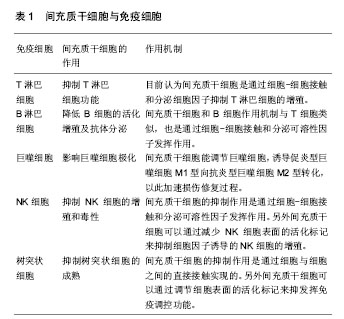
| [1] Dazzi F, Krampera M. Mesenchymal stem cells and autoimmune diseases. Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2011; 24(1):49-57.[2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.[3] Friedenstein AJ, Deriglasova UF, Kulagina NN, et al. Precursors for fibroblasts in different populations of hematopoietic cells as detected by the in vitro colony assay method. Exp Hematol. 1974;2(2):83-92.[4] Castro-Manrreza ME, Montesinos JJ. Immunoregulation by mesenchymal stem cells: biological aspects and clinical applications. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:394917.[5] Le Blanc K, Rasmusson I, Sundberg B, et al. Treatment of severe acute graft-versus-host disease with third party haploidentical mesenchymal stem cells. Lancet. 2004; 363(9419):1439-1441.[6] Ma S, Xie N, Li W, et al. Immunobiology of mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(2):216-225.[7] Krampera M. Mesenchymal stromal cells: more than inhibitory cells. Leukemia. 2011;25(4):565-566.[8] Li W, Ren G, Huang Y, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells: a double-edged sword in regulating immune responses. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(9):1505-1513.[9] English K. Mechanisms of mesenchymal stromal cell immunomodulation. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013;91(1):19-26.[10] Bartholomew A, Sturgeon C, Siatskas M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells suppress lymphocyte proliferation in vitro and prolong skin graft survival in vivo. Exp Hematol. 2002; 30(1): 42-48.[11] Krampera M, Glennie S, Dyson J, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the response of naive and memory antigen-specific T cells to their cognate peptide. Blood. 2003;101(9):3722-3729.[12] Djouad F, Plence P, Bony C, et al. Immunosuppressive effect of mesenchymal stem cells favors tumor growth in allogeneic animals. Blood. 2003;102(10):3837-3844.[13] Di Nicola M, Carlo-Stella C, Magni M, et al. Human bone marrow stromal cells suppress T-lymphocyte proliferation induced by cellular or nonspecific mitogenic stimuli. Blood. 2002;99(10):3838-3843.[14] Najar M, Raicevic G, Fayyad-Kazan H, et al. Immune-related antigens, surface molecules and regulatory factors in human-derived mesenchymal stromal cells: the expression and impact of inflammatory priming. Stem Cell Rev. 2012; 8(4):1188-1198.[15] Ren G, Zhao X, Zhang L, et al. Inflammatory cytokine-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in mesenchymal stem cells are critical for immunosuppression. J Immunol. 2010;184(5):2321-2328.[16] Ren G, Zhang L, Zhao X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-mediated immunosuppression occurs via concerted action of chemokines and nitric oxide. Cell Stem Cell. 2008; 2(2):141-150.[17] Han X, Yang Q, Lin L, et al. Interleukin-17 enhances immunosuppression by mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(11):1758-1768.[18] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005; 105(4):1815-1822.[19] Qu X, Liu X, Cheng K, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit Th17 cell differentiation by IL-10 secretion. Exp Hematol. 2012;40(9):761-770.[20] Luz-Crawford P, Noël D, Fernandez X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells repress Th17 molecular program through the PD-1 pathway. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45272.[21] Duffy MM, Pindjakova J, Hanley SA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell inhibition of T-helper 17 cell- differentiation is triggered by cell-cell contact and mediated by prostaglandin E2 via the EP4 receptor. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41(10):2840-2851.[22] Rafei M, Campeau PM, Aguilar-Mahecha A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by inhibiting CD4 Th17 T cells in a CC chemokine ligand 2-dependent manner. J Immunol. 2009;182(10):5994-6002.[23] Ghannam S, Pène J, Moquet-Torcy G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit human Th17 cell differentiation and function and induce a T regulatory cell phenotype. J Immunol. 2010; 185(1):302-312.[24] Luz-Crawford P, Kurte M, Bravo-Alegría J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells generate a CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T cell population during the differentiation process of Th1 and Th17 cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(3):65.[25] Prevosto C, Zancolli M, Canevali P, et al. Generation of CD4+ or CD8+ regulatory T cells upon mesenchymal stem cell- lymphocyte interaction. Haematologica. 2007;92(7):881-888.[26] Corcione A, Benvenuto F, Ferretti E, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate B-cell functions. Blood. 2006;107(1):367-372.[27] Rosado MM, Bernardo ME, Scarsella M, et al. Inhibition of B-cell proliferation and antibody production by mesenchymal stromal cells is mediated by T cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(1): 93-103.[28] Tabera S, Pérez-Simón JA, Díez-Campelo M, et al. The effect of mesenchymal stem cells on the viability, proliferation and differentiation of B-lymphocytes. Haematologica. 2008;93(9): 1301-1309.[29] Augello A, Tasso R, Negrini SM, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal progenitor cells inhibit lymphocyte proliferation by activation of the programmed death 1 pathway. Eur J Immunol. 2005;35(5):1482-1490.[30] Rasmusson I, Le Blanc K, Sundberg B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells stimulate antibody secretion in human B cells. Scand J Immunol. 2007;65(4):336-343.[31] Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, et al. Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity. 2014;41(1):14-20.[32] Bernardo ME, Fibbe WE. Mesenchymal stromal cells: sensors and switchers of inflammation. Cell Stem Cell. 2013; 13(4):392-402.[33] Prockop DJ. Concise review: two negative feedback loops place mesenchymal stem/stromal cells at the center of early regulators of inflammation. Stem Cells. 2013;31(10): 2042-2046.[34] Melief SM, Schrama E, Brugman MH, et al. Multipotent stromal cells induce human regulatory T cells through a novel pathway involving skewing of monocytes toward anti-inflammatory macrophages. Stem Cells. 2013;31(9): 1980-1991.[35] Giunti D, Parodi B, Usai C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells shape microglia effector functions through the release of CX3CL1. Stem Cells. 2012;30(9):2044-2053.[36] Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295.[37] Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Becchetti S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-natural killer cell interactions: evidence that activated NK cells are capable of killing MSCs, whereas MSCs can inhibit IL-2-induced NK-cell proliferation. Blood. 2006;107(4):1484-1490.[38] Spaggiari GM, Capobianco A, Abdelrazik H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit natural killer-cell proliferation, cytotoxicity, and cytokine production: role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2008;111(3): 1327-1333.[39] Selmani Z, Naji A, Zidi I, et al. Human leukocyte antigen-G5 secretion by human mesenchymal stem cells is required to suppress T lymphocyte and natural killer function and to induce CD4+CD25highFOXP3+ regulatory T cells. Stem Cells. 2008;26(1):212-222.[40] Ramasamy R, Fazekasova H, Lam EW, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit dendritic cell differentiation and function by preventing entry into the cell cycle. Transplantation. 2007; 83(1): 71-76.[41] Chiesa S, Morbelli S, Morando S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells impair in vivo T-cell priming by dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(42):17384-17389.[42] Spaggiari GM, Abdelrazik H, Becchetti F, et al. MSCs inhibit monocyte-derived DC maturation and function by selectively interfering with the generation of immature DCs: central role of MSC-derived prostaglandin E2. Blood. 2009;113(26): 6576-6583.[43] Djouad F, Charbonnier LM, Bouffi C, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells inhibit the differentiation of dendritic cells through an interleukin-6-dependent mechanism. Stem Cells. 2007;25(8): 2025-2032.[44] Waterman RS, Tomchuck SL, Henkle SL, et al. A new mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) paradigm: polarization into a pro-inflammatory MSC1 or an Immunosuppressive MSC2 phenotype. PLoS One. 2010;5(4):e10088.[45] Kim N, Cho SG. Overcoming immunoregulatory plasticity of mesenchymal stem cells for accelerated clinical applications. Int J Hematol. 2016;103(2):129-137.[46] Yan H, Wu M, Yuan Y, et al. Priming of Toll-like receptor 4 pathway in mesenchymal stem cells increases expression of B cell activating factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;448(2):212-217.[47] Waterman RS, Henkle SL, Betancourt AM. Mesenchymal stem cell 1 (MSC1)-based therapy attenuates tumor growth whereas MSC2-treatment promotes tumor growth and metastasis. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45590.[48] Lazarus HM, Haynesworth SE, Gerson SL, et al. Ex vivo expansion and subsequent infusion of human bone marrow-derived stromal progenitor cells (mesenchymal progenitor cells): implications for therapeutic use. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1995;16(4):557-564.[49] Ball LM, Bernardo ME, Roelofs H, et al. Multiple infusions of mesenchymal stromal cells induce sustained remission in children with steroid-refractory, grade III-IV acute graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol. 2013;163(4): 501-509.[50] von Bonin M, Stölzel F, Goedecke A, et al. Treatment of refractory acute GVHD with third-party MSC expanded in platelet lysate-containing medium. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2009;43(3):245-251.[51] Müller I, Kordowich S, Holzwarth C, et al. Application of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in pediatric patients following allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2008;40(1):25-32.[52] Li X, Wang D, Liang J, et al. Mesenchymal SCT ameliorates refractory cytopenia in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48(4): 544-550. |
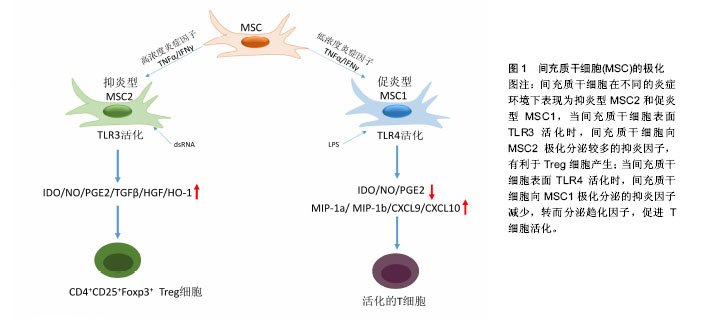
.jpg)
.jpg)