中国组织工程研究 ›› 2017, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (22): 3531-3535.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2017.22.015
• 材料生物相容性 material biocompatibility • 上一篇 下一篇
胶原海绵复合人脂肪干细胞促血管新生
薛静娴1,陈 绪1,许岩磊1,任伟业2,李 燕2,张宇轩1,姚 昶1
- 1南京中医药大学附属医院,江苏省南京市 210029;2无锡贝迪生物工程有限公司,江苏省无锡市 214902
Improving angiogenesis by collagen sponge carrying human adipose-derived stem cells
Xue Jing-xian1, Chen Xu1, Xu Yan-lei1, Ren Wei-ye2, Li Yan2, Zhang Yu-xuan1, Yao Chang1
- 1Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210029, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Wuxi Biot Bio-technology Co., Ltd., Wuxi 214902, Jiangsu Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
文题释义:
鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜:是研究促血管生成与抗血管生成的理想体内模型。生理情况下,血管形成主要发生在胚胎发育和女性月经周期内膜修复过程。另外,在很多病理情况下,血管生成都起着重要作用,如损伤修复、炎症、恶性肿瘤、风湿性关节炎、糖尿病视网膜病变、银屑病、创伤愈合等也常伴随发生血管新生,特别是肿瘤生长和转移与血管新生密切相关,实体瘤必须依赖血管生成才能生长、侵袭和转移。因为鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜是天然免疫缺陷宿主,而且可耐受一定的温度变化,有利于检测某些对温度敏感的肿瘤细胞的生物学行为。所以,鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜模型常作为移植性肿瘤的实验模型之一,也可作为肿瘤新生血管形成、肿瘤侵袭和远处脏器转移潜能,以及抗肿瘤药物作用机制探讨等方面研究的体内实验模型。
背景:研究发现,脂肪干细胞胶原复合物可促进脂肪干细胞向成熟脂肪细胞分化、成熟,并可促进血管新生。
目的:探查胶原海绵复合脂肪干细胞的生物学特性及其对血管新生的影响。
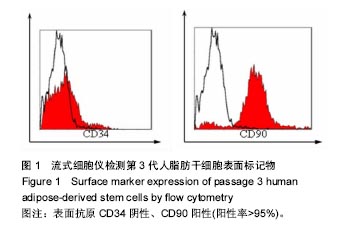
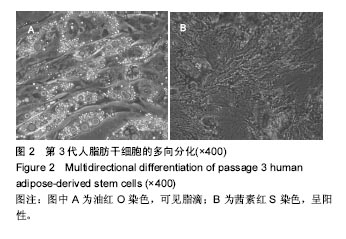
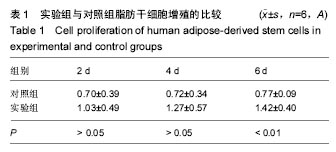
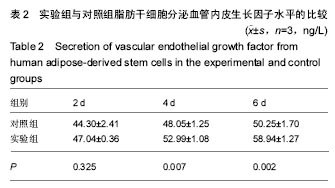
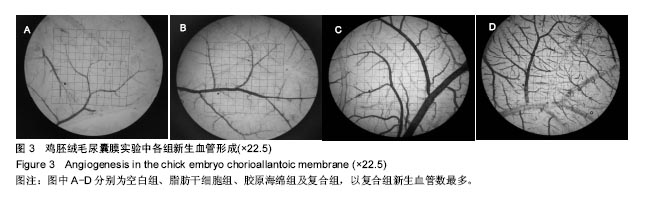
方法:①实验组将人脂肪干细胞接种于胶原海绵上,以细胞单独培养为阴性对照组,培养24 h后,检测细胞黏附率;培养第2,4,6天,检测细胞增殖与培养液中血管内皮生长因子水平;②鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜实验:暴露孵育7 d的鸡胚尿囊膜,分4组,空白组向尿囊膜加入0.2 mL无菌PBS,脂肪干细胞组加入0.2 mL 2×108 L-1第3代脂肪干细胞悬液,胶原海绵组加入胶原海绵,复合组加入2×108 L-1第3代脂肪干细胞悬液0.2 mL与胶原海绵。孵育7 d后,测定尿囊膜周围微血管计数。
结果与结论:①细胞黏附率:脂肪干细胞在胶原海绵上的黏附率为(93.04±0.67)%;②细胞增殖与培养液中血管内皮细胞生长因子水平:实验组培养第6天的细胞增殖A值高于对照组(P < 0.01),培养第4,6天的血管内皮生长因子水平高于对照组(P < 0.05);③鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜实验:脂肪干细胞组、胶原海绵组、复合组微血管计数高于空白组(P < 0.05),复合组高于脂肪干细胞组、胶原海绵组(P < 0.05);④结果表明:脂肪干细胞与胶原海绵具有良好的生物相容性,两者复合有良好的促进血管新生作用,其机制可能与促进脂肪干细胞增殖与分泌血管内皮生长因子相关。
中图分类号:
.jpg)