| [1] Bilgimol JC,Ragupathi S,Vengadassalapathy L,et al.Stem cells: An eventual treatment option for heart diseases.World J Stem Cells.2015;7(8):1118-1126.[2] Faiella W,Atoui R.Therapeutic use of stem cells for cardiovascular disease.Clin Transl Med.2016;5:34.[3] Der Sarkissian S,Lévesque T,Noiseux N.Optimizing stem cells for cardiac repair: Current status and new frontiers in regenerative cardiology.World J Stem Cells. 2017;9(1):9-25. [4] Gaffey AC,Chen MH,Venkataraman CM,et al.Injectable shear-thinning hydrogels used to deliver endothelial progenitor cells, enhance cell engraftment, and improve ischemic myocardium.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015;150(5):1268-1276.[5] Boopathy AV,Martinez MD,Smith AW,et al.Intramyocardial Delivery of Notch Ligand-Containing Hydrogels Improves Cardiac Function and Angiogenesis Following Infarction. Tissue Eng Part A.2015;21(17-18):2315-2322.[6] Mihic A,Cui Z,Wu J,et al.A Conductive Polymer Hydrogel Supports Cell Electrical Signaling and Improves Cardiac Function After Implantation into Myocardial Infarct. Circulation.2015;132(8):772-784.[7] Günter J,Wolint P,Bopp A,et al.Microtissues in Cardiovascular Medicine: Regenerative Potential Based on a 3D Microenvironment.Stem Cells Int.2016;2016:9098523.[8] Panda NC,Zuckerman ST,Mesubi OO,et al.Improved conduction and increased cell retention in healed MI using mesenchymal stem cells suspended in alginate hydrogel.J Interv Card Electrophysiol.2014;41(2):117-127.[9] Yang G,Xiao Z,Ren X,et al.Enzymatically crosslinked gelatin hydrogel promotes the proliferation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells.PeerJ.2016;4:e2497.[10] Yang G,Xiao Z,Ren X,et al.Obtaining spontaneously beating cardiomyocyte-like cells from adipose-derived stromal vascular fractions cultured on enzyme-crosslinked gelatin hydrogels.Sci Rep.2017;7:41781. [11] Lawrence PG,Patil PS,Leipzig ND,et al.Ionically Cross-Linked Polymer Networks for the Multiple-Month Release of Small Molecules.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(7):4323-4335.[12] Xu G,Wang X,Deng C,et al.Injectable biodegradable hybrid hydrogels based on thiolated collagen and oligo(acryloyl carbonate)-poly(ethylene glycol)-oligo(acryloyl carbonate) copolymer for functional cardiac regeneration.Acta Biomaterialia.2015;15:55-:64.[13] Deng B,Shen L,Wu Y,et al.Delivery of alginate-chitosan hydrogel promotes endogenous repair and preserves cardiac function in rats with myocardial infarction.J Biomed Mater Res A.2015;103(3):907-918. [14] 牡丹,原晖华,顾蓉,等.整合素连接激酶过表达促进猪骨髓间充质干细胞向心肌样细胞分化[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2016,24(9): 875-881.[15] Chen G,Chen J,Liu Q,et al.Enzymatic Formation of a Meta-stable Supramolecular Hydrogel for 3D Cell Culture. RSC Adv.2015;(5):30675-30678.[16] Liang Z,Liu C,Li L,et al.Double-Network Hydrogel with Tunable Mechanical Performance and Biocompatibility for the Fabrication of Stem Cells-Encapsulated Fibers and 3D Assemble. Sci Rep.2016;6:33462.[17] Lowenthal J,Gerecht S.Stem cell-derived vasculature: A potent and multidimensional technology for basic research, disease modeling, and tissue engineering.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2016;473(3):733-742.[18] Chaudhuri O,Gu L,Klumpers D,et al.Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity.Nat Mater. 2016;15(3):326-334.[19] Günter J,Wolint P,Bopp A,at al.Microtissues in Cardiovascular Medicine: Regenerative Potential Based on a 3D Microenvironment.Stem Cells Int.2016;2016:9098523.[20] Chen G,Hua Y,Ou C,et al.Nanostructure formation-induced fluorescence turn-on for selectively detecting protein thiols in solutions, bacteria and live cells.Chem Commun.2015; 51(53): 10758-10761.[21] Truskey GA.Advancing cardiovascular tissue engineering. Version 1.F1000Res.2016;5:F1000 Faculty Rev-1045.[22] McGann CL,Akins RE,Kiick KL.Resilin-PEG hybrid hydrogels yield degradable elastomeric scaffolds with heterogeneous microstructure.Biomacromolecules.2016;17(1):128-140.[23] McGann CL,Dumm RE,Jurusik AK,et al.Thiol-ene Photocrosslinking of Cytocompatible Resilin-like Polypeptide- PEG Hydrogels.Macromol Biosci.2016; 16(1):129-138.[24] Masumoto H,Nakane T,Tinney JP,et al.The myocardial regenerative potential of three-dimensional engineered cardiac tissues composed of multiple human iPS cell-derived cardiovascular cell lineages.Sci Rep.2016;6:29933.[25] Yang G,Xiao Z,Ren X,et al.Obtaining spontaneously beating cardiomyocyte-like cells from adipose-derived stromal vascular fractions cultured on enzyme-crosslinked gelatin hydrogels.Sci Rep.2017;7:41781.[26] Lister Z,Rayner KJ,Suuronen EJ.How Biomaterials Can Influence Various Cell Types in the Repair and Regeneration of the Heart after Myocardial Infarction.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2016;4:62. |
.jpg)

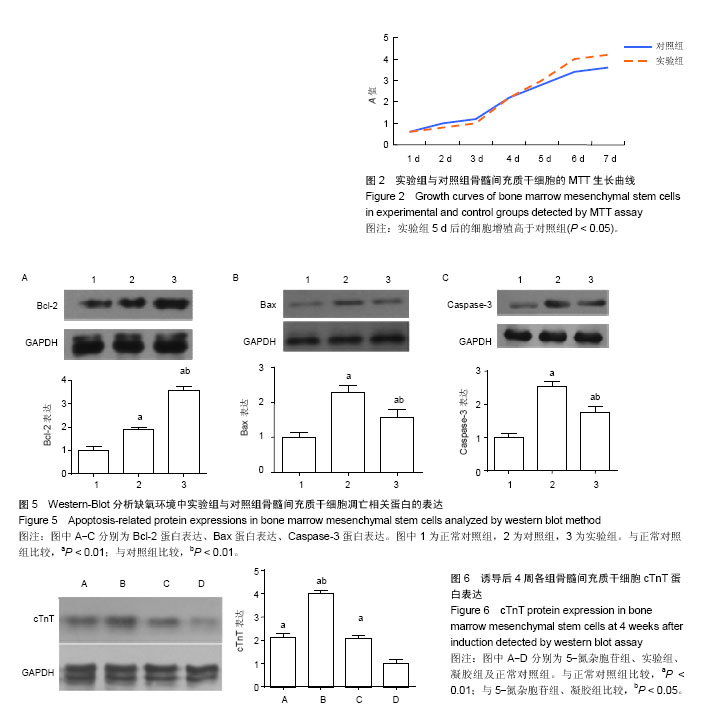
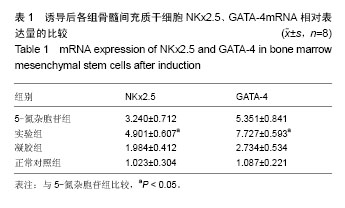
.jpg)
.jpg)