| [1] 徐高伟,董斌,崔海勇,等. 有限元分析全膝关节置换股骨假体置入定位参数及临床优化验证[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016, 20(17): 4411-4418.[2] Aumiller WD, Dollahite HA. Advances in total knee arthroplasty. JAAPA. 2016;29(3):27-31.[3] Canata GL, Casale V, Chiey A. Pain management in total knee arthroplasty: efficacy of a multimodal opiate-free protocol. Joints. 2016;4(4):222-227.[4] Baert I A, Lluch E, Mulder T, et al. Does pre-surgical central modulation of pain influence outcome after total knee replacement? A systematic review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(2):213-223.[5] Doury-Panchout F, Metivier JC, Fouquet B. Kinesiophobia negatively influences recovery of joint function following total knee arthroplasty. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2015;51(2):155-161.[6] Kori SH, Miller RP, Todd DD. Kinisophobia: A new view of chronic pain behavior. 1990;3(1):35-43.[7] Lee DY, Karim SA, Chang HC. Return to sports after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction-a review of patients with minimum 5-year follow-up. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2008; 37(4):273-278.[8] Wood DW, Haig AJ, Yamakawa KS. Fear of movement/(re)injury and activity avoidance in persons with neurogenic versus vascular claudication. Spine J. 2012;12(4):292-300.[9] 李星凤,熊钰,邓诗佳,等. 腰椎间盘突出症患者疼痛信念与生活质量的相关性分析[J].护理学杂志,2016,31(2):51-53.[10] 刘丽丽,王维宁. 疼痛日记对腰椎间盘突出症患者恐动症和恐惧回避信念的影响[J]. 护理学杂志, 2015,30(10):25-28.[11] 伍青,郭爱敏. 慢性阻塞性肺疾病患者呼吸困难信念的相关概念及测量[J]. 中华护理杂志, 2015,50(4):454-459.[12] Murphy WJ, Altman RD. Updated osteoarthritis reference standard. J Rheumatol Suppl. 1995;43:56-59.[13] Vlaeyen JW, Crombez G. Fear of movement/(re)injury, avoidance and pain disability in chronic low back pain patients. Man Ther. 1999;4(4):187-195.[14] 杜慧晴,梅迎雪,代文娟,等. 非药物干预对人工全膝关节置换术后患者疼痛的影响[J]. 宁夏医学杂志, 2016,38(4):349-350.[15] 唐侠. 早期功能锻炼对膝关节置换术后功能恢复的影响[J]. 中华全科医学, 2014,12(8):1331-1332,1343.[16] Severijns P, Vanslembrouck M, Vermulst J, et al. High-demand motor tasks are more sensitive to detect persisting alterations in muscle activation following total knee replacement . Gait Posture. 2016;50(3):151-158.[17] Fiala B, Rhodes RE, Blanchard C, et al. Using social-cognitive constructs to predict preoperative exercise before total joint replacement. Rehabil Psychol, 2013;58(2): 137-147.[18] Morone NE, Abebe KZ, Morrow LA, et al. Pain and decreased cognitive function negatively impact physical functioning in older adults with knee osteoarthritis. Pain Med. 2014;15(9): 1481-1487.[19] Focht BC, Garver MJ, Devor ST, et al. Improving maintenance of physical activity in older, knee osteoarthritis patients trial-pilot (IMPACT-P): design and methods. Contemp Clin Trials. 2012;33(5):976-982.[20] Kavak F, Unal S, Yilmaz E. Effects of Relaxation Exercises and Music Therapy on the Psychological Symptoms and Depression Levels of Patients with Schizophrenia. Arch Psychiatr Nurs. 2016;30(5):508-512.[21] 刘薇,周小萍,邵艳霞,等. 放松训练对急性创伤患者心理健康的影响[J]. 第三军医大学学报, 2015,37(21):2169-2173.[22] Neblett R, Hartzell MM, Mayer TG, et al. Establishing clinically meaningful severity levels for the Tampa Scale for Kinesiophobia (TSK-13). Eur J Pain. 2016;20(5):701-710.[23] Koho P, Borodulin K, Kautiainen H, et al. Finnish version of the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia: Reference values in the Finnish general population and associations with leisure-time physical activity . J Rehabil Med. 2015;47(3):249-255.