| [1] Land WG. Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: The Work of DAMPs. Transfus Med Hemother. 2013;40(1):3-13.[2] Popovsky MA. Transfusion-Related Acute Lung Injury: Incidence, Pathogenesis and the Role of Multicomponent Apheresis in Its Prevention. Transfus Med Hemother. 2008; 35(2):76-79. [3] Toy P, Gajic O, Bacchetti P, et al. Transfusion-related acute lung injury: incidence and risk factors. Blood. 2012;119(7): 1757-1767.[4] Yost CS, Matthay MA, Gropper MA. Etiology of acute pulmonary edema during liver transplantation : a series of cases with analysis of the edema fluid. Chest. 2001;119(1):219-223.[5] Gilliss BM, Looney MR. Experimental models of transfusion- related acute lung injury. Transfus Med Rev. 2011;25(1):1-11.[6] Sayah DM, Looney MR, Toy P. Transfusion reactions: newer concepts on the pathophysiology, incidence, treatment, and prevention of transfusion-related acute lung injury. Crit Care Clin. 2012;28(3):363-372.[7] Lindenmair A, Hatlapatka T, Kollwig G, et al. Mesenchymal stem or stromal cells from amnion and umbilical cord tissue and their potential for clinical applications. Cells. 2012;1(4): 1061-1088.[8] 胡泽斌,王立生,崔春萍,等.干细胞临床应用安全性评估报告[J],中国医药生物技术,2013,8(5):349-361.[9] Kharaziha P, Hellström PM, Noorinayer B, et al. Improvement of liver function in liver cirrhosis patients after autologous mesenchymal stem cell injection: a phase I-II clinical trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;21(10):1199-1205.[10] 杨华强,张荣环,杜玲,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的临床研究[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(3):518-521.[11] Amable PR, Teixeira MV, Carias RB, et al. Protein synthesis and secretion in human mesenchymal cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue and Wharton's jelly. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(2):53.[12] de Girolamo L, Lucarelli E, Alessandri G, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: a new ''cells as drugs'' paradigm. Efficacy and critical aspects in cell therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2013; 19(13):2459-2473.[13] 牟乐明,孙占胜,王伯珉,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对脊髓损伤大鼠Toll样受体4表达的影响[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2014, 52(1): 37-41.