| [1] Terzis JK, Sun DD, Thanos PK. Historical and basic science review: past, present, and future of nerve repair. J Reconstr Microsurg. 1997;13(3):215-225.[2] Micera A, Puxeddu I, Aloe L, et al. New insights on the involvement of Nerve Growth Factor in allergic inflammation and fibrosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2003;14(5): 369-374.[3] 陈渝,王大勇,王祖贵,等.腺病毒介导的神经生长因子基因治疗大鼠坐骨神经损伤的疗效研究[J].第三军医大学报, 2008,30(23): 2191-2193. [4] Mukhopadhyay G, Doherty P, Walsh FS, et al. A novel role for myelin-associated glycoprotein as an inhibitor of axonal regeneration. Neuron. 1994;13(3):757-767.[5] Tomita K, Kubo T, Matsuda K, et al. Myelin-associated glycoprotein reduces axonal branching and enhances functional recovery after sciatic nerve transection in rats. Glia. 2007;55(14):1498-1507.[6] 周廷冲.多肽生长因子基础与临床[M].北京:中国科学技术出版社,1992:105-135.[7] 许家军,何成,朱田斌.等.周围神经损伤后外源性神经生长因子及睫状神经营养因子对神经元的保护作用[J].中华显微外科杂志, 1997,20(1):32-35.[8] Aloe L. Rita Levi-Montalcini and the discovery of nerve growth factor: past and present studies. Arch Ital Biol. 2003;141(2-3): 65-83.[9] Xu K, Uchida K, Nakajima H, et al. Targeted retrograde transfection of adenovirus vector carrying brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene prevents loss of mouse (twy/twy) anterior horn neurons in vivo sustaining mechanical compression. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(17): 1867-1874.[10] 高延明,李靖年.局部应用神经生长因子对坐骨神经损伤模型大鼠修复与再生的影响[J].大连医科大学学报, 2013,35(4): 336-340.[11] Miller C, Jeftinija S, Mallapragada S. Synergistic effects of physical and chemical guidance cues on neurite alignment and outgrowth on biodegradable polymer substrates. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(3):367-378.[12] Lesný P, De Croos J, Prádný M, et al. Polymer hydrogels usable for nervous tissue repair. J Chem Neuroanat. 2002; 23(4):243-247.[13] Miller C, Jeftinija S, Mallapragada S. Micropatterned Schwann cell-seeded biodegradable polymer substrates significantly enhance neurite alignment and outgrowth. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(6):705-715.[14] Cao Z, Qiu J, Domeniconi M, et al. The inhibition site on myelin-associated glycoprotein is within Ig-domain 5 and is distinct from the sialic acid binding site. J Neurosci. 2007; 27(34):9146-9154.[15] DeBellard ME, Tang S, Mukhopadhyay G, et al. Myelin-associated glycoprotein inhibits axonal regeneration from a variety of neurons via interaction with a sialoglycoprotein. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1996;7(2):89-101.[16] Quarles RH. Myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG): past, present and beyond. J Neurochem. 2007;100(6):1431-1448.[17] Cao Z, Gao Y, Deng K, et al. Receptors for myelin inhibitors: Structures and therapeutic opportunities. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;43(1):1-14. [18] McLean J, Batt J, Doering LC, et al. Enhanced rate of nerve regeneration and directional errors after sciatic nerve injury in receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma knock-out mice. J Neurosci. 2002;22(13):5481-5491.[19] Mukhopadhyay G, Doherty P, Walsh FS, et al. A novel role for myelin-associated glycoprotein as an inhibitor of axonal regeneration. Neuron. 1994;13(3):757-767.[20] Quarles RH. A hypothesis about the relationship of myelin-associated glycoprotein's function in myelinated axons to its capacity to inhibit neurite outgrowth. Neurochem Res. 2009;34(1):79-86. [21] Filbin MT. Myelin-associated inhibitors of axonal regeneration in the adult mammalian CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4(9): 703-713.[22] Boyd JG, Gordon T. A dose-dependent facilitation and inhibition of peripheral nerve regeneration by brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Eur J Neurosci. 2002;15(4):613-626.[23] Xie F, Li QF, Gu B, et al. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of a biodegradable chitosan-PLA composite peripheral nerve guide conduit material. Microsurgery. 2008;28(6):471-479. [24] Blits B, Dijkhuizen PA, Carlstedt TP, et al. Adenoviral vector-mediated expression of a foreign gene in peripheral nerve tissue bridges implanted in the injured peripheral and central nervous system. Exp Neurol. 1999;160(1):256-267.[25] Ruitenberg MJ, Plant GW, Hamers FP, et al. Ex vivo adenoviral vector-mediated neurotrophin gene transfer to olfactory ensheathing glia: effects on rubrospinal tract regeneration, lesion size, and functional recovery after implantation in the injured rat spinal cord. J Neurosci. 2003; 23(18):7045-7058.[26] Hendriks WT, Eggers R, Carlstedt TP, et al. Lentiviral vector-mediated reporter gene expression in avulsed spinal ventral root is short-term, but is prolonged using an immune "stealth" transgene. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2007;25(5-6): 585-599.[27] Blits B, Dijkhuizen PA, Boer GJ, et al. Intercostal nerve implants transduced with an adenoviral vector encoding neurotrophin-3 promote regrowth of injured rat corticospinal tract fibers and improve hindlimb function. Exp Neurol. 2000; 164(1):25-37.[28] Blits B, Kitay BM, Farahvar A, et al. Lentiviral vector-mediated transduction of neural progenitor cells before implantation into injured spinal cord and brain to detect their migration, deliver neurotrophic factors and repair tissue. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2005;23(5-6):313-324.[29] Dijkhuizen PA, Pasterkamp RJ, Hermens WT, et al. Adenoviral vector-mediated gene delivery to injured rat peripheral nerve. J Neurotrauma. 1998;15(6):387-397.[30] Blits B, Dijkhuizen PA, Hermens WT, et al. The use of adenoviral vectors and ex vivo transduced neurotransplants: towards promotion of neuroregeneration. Cell Transplant. 2000;9(2):169-178.[31] Joung I, Kim HS, Hong JS, et al. Effective gene transfer into regenerating sciatic nerves by adenoviral vectors: potentials for gene therapy of peripheral nerve injury. Mol Cells. 2000; 10(5):540-545.[32] Koda M, Kamada T, Hashimoto M, et al. Adenovirus vector-mediated ex vivo gene transfer of brain-derived neurotrophic factor to bone marrow stromal cells promotes axonal regeneration after transplantation in completely transected adult rat spinal cord. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(12): 2206-2214. [33] Sapolsky RM, Steinberg GK. Gene therapy using viral vectors for acute neurologic insults. Neurology. 1999;53(9): 1922-1931. |
.jpg)
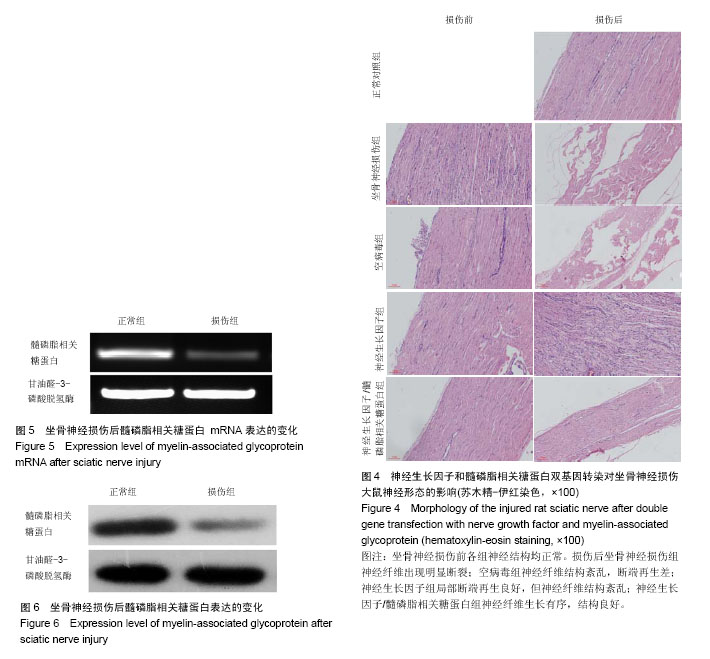
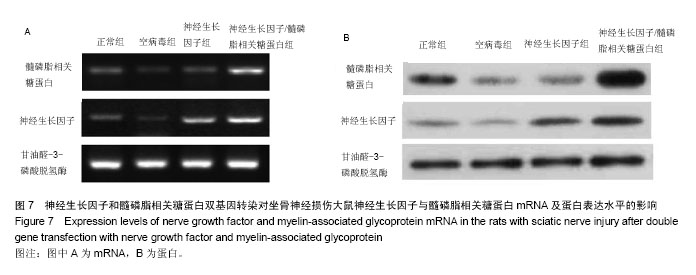
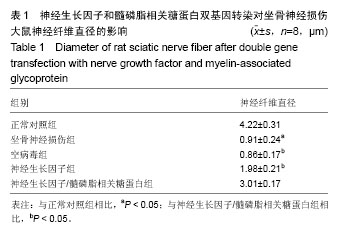
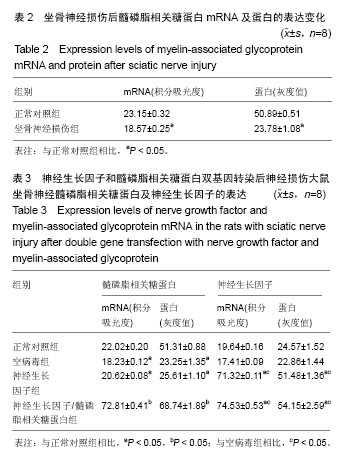
.jpg)
.jpg)