[24] Acar S, Savci S, Keskinoglu P, et al. Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia for Heart Turkish Version Study: cross-cultural adaptation, exploratory factor analysis, and reliability. J Pain Res. 2016;9(1):445-451.[25] 胡文. 简体中文版TSK和FABQ量表的文化调适及其在退行性腰腿痛中的应用研究[D]. 第二军医大学, 2012.[26] nsall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, et al. Rationale of the Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989; (248):13-14.[27] Tjong VK, Devitt BM, Murnaghan ML, et al. A Qualitative Investigation of Return to Sport After Arthroscopic Bankart Repair: Beyond Stability. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(8): 2005-2011.[28] Maempel JF, Clement ND, Brenkel IJ, et al. Validation of a prediction model that allows direct comparison of the Oxford Knee Score and American Knee Society clinical rating system . Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(4):503-509.[29] Civinini R, Carulli C, Matassi F, et al. The Survival of Total Knee Arthroplasty: Current Data from Registries on Tribology: Review Article. HSS J. 2017;13(1):28-31.[30] Bunzli S, Smith A, Watkins R, et al. What Do People Who Score Highly on the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia Really Believe? A Mixed Methods Investigation in People With Chronic Nonspecific Low Back Pain . Clin J Pain. 2015;31(7): 621-632.[31] Tait MA, Dredge C, Barnes CL. Preoperative Patient Education for Hip and Knee Arthroplasty: Financial Benefit? J Surg Orthop Adv.2015;24(4):246-251.[32] Aasvang EK, Luna IE, Kehlet H. Challenges in postdischarge function and recovery: the case of fast-track hip and knee arthroplasty. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(6):861-866.[33] Monticone M, Ambrosini E, Cazzaniga D, et al. Adults with idiopathic scoliosis improve disability after motor and cognitive rehabilitation: results of a randomised controlled trial . Eur Spine J. 2016;25(10):3120-3129.[34] Richmond H. Using a CBT approach to manage low back pain. Nurs Times.2016;112(18):12-14.[35] Bragard I, Etienne AM, Faymonville ME, et al. A Nonrandomized Comparison Study of Self-Hypnosis, Yoga, and Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy to Reduce Emotional Distress in Breast Cancer Patients. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2017;65(2):189-209.[36] Tanuma K, Watanabe F, Maeda H, et al. Development and Validation of a Training Program Using a Cognitive Behavioral Therapy Approach with the Purpose of Enabling Community Pharmacists to Provide Empathic Patient Counseling. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2017;137(2):227-240.[37] Fagevik OM, Slobo M, Klarin L, et al. Physical function and pain after surgical or conservative management of multiple rib fractures - a follow-up study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2016;24(1):128.[38] Brown ML, Plate JF, Von Thaer S, et al. Decreased Range of Motion After Total Knee Arthroplasty Is Predicted by the Tampa Scale of Kinesiophobia. J Arthroplasty. 2016;31(4): 793-797.[39] Filardo G, Roffi A, Merli G, et al. Patient kinesiophobia affects both recovery time and final outcome after total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(10):3322-3328.[40] Schotanus MG, Boonen B, Kort NP. Patient specific guides for total knee arthroplasty are ready for primetime. World J Orthop. 2016;7(1):61-68. |
.jpg)
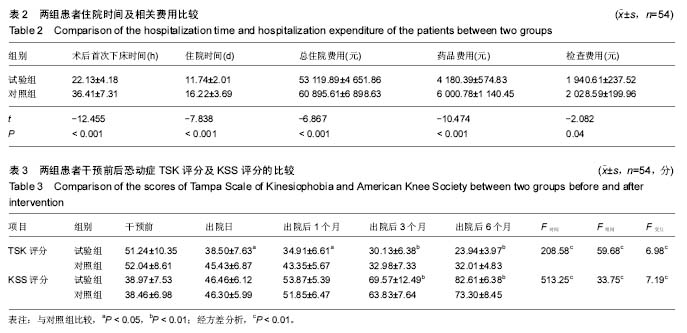
.jpg)
.jpg)