[14] Sun ZM, Liu HL, Geng LQ, et al. HLA-matched sibling transplantation with G-CSF mobilized PBSCs and BM decreases GVHD in adult patients with severe aplastic anemia. J Hematol Oncol. 2010;3:51.[15] Saito S, Lin YC, Murayama Y, et al. Human amnion-derived cells as a reliable source of stem cells. Curr Mol Med. 2012; 12(10):1340-1349.[16] 蒋旭宏,黄小民,何煜舟.痰热清注射液对急性肺损伤大鼠肺组织抗氧化作用的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2012,30(5): 1043-1045.[17] 闫龙,黄小民.痰热清注射液对急性肺损伤大鼠保护机制的实验研究[J].中国中医急症,2011,20(4):587-589.[18] 李丽玮,花紫菱,张惠箴,等.输血相关急性肺损伤大鼠模型建立及肺组织病理研究[J].中国输血杂志,2012,25(11):1121-1124.[19] 刘晓宇,闫浩,朱清仙,等.标准化粉尘螨疫苗免疫治疗哮喘小鼠肺组织病理变化动态观察[J].热带医学杂志,2011,11(11): 1234-1247.[20] 赵敏,师霞,邱桐,等. 黄芪对急性肺损伤大鼠模型肺组织中角质细胞生长因子表达的影响[J].中医临床研究,2013,5(5):11-13.[21] 万巧凤,顾立刚,殷胜骏,等.黄芩苷对 FM1 肺炎小鼠肺组织细胞凋亡FAS / FAS-L 系统的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(11): 1555-1559.[22] 王方,张小岗,张静,等.自体骨髓干细胞治疗失代偿期肝硬化患者50例疗效观察[J].实用肝脏病杂志,2010,13(4):272-274.[23] Ma S, Xie N, Li W, et al. Immunobiology of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(2):216-225.[24] Cuiffo BG, Karnoub AE. Mesenchymal stem cells in tumor development: emerging roles and concepts. Cell Adh Migr. 2012;6(3):220-230.[25] Parolini O, Caruso M. Review: Preclinical studies on placenta-derived cells and amniotic membrane: an update. Placenta. 2011;32 Suppl 2:S186-195.[26] Manochantr S, U-pratya Y, Kheolamai P, et al. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from amnion, placenta, Wharton's jelly and umbilical cord. Intern Med J. 2013;43(4):430-439.[27] 朴正福,张海燕,丁淑芹,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞的生物学特性鉴定[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2010,33(3):157-162.[28] 王利梅.痰热清注射液的作用机制及不良反应[J].中医药临床杂志,2015,27(1):110-111.[29] 祝晨,黄小民.痰热清注射液对内毒素型急性肺损伤大鼠的保护作用[J].中华中医药学刊,2012,30(8):1743-1745.[30] 梁迪思,张智琳,江桂英,等.不同剂量痰热清注射液对急性肺损伤大鼠白细胞介素-6的影响[J].广东医学,2013,34(8):1170-1172.[31] 闫龙,来毅.痰热清注射液对急性肺损伤大鼠的肺组织核因子-κB表达的影响[J].中国中医急症,2015,24(1):38-41.[32] 蒋旭宏,黄小民,何煜舟.痰热清注射液对急性肺损伤大鼠肺组织抗氧化作用的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2012,30(5):1043-1045. |
.jpg)
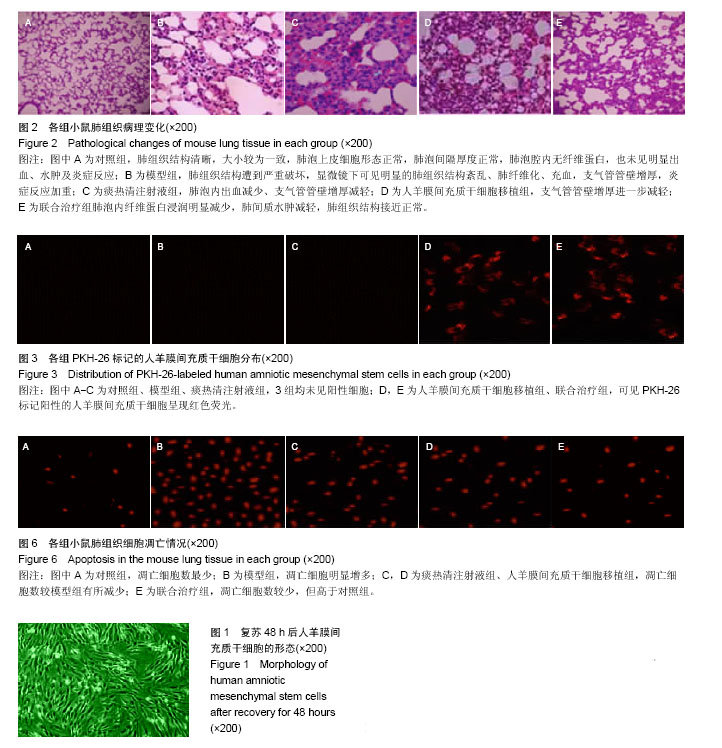
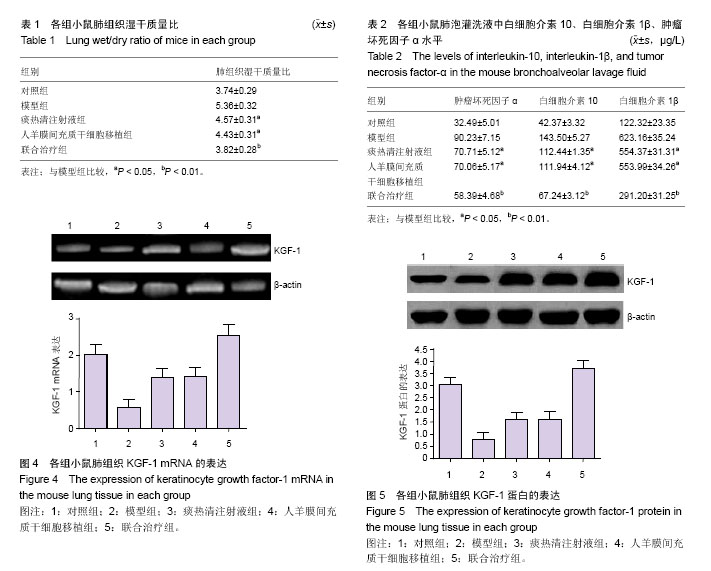
.jpg)