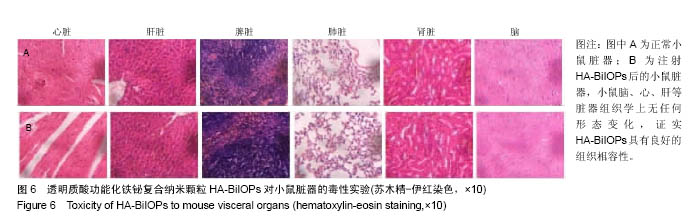
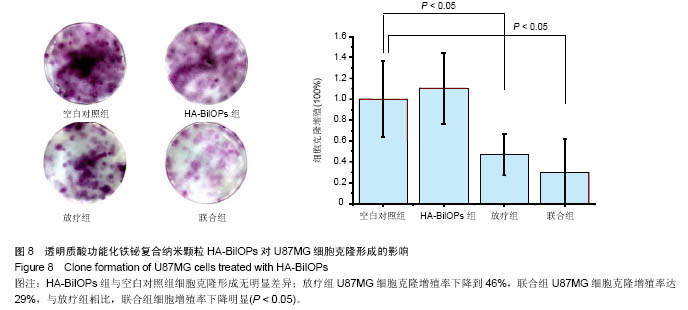
| [1]Sun L,Joh DY,Al-Zaki A.Theranostic application of mixed gold and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle micelles in Glioblastoma multiforme.J Biomed Nanotechnol.2016;2(2): 347-356.[2]Dolecek TA,Propp JM,Stroup NE,et al.CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2005-2009. Neuro Oncol. 2012;14 (suppl 5):v1-49.[3]Dhermain F.Radiotherapy of high-grade gliomas: current standards and new concepts, innovations in imaging and radiotherapy, and new therapeutic approaches.Chin J Cancer. 2014;33(1):16-24.[4]Harrison L,Blackwell K.Hypoxia and anemia: factors in decreased sensitivity to radiation therapy and chemotherapy.Oncologist.2004;9(suppl 5):31-40. [5]Klaus M,Frank U,Dirk N,et al.Efficacy and safety of intratumoral thermotherapy using magnetic iron-oxide nanoparticles combined with external beam radiotherapy on patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme.Neurooncol. 2011;103(2):317-324.[6]Kakuta T,Takashima Y,Nakahata M,et al.Preorganized hydrogel: self-healing properties of supramolecular hydrogels formed by polymerization of host-guest-monomers that contain cyclodextrins and hydrophobic guest groups.Adv Mater.2013;25(20): 2849-2853.[7]Gu JH,Zhang QY,Zhang W,et al.Preparation of amphiphilic superparamagneticcomposite particles with tumor targeted MRIcontrast agent.Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2014;18(30): 4823-4830.[8]Huang Y,LuoY,Zheng W.Rational design of cancer-targeted BSA protein nanoparticles as radiosensitizer to overcome cancer radioresistance.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2014; 6(21):19217-19228.[9]Borchiellini D,Etienne-Grimaldi MC,Thariat J,et al.The impact of pharmacogenetics on radiation therapy outcome in cancer patients. A focus on DNA damage response genes .Cancer Treat Rev.2012;38(6):737-759. [10]Corso CD,Ali AN,Diaz R.Radiation-induced tumor neoantigens: imaging and therapeutic implications.Am J Cancer Res.2011;1(3):390-412. [11]Kleinauskas A,Rocha S,Sahu S.Carbon-core silver-shell nanodots as sensitizers for phototherapy and radiotherapy.Nanotechnology.2013;24(32):325103.[12]Subiel A,Ashmore R,Schettino G.Standards and methodologies for characterizing radiobiological impact of high-Z nanoparticles.Theranostics.2016;6(10):1651-1671. [13]Li M,Zhao Q,Yi X,et al.Au@MnS@ZnS core/shell/shell nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging and enhanced cancer radiation therapy.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016; 8(15):9557-9564.[14]Xing H,Zheng X,Ren Q,et al.Computed tomography imaging-guided radiotherapy by targeting upconversion nanocubes with significant imaging and radiosensitization enhancements.Sci Rep.2013;3:1751-1759.[15]李慧,王大新,顾健.超顺磁性纳米颗粒治疗肿瘤的应用进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(51):10133-10136.[16]Bogart LK,Pourroy G,Murphy CJ,et al.Nanoparticles for imaging, sensing, and therapeutic intervention.ACS Nano. 2014;8(4):3107-3122.[17]Dev KC,Parmeswaran D,Sunil K.Nanoparticle-mediated hyperthermia in cancer therapy .NIH Public Access Author Manuscript.2011;2(8):1001-1014. [18]Bazak R,Houri M,EI Achy S,et al.Cancer active targeting by nanoparticles: a comprehensive review of literature.