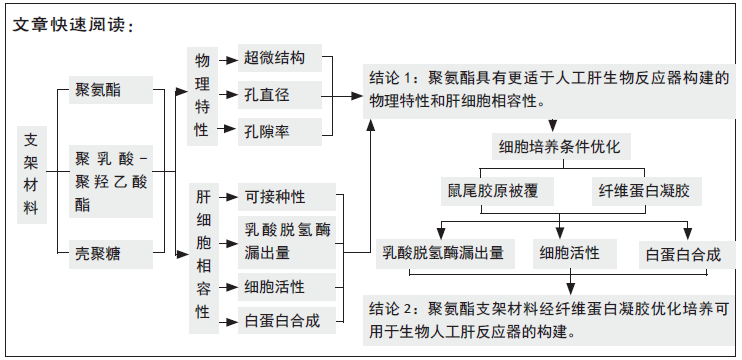
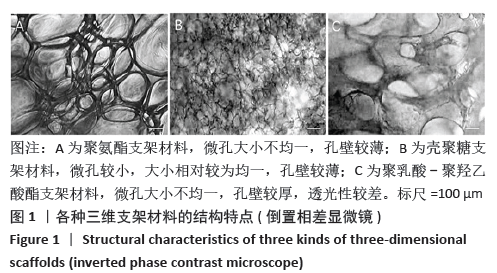
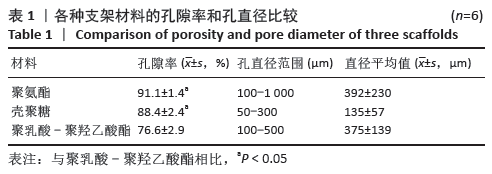
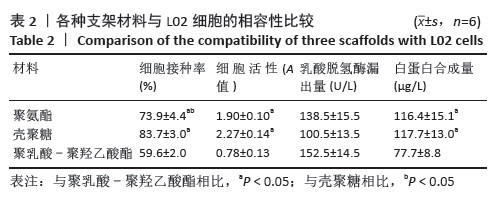
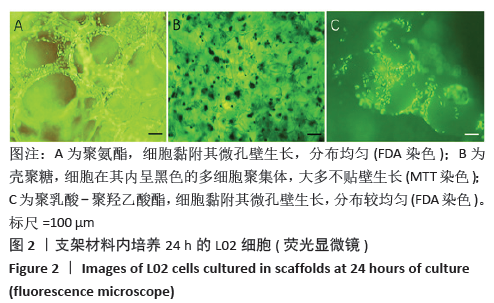
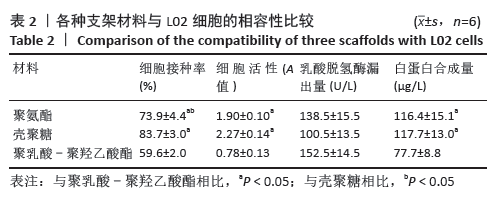
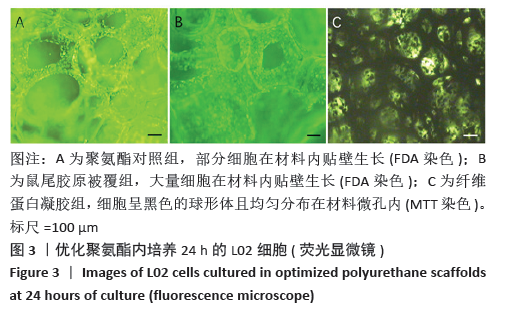
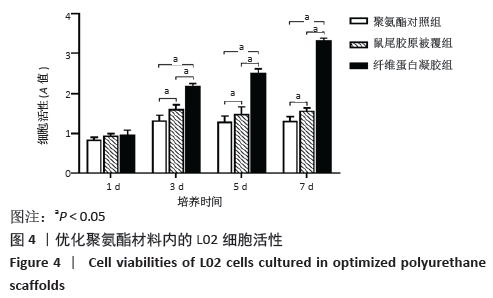
[1] HE YT, QI YN, ZHANG BQ, et al. Bioartificial liver support systems for acute liver failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical and preclinical literature. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(27):3634-3648.
[2] STRAIN AJ, NEUBERGER JM. A bioartificial liver--state of the art. Science. 2002; 295(5557):1005-1009.
[3] SHI XL, GAO Y, YAN Y, et al. Improved survival of porcine acute liver failure by a bioartificial liver device implanted with induced human functional hepatocytes. Cell Res. 2016;26(2):206-216.
[4] LI LJ, DU WB, ZHANG YM, et al. Evaluation of a bioartificial liver based on a nonwoven fabric bioreactor with porcine hepatocytes in pigs. J Hepatol. 2006;44(2):317-324.
[5] KATAOKA K, NAGAO Y, NUKUI T, et al. An organic-inorganic hybrid scaffold for the culture of HepG2 cells in a bioreactor. Biomaterials. 2005;26(15):2509-2516.
[6] DAVIDSON AJ, ELLIS MJ, CHAUDHURI JB. A theoretical method to improve and optimize the design of bioartificial livers. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010;106(6):980-988.
[7] ZHANG SC, LIU T, WANG YJ. Porous and single-skinned polyethersulfone membranes support the growth of HepG2 cells: a potential biomaterial for bioartificial liver systems. J Biomater Appl. 2012;27(3):359-366.
