| [1] Arden NK, Leyland KM. Osteoarthritis year 2013 in review: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(10): 1409-1413.[2] Dziedzic KS, Healey EL, Porcheret M, et al. Implementing the NICE osteoarthritis guidelines: a mixed methods study and cluster randomised trial of a model osteoarthritis consultation in primary care--the Management of OsteoArthritis In Consultations (MOSAICS) study protocol. Implement Sci. 2014;9: 95.[3] Gbejuade HO, Lovering AM, Webb JC. The role of microbial biofilms in prosthetic joint infections. Acta Orthop. 2015;86(2): 147-158.[4] Mortazavi SM, Molligan J, Austin MS, et al, Parvizi J. Failure following revision total knee arthroplasty: infection is the major cause. Int Orthop. 2011;35(8): 1157-1164.[5] Patel A, Pavlou G, Mújica-Mota RE, et al. The epidemiology of revision total knee and hip arthroplasty in England and Wales: a comparative analysis with projections for the United States. A study using the National Joint Registry dataset. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(8): 1076-1081.[6] Nelson CL, Elkassabany NM, Kamath AF, et al. Low Albumin Levels, More Than Morbid Obesity, Are Associated With Complications After TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473(10): 3163-3172.[7] 周宗科,翁习生,曲铁兵,等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复——围术期管理策略专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016, 9(1):1-9.[8] Jämsen E, Nevalainen P, Eskelinen A, et al. Obesity, diabetes, and preoperative hyperglycemia as predictors of periprosthetic joint infection: a single-center analysis of 7181 primary hip and knee replacements for osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2012;94(14): e101.[9] Hwang JS, Kim SJ, Bamne AB, et al. Do glycemic markers predict occurrence of complications after total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(5): 1726-1731.[10] Dowsey MM, Choong PF. Obese diabetic patients are at substantial risk for deep infection after primary TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2009;467(6): 1577-1581.[11] Watts CD, Wagner ER, Houdek MT, et al. Morbid Obesity: Increased Risk of Failure After Aseptic Revision TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(8): 2621-2627.[12] Kunutsor SK, Whitehouse MR, Blom AW, et al. Patient-Related Risk Factors for Periprosthetic Joint Infection after Total Joint Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(3): e0150866.[13] Smith TO, Aboelmagd T, Hing CB, et al. Does bariatric surgery prior to total hip or knee arthroplasty reduce post-operative complications and improve clinical outcomes for obese patients? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(9): 1160-1166.[14] Martin JR, Watts CD, Taunton MJ. Bariatric surgery does not improve outcomes in patients undergoing primary total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2015;97-B(11): 1501-1505.[15] Lui M, Jones CA, Westby MD. Effect of non-surgical, non-pharmacological weight loss interventions in patients who are obese prior to hip and knee arthroplasty surgery: a rapid review. Syst Rev. 2015; 4: 121.[16] Ravi B, Croxford R, Hollands S, et al. Increased risk of complications following total joint arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(2): 254-263.[17] LoVerde ZJ, Mandl LA, Johnson BK, et al. Rheumatoid Arthritis Does Not Increase Risk of Short-term Adverse Events after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Case-control Study. J Rheumatol. 2015;42(7): 1123-1130.[18] Kadota Y, Nishida K, Hashizume K, et al. Risk factors for surgical site infection and delayed wound healing after orthopedic surgery in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Mod Rheumatol. 2016. 26(1): 68-74.[19] Ravi B, Escott B, Shah PS, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis comparing complications following total joint arthroplasty for rheumatoid arthritis versus for osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(12): 3839-3849.[20] Bala A, Penrose CT, Seyler TM, et al. Outcomes after Total Knee Arthroplasty for post-traumatic arthritis. Knee. 2015; 22(6): 630-639.[21] Frangiamore SJ, Siqueira MB, Saleh A, et al. Synovial Cytokines and the MSIS Criteria Are Not Useful for Determining Infection Resolution After Periprosthetic Joint Infection Explantation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(7): 1630-1639.[22] Saleh H, Yu S, Vigdorchik J, et al. Total knee arthroplasty for treatment of post-traumatic arthritis: Systematic review. World J Orthop. 