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.2015;141(5):769-784.[19]Xing H,Zheng X,Ren Q,et al.Computed tomography imaging-guided radiotherapy by targeting upconversion nanocubes with significant imaging and radiosensitization enhancements.Sci Rep.2013;3:1751.[20]Yao MH,Ma M,Chen Y,et al.Multifunctional Bi2S3/PLGA nanocapsule for combined HIFU/radiation therapy. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8197-8205.[21]Huang HH,Chen J,Meng YZ,et al.Synthesis and characterization of Bi2S3 composite nanoparticles with high X-ray absorption.Mater Res Bull.2013;48:3800-3804.[22]Ai K,Liu Y,Liu J,et al.Large-scale synthesis of Bi2S3 nanodots as a contrast agent for in vivo X-ray computed tomography imaging.Adv Mater.2011;23(42):4886-4891.[23]Mesbahi A.A review on gold nanoparticles radiosensitization effect in radiation therapy of cancer. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother. 2010;15(6):176-180.[24]Lee CT,Boss MK,Dewhirst MW.Imaging tumor hypoxia to advance radiation oncology.Antioxid Redox Signal.2014; 21(2):313-337. [25]Lammers T,Aime S,Hennink WE,et al.Theranostic nanomedicine.Acc Chem Res.2011;44(10):1029-1038.[26]Hu F,Jia Q,Li Y,et al.Facile synthesis of ultrasmall PEGylated iron oxide nanoparticles for dual-contrast T1-and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Nanotechnology.2011;22(24): 245604-245611.[27]Phillipsa WT,Bao A,Brenner AJ,et al.Image-guided interventional therapy for cancer with radiotherapeutic nanoparticles.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2014;76:39-59.[28]Yu M,Jambhrunkar S,Thorn P,et al.Hyaluronic acid modified mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery to CD44-overexpressing cancer cells. Nanoscale. 2013;5: 178-183.[29]Ma M,Huang Y,Chen H,et al.Bi2S3-embedded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for efficient drug delivery and interstitial radiotherapy sensitization.Biomaterials.2015;37:447-455.[30]Babaei M,Ganjalikhani M.The potential effectiveness of nanoparticles as radio sensitizers for radiotherapy.Bioimpacts. 2014;4(1):15-20. [31]Yang Y,Zhang L,Cai J,et al.Tumor angiogenesis targeted radiosensitization therapy using gold nanoprobes guided by MRI/SPECT imaging. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.2016; 8(3): 1718-1732.[32]Gao B,Shen L,He KW.GNRs@SiO2-FA in combination with radiotherapy induces the apoptosis of HepG2 cells by modulating the expression of apoptosis-related proteins.Int J Mol Med.2015;36(5):1282-1290. [33]Miladi I,Aloy MT,Armandy E,et al.Combining ultrasmall gadolinium-based nanoparticles with photon irradiation overcomes radioresistance of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Nanomedicine.2015;11(1):247-257.[34]Retif P,Pinel S,Toussaint M,et al.Nanoparticles for radiation therapy enhancement: the key parameters.Theranostics. 2015;5(9):1030-1044.[35]Runowski M,Grzyb T,Lis S.Magnetic and luminescent hybrid nanomaterial based on Fe3O4 nanocrystals and GdPO4: Eu(3+) nanoneedles.Nanopart Res.2012;14(10):1188. |
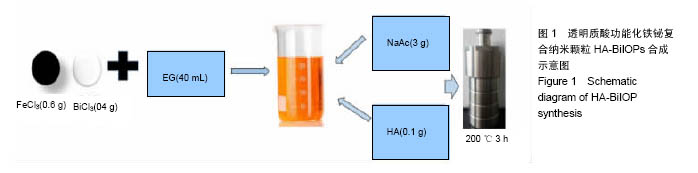
.jpg)
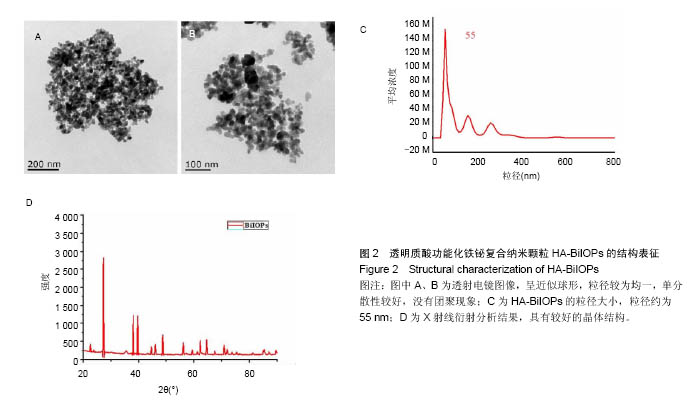

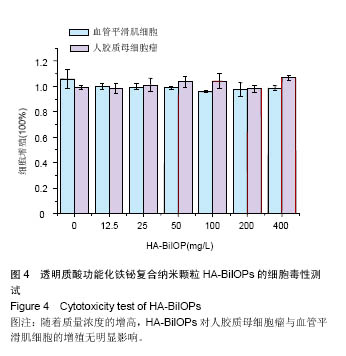
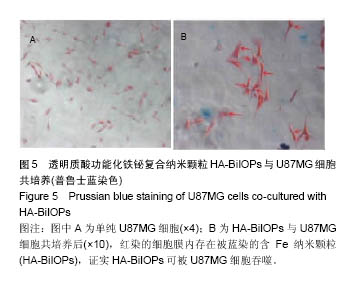

.jpg)