| [1] Yamaguchi M, Seki T, Imayoshi I, et al. Neural stem cells and neuro/gliogenesis in the central nervous system: understanding the structural and functional plasticity of the developing, mature, and diseased brain. J Physiol Sci. 2016;66(3):197-206.[2] Conti L, Cattaneo E. Neural stem cell systems: physiological players or in vitro entities. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11(3): 176-187.[3] Akerblom M, Sachdeva R, Jakobsson J. Functional Studies of microRNAs in Neural Stem Cells: Problems and Perspectives. Front Neurosci. 2012;6:14.[4] Reynolds BA, Tetzlaff W, Weiss S. A multipotent EGF-responsive striatal embryonic progenitor cell produces neurons and astrocytes. J Neurosci. 1992;12(11):4565- 4574.[5] English D, Sharma NK, Sharma K, et al. Neural stem cells- trends and advances. J Cell Biochem. 2013;114(4): 764-772.[6] Gaspard N, Vanderhaeghen P. From stem cells to neural networks: recent advances and perspectives for neurodevelopmental disorders. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2011;53(1):13-17.[7] Walker T, Huang J, Young K. Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells in Nervous System Function and Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:1890568.[8] Duncan T, Valenzuela M. Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and stem cell therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1):111.[9] Ottoboni L, Merlini A, Martino G. Neural Stem Cell Plasticity: Advantages in Therapy for the Injured Central Nervous System. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2017;5:52.[10] Azari H, Sharififar S, Rahman M, et al. Establishing embryonic mouse neural stem cell culture using the neurosphere assay. J Vis Exp. 2011;(47): 2457. [11] Torrado EF, Gomes C, Santos G, et al. Directing mouse embryonic neurosphere differentiation toward an enriched neuronal population. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014;37:94-99.[12] Ma QH, Futagawa T, Yang WL, et al. A TAG1-APP signalling pathway through Fe65 negatively modulates neurogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2008;10(3):283-294.[13] 张涛,李文杰,王峰,等. 小鼠室管膜下区神经干细胞增殖及分化研究[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(6):766-771.[14] 许汉鹏,苟琳,杨浩. 中枢神经系统不同部位来源的神经干细胞在体外生长特性的比较[J].解剖学报,2004,35(4): 358-362.[15] 白连琴,刘娜,李腾腾,等. 新生鼠和胎鼠海马神经干细胞分离和培养方法的比较[J].神经解剖学杂志,2015,31(4):481-486.[16] 张蓬勃,李卫松,高明,等. 小鼠胚胎神经干细胞的体外培养与鉴定[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2011, 13(3):244-247.[17] Cao F, Hata R, Zhu P, et al. Conditional deletion of Stat3 promotes neurogenesis and inhibits astrogliogenesis in neural stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(3): 843-847.[18] Ao X, Liu Y, Qin M, et al. Expression of Dbn1 during mouse brain development and neural stem cell differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;449(1):81-87.[19] 杨蓬勃,张军峰,张建水,等. 人胎脑额叶和海马中星形胶质细胞的发育性变化[J].西安交通大学学报,2014,35(5):576-580.[20] Vishwakarma SK, Bardia A, Tiwari SK, et al. Current concept in neural regeneration research: NSCs isolation, characterization and transplantation in various neurodegenerative diseases and stroke: A review. J Adv Res. 2014;5(3):277-294.[21] 闵娜,胡强夫,李晓培,等. 异氟醚对新生大鼠海马神经干细胞增殖及分化的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(1):118-122.[22] Telias M, Ben-Yosef D.Neural stem cell replacement: a possible therapy for neurodevelopmental disorders?Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(2): 180-182.