2016;7(9): 584-591.[23] Peersman G, Laskin R, Davis J, et al. Infection in total knee replacement: a retrospective review of 6489 total knee replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001;(392): 15-23.[24] Pulido L, Ghanem E, Joshi A, et al. Periprosthetic joint infection: the incidence, timing, and predisposing factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008;466(7): 1710-1715.[25] Poultsides LA, Ma Y, Della VAG, et al. In-hospital surgical site infections after primary hip and knee arthroplasty-- incidence and risk factors. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(3): 385-389.[26] Lee QJ, Mak WP, Wong YC. Risk factors for periprosthetic joint infection in total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2015;23(3): 282-286.[27] Meehan JP, Danielsen B, Kim SH, et al. Younger age is associated with a higher risk of early periprosthetic joint infection and aseptic mechanical failure after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(7): 529-535.[28] Namba RS, Inacio MC, Paxton EW. Risk factors associated with deep surgical site infections after primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 56,216 knees. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(9): 775-782.[29] Willis-Owen CA, Konyves A, Martin DK. Factors affecting the incidence of infection in hip and knee replacement: an analysis of 5277 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(8): 1128-1133.[30] Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Lau E, et al. Prosthetic joint infection risk after TKA in the Medicare population. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1): 52-56.[31] Fierer N, Hamady M, Lauber CL, et al. The influence of sex, handedness, and washing on the diversity of hand surface bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(46): 17994-17999.[32] Kim MK, Patel RA, Shinn AH, et al. Evaluation of gender difference in skin type and pH. J Dermatol Sci. 2006;41(2): 153-156.[33] Chaiyakit P, Meknavin S, Pakawattana V. Results of peri-articular steroid injection in the treatment of chronic extra-articular pain after total knee arthroplasty. J Med Assoc Thai. 2012;95 Suppl 10: S48-52.[34] Horne G, Devane P, Davidson A, et al. The influence of steroid injections on the incidence of infection following total knee arthroplasty. N Z Med J. 2008;121(1268): U2896.[35] Zhou Y, Li L, Zhou Q, et al. Lack of efficacy of prophylactic application of antibiotic-loaded bone cement for prevention of infection in primary total knee arthroplasty: results of a meta-analysis. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2015;16(2): 183-187.[36] Schiavone PA, Corona K, Giulianelli M, et al. Antibiotic-loaded bone cement reduces risk of infections in primary total knee arthroplasty? A systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 .[37] Del PJL, Patel R. Clinical practice. Infection associated with prosthetic joints. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(8): 787-794.[38] Spicer E, Thomas GR, Rumble EJ. Comparison of the major intraoperative and postoperative complications between unilateral and sequential bilateral total knee arthroplasty in a high-volume community hospital. Can J Surg. 2013;56(5): 311-317.[39] Poultsides LA, Memtsoudis SG, Vasilakakos T, et al. Infection following simultaneous bilateral total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(8 Suppl): 92-95.[40] Sheth DS, Cafri G, Paxton EW, et al. Bilateral Simultaneous vs Staged Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparison of Complications and Mortality. J Arthroplasty. 2016; 31(9 Suppl): 212-216.[41] Huang Z, Ma J, Shen B, et al. General anesthesia: to catheterize or not? A prospective randomized controlled study of patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2015;30(3): 502-506.[42] Li N, Liu M, Wang D, et al. Comparison of complications in one-stage bilateral total knee arthroplasty with and without drainage. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10: 3.[43] Liu XH, Fu PL, Wang SY, et al. The effect of drainage tube on bleeding and prognosis after total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9: 27.[44] Zhang X, Li G, Ma J, et al. [A meta-analysis for the efficacy and safety of drainage after primary total knee arthroplasty]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94(29): 2282-2285.[45] Fan Y, Liu Y, Lin J, et al. Drainage does not promote post-operative rehabilitation after bilateral total knee arthroplasties compared with nondrainage. Chin Med Sci J. 2013;28(4): 206-210.