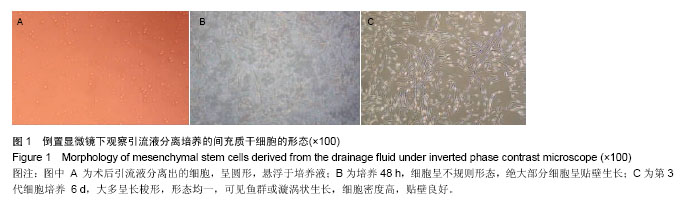
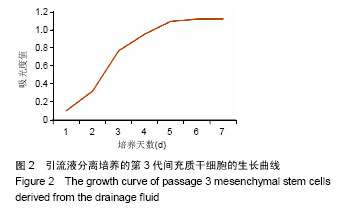
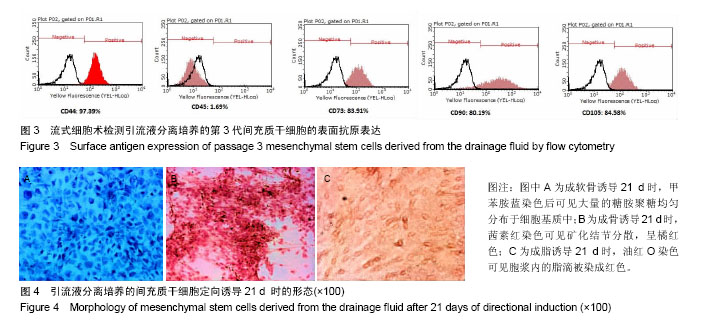
| [1] 李波,刘杨,杨鹏.间充质干细胞应用进展[J].临床军医杂志, 2016, 44(2):205-208.[2] Viganò M, Sansone V, d'Agostino MC, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells as therapeutic target of biophysical stimulation for the treatment of musculoskeletal disorders. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):163.[3] Cui GH, Wang YY, Li CJ, et al. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in treating patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: A meta-analysis. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(5):3390-3400.[4] 李明.间充质干细胞临床应用的研究进展[J].复旦学报:医学版, 2016,43(4):469-474.[5] 蒋曲,张红宾.间充质干细胞在造血干细胞移植中的作用[J].重庆医学, 2015,44(36):5164-5167.[6] Goldberg A, Mitchell K, Soans J, et al. The use of mesenchymal stem cells for cartilage repair and regeneration: a systematic review. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):39.[7] 王向辉,丁琼浩.膝骨关节炎的骨髓间充质干细胞疗法[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2015,24(4):451-453.[8] 朱瑜琪,王金荣,王智耀.间充质干细胞促进关节软骨的修复与再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(50):8195-8200.[9] 张星星,邓常文,屈玉兰,等.间充质干细胞及其在临床中的应用[J]. 医学研究杂志, 2015,44(10):8-11.[10] 鲁先闯,张志峰,黄健.骨髓间充质干细胞修复软骨缺损的应用前景[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(19):3083-3088.[11] Fellows CR, Matta C, Zakany R, et al. Adipose, Bone Marrow and Synovial Joint-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cartilage Repair. Front Genet. 2016;7:213.[12] 冯萌,邱裕生,陈迁,等.骨关节炎骨软骨损伤修复的研究现状[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2016,24(14):1295-1299.[13] 王永成,袁雪凌,汪爱媛,等.膝关节骨软骨损伤的治疗策略[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2014,28(1):113-118.[14] 潘育松,丁国新,王静.关节软骨损伤和缺损修复策略[J].中国骨伤, 2013,26(2):175-178.[15] Tuan RS, Chen AF, Klatt BA. Cartilage regeneration. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013;21(5):303-311.[16] Akkiraju H, Nohe A. Role of Chondrocytes in Cartilage Formation, Progression of Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration. J Dev Biol. 2015;3(4):177-192.[17] 李元城,张卫国.关节软骨损伤治疗进展[J].解放军医学杂志, 2013,38(5):423-427.[18] 彭程,林绵辉,肖涛.细胞因子与软骨损伤及修复研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2006,27(4):239-243.[19] 李海鹏,刘玉杰,王志刚,等.关节镜下微骨折术治疗膝关节软骨损伤[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2007,15(10):731-733.[20] 杨久山.关节镜下微骨折术合中药治疗膝骨性关节炎软骨缺损82例[J].山东中医杂志, 2013,32(6):386-387.[21] 姜骆永,陈洁琳,崔家鸣,等.自体软骨细胞移植技术修复关节软骨损伤研究进展[J].中国运动医学杂志, 2016,35(8):784-788.[22] 王泽民,黄江鸿,段莉,等.自体软骨细胞移植术治疗关节软骨损伤的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2015,23(4):328-331.[23] 周建林,方洪松,彭昊,等.自体、异体骨软骨移植及组织工程材料修复的关节软骨损伤[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015,19(34): 5530-5535.[24] 李海鹏,刘玉杰,刘智.同种异体骨软骨移植修复软骨损伤的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009,17(12):912-914.[25] Saltz A, Kandalam U. Mesenchymal stem cells and alginate microcarriers for craniofacial bone tissue engineering: A review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2016;104(5):1276-1284.[26] Li H, Qian J, Chen J, et al. Osteochondral repair with synovial membrane?derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(3):2071-2077.[27] Davatchi F, Sadeghi Abdollahi B, Mohyeddin M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for knee osteoarthritis: 5 years follow-up of three patients. Int J Rheum Dis. 2016;19(3): 219-225.[28] Tavassoli A, Matin MM, Niaki MA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can survive on the extracellular matrix-derived decellularized bovine articular cartilage scaffold. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(12):1221-1227.[29] 毛建水,张慎启,何颖韬,等.关节软骨损伤干细胞治疗研究进展[J]. 中国中医骨伤科杂志, 2013,21(9):70-72.[30] Afizah H, Hui JH. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy for osteoarthritis. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2016;7(3):177-182.[31] Ng J, Bernhard J, Vunjak-Novakovic G. et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Osteochondral Tissue Engineering. Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1416:35-54.[32] Nurkovic J, Dolicanin Z, Mustafic F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative rehabilitation. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016; 28(6):1943-1948.[33] Blair HC, Larrouture QC, Li Y, et al. Osteoblast Differentiation and Bone Matrix Formation In Vivo and In Vitro. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2016 Dec 27. [Epub ahead of print][34] Oda T, Sakai T, Hiraiwa H, et al. Osteoarthritis-derived chondrocytes are a potential source of multipotent progenitor cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;479(3):469-475.[35] Yang YJ, Li XL, Xue Y, et al. Bone marrow cells differentiation into organ cells using stem cell therapy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2016;20(13):2899-2907.[36] Shin YS, Choi JW, Park JK, et al. Tissue-engineered tracheal reconstruction using mesenchymal stem cells seeded on a porcine cartilage powder scaffold. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015; 43(4):1003-1013.[37] Zhang F, Yao Y, Su K, et al. Co-transduction of lentiviral and adenoviral vectors for co-delivery of growth factor and shRNA genes in mesenchymal stem cells-based chondrogenic system. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(9):1036-1045.[38] 徐佳佳,干耀恺,童文学,等.骨和软骨干细胞的分化调控与细胞治疗[J].生命科学, 2016,28(8):921-927.[39] 李文雄,张晶宇,杨锋.中药调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究进展[J].中医正骨, 2016,28(7):68-71.[40] 金瑛,李豫皖,张承昊,等.体外诱导人羊膜间充质干细胞向韧带细胞分化的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2016,30(2): 237-244.[41] Wegener B, Schrimpf FM, Bergschmidt P, et al. Cartilage regeneration by bone marrow cells-seeded scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95(3):735-740.[42] Cavallo C, Desando G, Cattini L, et al. Bone marrow concentrated cell transplantation: rationale for its use in the treatment of human osteochondral lesions. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2013;27(1):165-175.[43] Marmotti A, de Girolamo L, Bonasia DE, et al. Bone marrow derived stem cells in joint and bone diseases: a concise review. Int Orthop. 2014;38(9):1787-1801.[44] Qingqing M, Xin Z, Meizhong S. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells altered the immunoregulatory activities of hepatic natural killer cells. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2014; 38(6):689-698.[45] Chen H, Chevrier A, Hoemann CD, et al. Bone marrow stimulation induces greater chondrogenesis in trochlear vs condylar cartilage defects in skeletally mature rabbits. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(7):999-1007.[46] Zhang Y, Wang F, Chen J, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus bone marrow nucleated cells in the treatment of chondral defects. Int Orthop. 2012;36(5): 1079-1086.[47] Arufe MC, De la Fuente A, Fuentes I, et al. Umbilical cord as a mesenchymal stem cell source for treating joint pathologies. World J Orthop. 2011;2(6):43-50.[48] 黄志行,田春芳.脐带血的研究现状及其临床应用进展[J].医学综述, 2015,21(8):1375-1377.[49] 鲁斌,王岩松.脐带血干细胞的研究进展[J].实用医学杂志, 2016, 32(7):1189-1191.[50] 邵帅,周晨红,徐丽丽.体外诱导骨髓与脐血间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化及其成骨活性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(23):3652-3657.[51] Wilson R. Umbilical cord stromal cell differentiation: little correlation with known markers of the chondrocyte phenotype or cartilage extracellular matrix. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2012; 11(4):L111.[52] Harris DT. Umbilical cord tissue mesenchymal stem cells: characterization and clinical applications. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;8(5):394-399.[53] 常正奇,许建中,梁进,等.人脐带间充质干细胞的新分离方法及其作为骨组织工程种子细胞的相关研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2015,37(19):1930-1935.[54] 韩洪祯.脐血库造血干细胞冻存方法的研究现状[J].北京医学, 2016,38(6):610-612.[55] 易桥,卢燕勤,黄宏宇,等.间充质干细胞在免疫调节过程中的作用与应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(41):6216-6224.[56] Pascarella A, Ciatti R, Pascarella F, et al. Treatment of articular cartilage lesions of the knee joint using a modified AMIC technique.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(4):509-513. |
.jpg)
.jpg)