[23] 石海杉,吴文,徐建兰.内源性神经干细胞的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志,2013,29(19): 3252-3254.[24] 孙鼐,李春伟,赵伟新,等. 异氟醚抑制海马神经干细胞增殖并可促其向神经元分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(10): 1488-1493.[25] Jiang XF,Yng K,Yang XQ,et al.Elastic modulus affects the growth and differentiation of neural stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(9): 1523-1527.[26] Louis SA, Mak CK, Reynolds BA. Methods to culture, differentiate, and characterize neural stem cells from the adult and embryonic mouse central nervous system. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;946:479-506.[27] De Waele J, Reekmans K, Daans J, et al. 3D culture of murine neural stem cells on decellularized mouse brain sections. Biomaterials. 2015;41:122-131.[28] Lee DY, Yeh TH, Emnett RJ, et al. Neurofibromatosis-1 regulates neuroglial progenitor proliferation and glial differentiation in a brain region-specific manner. Genes Dev. 2010;24(20):2317-2329.[29] 张在金,董艳,卢亦成. 大鼠胎脑不同部位神经干细胞比较性培养的研究[J]. 中华神经外科疾病研究杂志, 2008,7(4):325-327.[30] 马浚宁,高俊玮,候博儒,等, 新生小鼠海马、嗅球及皮质神经干细胞的分离培养及鉴定[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18 (45): 7266-7272.[31] Seaberg RM, Smukler SR, van der Kooy D. Intrinsic differences distinguish transiently neurogenic progenitors from neural stem cells in the early postnatal brain. Dev Biol.2005;278(1):71-85.[32] Maslov AY, Barone TA, Plunkett RJ, et al. Neural stem cell detection, characterization, and age-related changes in the subventricular zone of mice. J Neurosci. 2004;24(7): 1726-1733.[33] Guo W, Patzlaff NE, Jobe EM, et al. Isolation of multipotent neural stem or progenitor cells from both the dentate gyrus and subventricular zone of a single adult mouse. Nat Protoc. 2012;7(11):2005-2012.[34] Bonaventura G, Chamayou S, Liprino A, et al. Different Tissue-Derived Stem Cells: A Comparison of Neural Differentiation Capability. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0140790.[35] Xu R, Wu C, Tao Y, et al. Description of distributed features of the nestin-containing cells in brains of adult mice: a potential source of neural precursor cells. J Neurosci Res. 2010;88(5): 945-956.[36] Lee R, Kim IS, Han N, et al. Real-time discrimination between proliferation and neuronal and astroglial differentiation of human neural stem cells. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6319.[37] Zhang J, Jiao J. Molecular Biomarkers for Embryonic and Adult Neural Stem Cell and Neurogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:727542.[38] Farzanehfar P, Lu SS, Dey A, et al. Evidence of functional duplicity of Nestin expression in the adult mouse midbrain. Stem Cell Res. 2017;19:82-93.[39] 刘吉星,候博儒,杨文桢,等.神经干细胞体外培养鉴定及诱导分化的表型特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(19):3054-3060.[40] Mine Y, Tatarishvili J, Oki K, et al. Grafted human neural stem cells enhance several steps of endogenous neurogenesis and improve behavioral recovery after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2013;52:191-203.[41] Lucchinetti E, Zeisberger SM, Baruscotti I, et al. Stem cell-like human endothelial progenitors show enhanced colony-forming capacity after brief sevoflurane exposure: preconditioning of angiogenic cells by volatile anesthetics. Anesth Analg. 2009;109(4):1117-1126.[42] 刘罡,吴毅,贾杰,等.神经干细胞体外分化抗原表达的研究[J].中国运动医学杂志,2009,28(1):55-59. |
.jpg)
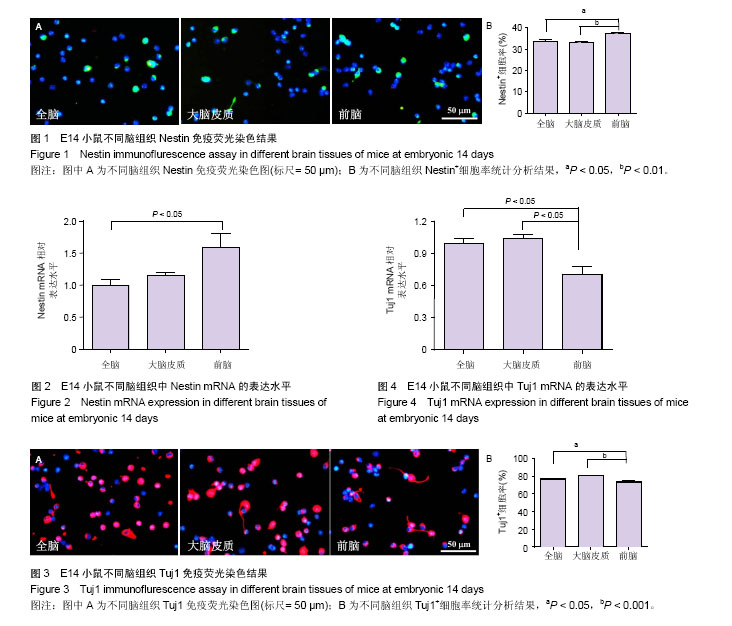
.jpg)