[46] Frisch NB, Wessell NM, Charters MA, et al. Predictors and complications of blood transfusion in total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(9 Suppl): 189-192.[47] 周宗科, 翁习生, 向兵,等. 中国髋、膝关节置换术加速康复--围术期贫血诊治专家共识[J]. 中华骨与关节外科杂志, 2016, 9(1): 10-15.[48] Ku?era B, Náhlík D, Hart R, et al. [Post-operative retransfusion and intra-operative autotransfusion systems in total knee arthroplasty. A comparison of their efficacy]. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech. 2012;79(4): 361-366.[49] Chimento GF, Huff T, Ochsner JL, et al. An evaluation of the use of topical tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2013;28(8 Suppl): 74-77.[50] Wang C, Han Z, Zhang T, et al. The efficacy of a thrombin-based hemostatic agent in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9: 90.[51] Bozic KJ, Kurtz SM, Lau E, et al. The epidemiology of revision total knee arthroplasty in the United States. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2010;468(1): 45-51.[52] Della VC, Parvizi J, Bauer TW, et al. Diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010; 18(12): 760-770.[53] Parvizi J, Della VCJ. AAOS Clinical Practice Guideline: diagnosis and treatment of periprosthetic joint infections of the hip and knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2010;18(12): 771-772.[54] Ahmad SS, Becker R, Chen AF, et al. EKA survey: diagnosis of prosthetic knee joint infection. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016; 24(10): 3050-3055.[55] Parvizi J, Gehrke T. Definition of periprosthetic joint infection. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(7):1331.[56] Tsukayama DT, Goldberg VM, Kyle R. Diagnosis and management of infection after total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 1: S75-80.[57] Leone JM, Hanssen AD. Management of infection at the site of a total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(10): 2335-2348.[58] Bengston S, Knutson K, Lidgren L. Treatment of infected knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989;(245): 173-178.[59] Hanssen AD, Rand JA. Evaluation and treatment of infection at the site of a total hip or knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 1999;48: 111-122.[60] Holmberg A, Thórhallsdóttir VG, Robertsson O, et al. 75% success rate after open debridement, exchange of tibial insert, and antibiotics in knee prosthetic joint infections. Acta Orthop. 2015;86(4): 457-462.[61] Koh IJ, Han SB, In Y, et al. Open debridement and prosthesis retention is a viable treatment option for acute periprosthetic joint infection after total knee arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(6): 847-855.[62] Kim JG, Bae JH, Lee SY, et al. The parameters affecting the success of irrigation and debridement with component retention in the treatment of acutely infected total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2015;7(1): 69-76.[63] Haleem AA, Berry DJ, Hanssen AD. Mid-term to long-term followup of two-stage reimplantation for infected total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;(428): 35-39.[64] Jämsen E, Stogiannidis I, Malmivaara A, et al. Outcome of prosthesis exchange for infected knee arthroplasty: the effect of treatment approach. Acta Orthop. 2009;80(1): 67-77.[65] Leone JM, Hanssen AD. Management of infection at the site of a total knee arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2006;55: 449-461.[66] Silvestre A, Almeida F, Renovell P, et al. Revision of infected total knee arthroplasty: two-stage reimplantation using an antibiotic-impregnated static spacer. Clin Orthop Surg. 2013; 5(3): 180-187.[67] Nagra NS, Hamilton TW, Ganatra S, et al. One-stage versus two-stage exchange arthroplasty for infected total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016;24(10): 3106-3114.[68] Haddad FS, Sukeik M, Alazzawi S. Is single-stage revision according to a strict protocol effective in treatment of chronic knee arthroplasty infections. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473(1): 8-14.[69] Zahar A, Kendoff DO, Klatte TO, et al. Can Good Infection Control Be Obtained in One-stage Exchange of the Infected TKA to a Rotating Hinge Design? 10-year Results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2016;474(1): 81-87. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: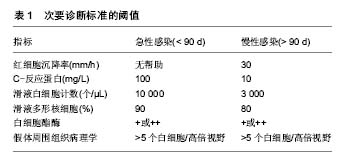
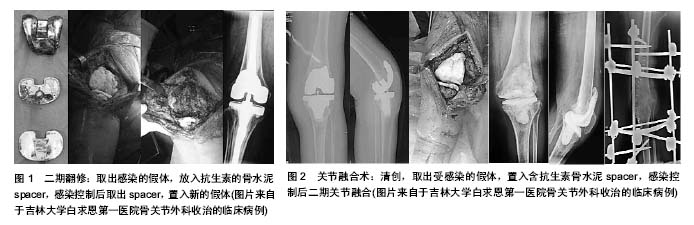
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: