration strategy using Wharton's jelly mesenchymal stem cells as an off-the-shelf 'unlimited' therapeutic agent: results from the Acute Myocardial Infarction First-in-Man Study. Postepy Kardiol Interwencyjnej. 2015;11(2):100-107.[24] Li T, Ma Q, Ning M, et al. Cotransplantation of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical cord blood-derived CD34? cells in a rabbit model of myocardial infarction. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;387(1-2): 91-100.[25] Zhang W, Liu XC, Yang L, et al. Wharton's jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote myocardial regeneration and cardiac repair after miniswine acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 2013;24(7):549-558.[26] 王巍,李肖甫,李中健,等.胎儿脐血间充质干细胞治疗大鼠急性心肌梗死[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(41):6616-6622.[27] 王巍,李肖甫,李中健,等.不同孕周人脐带间充质干细胞移植改善心肌梗死模型心脏功能的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016, 20(6):799-806.[28] Martinez EC, Vu DT, Wang J, et al. Grafts enriched with subamnion-cord-lining mesenchymal stem cell angiogenic spheroids induce post-ischemic myocardial revascularization and preserve cardiac function in failing rat hearts. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(23):3087-3099.[29] Kang BJ, Kim H, Lee SK, et al. Umbilical-cord-blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded onto fibronectin-immobilized polycaprolactone nanofiber improve cardiac function. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(7):3007-3017.[30] Li X, Hu YD, Guo Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of intracoronary human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cell treatment for very old patients with coronary chronic total occlusion. Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(11):1426-1432. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子:主要由体内激活的 T细胞、单核巨噬细胞等产生。近年研究发现它是一种有广泛免疫活性的效应因子,在激活免疫反应中起重要作用,参与特异性抗体的产生。主要作用于髓系祖细胞,通过与其高亲和力受体结合发挥生物学效应,使其迅速进入细胞周期向粒系和巨噬系分化,最后为成熟细胞,并能延长成熟细胞的寿命,增强成熟细胞的功能。
转化生长因子β:是指具有刺激细胞从贴壁依赖性生长转变成为贴壁非依赖性生长的一类物质,广泛存在于动物正常组织细胞及转化细胞中,人体内几乎所有细胞均可产生转化生长因子β。其生物学功能有促进胚胎发育,调节免疫,创伤修复,促进血管生成和细胞外基质沉积等。
文题释义:
粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子:主要由体内激活的 T细胞、单核巨噬细胞等产生。近年研究发现它是一种有广泛免疫活性的效应因子,在激活免疫反应中起重要作用,参与特异性抗体的产生。主要作用于髓系祖细胞,通过与其高亲和力受体结合发挥生物学效应,使其迅速进入细胞周期向粒系和巨噬系分化,最后为成熟细胞,并能延长成熟细胞的寿命,增强成熟细胞的功能。
转化生长因子β:是指具有刺激细胞从贴壁依赖性生长转变成为贴壁非依赖性生长的一类物质,广泛存在于动物正常组织细胞及转化细胞中,人体内几乎所有细胞均可产生转化生长因子β。其生物学功能有促进胚胎发育,调节免疫,创伤修复,促进血管生成和细胞外基质沉积等。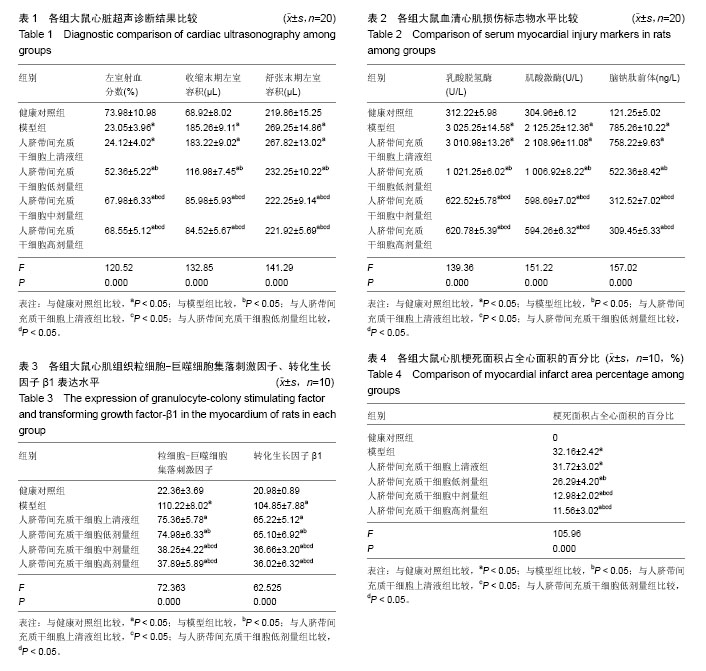
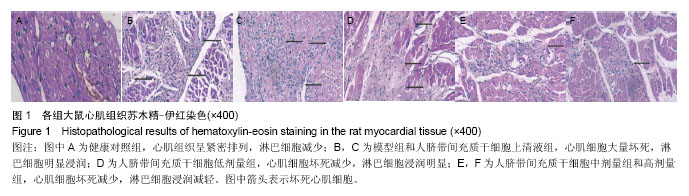
.jpg) 文题释义:
粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子:主要由体内激活的 T细胞、单核巨噬细胞等产生。近年研究发现它是一种有广泛免疫活性的效应因子,在激活免疫反应中起重要作用,参与特异性抗体的产生。主要作用于髓系祖细胞,通过与其高亲和力受体结合发挥生物学效应,使其迅速进入细胞周期向粒系和巨噬系分化,最后为成熟细胞,并能延长成熟细胞的寿命,增强成熟细胞的功能。
转化生长因子β:是指具有刺激细胞从贴壁依赖性生长转变成为贴壁非依赖性生长的一类物质,广泛存在于动物正常组织细胞及转化细胞中,人体内几乎所有细胞均可产生转化生长因子β。其生物学功能有促进胚胎发育,调节免疫,创伤修复,促进血管生成和细胞外基质沉积等。
文题释义:
粒细胞-巨噬细胞集落刺激因子:主要由体内激活的 T细胞、单核巨噬细胞等产生。近年研究发现它是一种有广泛免疫活性的效应因子,在激活免疫反应中起重要作用,参与特异性抗体的产生。主要作用于髓系祖细胞,通过与其高亲和力受体结合发挥生物学效应,使其迅速进入细胞周期向粒系和巨噬系分化,最后为成熟细胞,并能延长成熟细胞的寿命,增强成熟细胞的功能。
转化生长因子β:是指具有刺激细胞从贴壁依赖性生长转变成为贴壁非依赖性生长的一类物质,广泛存在于动物正常组织细胞及转化细胞中,人体内几乎所有细胞均可产生转化生长因子β。其生物学功能有促进胚胎发育,调节免疫,创伤修复,促进血管生成和细胞外基质沉积等。