[8] ZHANG S, LIU T, CHEN L, et al. Bifunctional polyethersulfone hollow fiber with a porous, single-layer skin for use as a bioartificial liver bioreactor. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012;23(8):2001-211.
[9] YE H, XIA Z, FERGUSON DJ, et al. Studies on the use of hollow fibre membrane bioreactors for tissue generation by using rat bone marrow fibroblastic cells and a composite scaffold. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2007;18(4):641-648.
[10] ROZGA J, WILLIAMS F, RO MS, et al. Development of a bioartificial liver: properties and function of a hollow-fiber module inoculated with liver cells. Hepatology. 1993;17(2):258-265.
[11] DE BARTOLO L, SALERNO S, CURCIO E, et al. Human hepatocyte functions in a crossed hollow fiber membrane bioreactor. Biomaterials. 2009;30(13):2531-2543.
[12] YE SH, WATANABE J, TAKAI M, et al. Design of functional hollow fiber membranes modified with phospholipid polymers for application in total hemopurification system. Biomaterials. 2005;26(24):5032-5041.
[13] SAKIYAMA R, HAMADA H, BLAU B, et al. Evaluation of the mass transfer rate using computer simulation in a three-dimensional interwoven hollow fiber-type bioartificial liver. Biotechnol Lett. 2018;40(11-12):1567-1578.
[14] CHEN G, PALMER AF. Mixtures of hemoglobin-based oxygen carriers and perfluorocarbons exhibit a synergistic effect in oxygenating hepatic hollow fiber bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2010;105(3):534-542.
[15] FLENDRIG LM, LA SOE JW, JORNING GG, et al. In vitro evaluation of a novel bioreactor based on an integral oxygenator and a spirally wound nonwoven polyester matrix for hepatocyte culture as small aggregates. J Hepatol. 1997;26(6):1379-1392.
[16] ZHANG S, CHEN L, LIU T, et al. Integration of single-layer skin hollow fibers and scaffolds develops a three-dimensional hybrid bioreactor for bioartificial livers. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2014;25(1):207-216.
[17] NAHMIAS Y, BERTHIAUME F, YARMUSH ML. Integration of technologies for hepatic tissue engineering. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2007;103:309-329.
[18] HOU YT, HSU CC. Development of a 3D porous chitosan/gelatin liver scaffold for a bioartificial liver device. J Biosci Bioeng. 2020;129(6):741-748.
[19] MORGAN SM, TILLEY S, PERERA S, et al. Expansion of human bone marrow stromal cells on poly-(DL-lactide-co-glycolide) (PDL LGA) hollow fibres designed for use in skeletal tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2007;28(35):5332-5343.
[20] BELANGER MC, MAROIS Y, ROY R, et al. Selection of a polyurethane membrane for the manufacture of ventricles for a totally implantable artificial heart: blood compatibility and biocompatibility studies. Artif Organs. 2000;24(11):879-888.
[21] SEO SJ, CHOI YJ, AKAIKE T, et al. Alginate/galactosylated chitosan/heparin scaffold as a new synthetic extracellular matrix for hepatocytes. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(1):33-44.
[22] DE BARTOLO L, CATAPANO G, DELLA VOLPE C, et al. The effect of surface roughness of microporous membranes on the kinetics of oxygen consumption and ammonia elimination by adherent hepatocytes. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1999;10(6):641-655.
[23] GRANT MH, MORGAN C, HENDERSON C, et al. The viability and function of primary rat hepatocytes cultured on polymeric membranes developed for hybrid artificial liver devices. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;73(3):367-375.
[24] HASIRCI V, BERTHIAUME F, BONDRE SP, et al. Expression of liver-specific functions by rat hepatocytes seeded in treated poly(lactic-co-glycolic) acid biodegradable foams. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(4):385-394.
[25] CONCARO S, NICKLASSON E, ELLOWSSON L, et al. Effect of cell seeding concentration on the quality of tissue engineered constructs loaded with adult human articular chondrocytes. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2008;2(1):14-21.
[26] SHI C, ZHU Y, RAN X, et al. Therapeutic potential of chitosan and its derivatives in regenerative medicine. J Surg Res. 2006;133(2):185-192.
[27] GRIFFON DJ, SEDIGHI MR, SENDEMIR-URKMEZ A, et al. Evaluation of vacuum and dynamic cell seeding of polyglycolic acid and chitosan scaffolds for cartilage engineering. Am J Vet Res. 2005;66(4):599-605.
[28] KARAGEORGIOU V, KAPLAN D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27):5474-5491.
[29] DU Y, HAN R, WEN F, et al. Synthetic sandwich culture of 3D hepatocyte monolayer. Biomaterials. 2008;29(3):290-301.
[30] DU Y, CHIA SM, HAN R, et al. 3D hepatocyte monolayer on hybrid RGD/galactose substratum. Biomaterials. 2006;27(33):5669-5680.
[31] UNDERHILL GH, CHEN AA, ALBRECHT DR, et al. Assessment of hepatocellular function within PEG hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2007;28(2):256-270.
[32] NONAKA H, ISE H, SUGIHARA N, Et al. Development of highly functional long-term culture method of liver slice embedded in agarose gel for bioartificial liver. Cell Transplant. 2003;12(5):491-498
[33] LIU TSANG V, CHEN AA, CHO LM, et al. Fabrication of 3D hepatic tissues by additive photopatterning of cellular hydrogels. FASEB J. 2007;21(3):790-801.
|