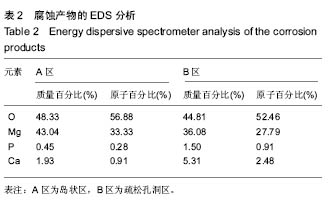
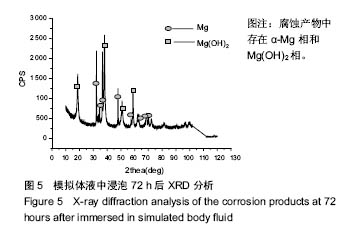
| [1]张广道. AZ31B生物可降解镁合金植入兔下颌骨生物学行为研究[D].沈阳:中国医科大学,2009.[2]郑玉峰,顾雪楠,李楠,等. 生物可降解镁合金的发展现状与展望[J]. 中国材料进展, 2011,30(4):30-43.[3]Tan L,Yu X, Wan P,et al. Biodegradable Materials for Bone Repairs:A Review. Journal of Materials Science & Technology. 2013; 29(6):503-513.[4]袁广银,章晓波,牛佳林. 新型可降解生物医用镁合金JDBM的研究进展[J].中国有色金属学报,2011,21(10):2476-2488.[5]赵虹,刘西伟,侯理达.医用镁合金生物降解行为研究进展[J].材料导报,2013,27(19):78-85.[6]汪园园,马爱斌,李玉华,等. 可吸收医用镁合金缝合线的研究进展[J].功能材料, 2015,46(S2):32-37.[7]赵辉,雷民. 新型可吸收镁合金支架在血管内应用及生物相容性[J].中国组织工程研究, 2016,20(8):1165-1170.[8]刘迎娟,余志永,韩彦龙. 力学环境对镁合金降解的定性影响[J]. 河北联合大学学报:自然科学版,2016,38(2):10-13.[9]Wang B,Gao J, Wang L,et al. Biocorrosion of coated Mg-Zn-Ca alloy under constant compressive stress close to that of human tibia. Materials Letters. 2012;70(3):174-176.[10]尹冬松. 医用镁合金力学性能与腐蚀行为[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2009.[11]叶新羽,陈民芳,由臣,等.Zr对Mg-Zn合金力学性能及体外降解行为的影响[J].金属热处理,2010,35(7):9-13.[12]崔彤,管仁国,刘超杰. Mg-4.0Zn-2.5Sr 合金 HA 涂层体外降解及生物相容性[J].材料热处理学报,2015,36(S2):150-154.[13]Gao JC, Wu S, Qiao LY, et al. Corrosion behavior of Mg and Mg-Zn alloys in simulated body fluid. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China. 2008; 18(3):588-592.[14]Niu J, Yuan G, Liao Y, et al. Enhanced biocorrosion resistance and biocompatibility of degradable Mg-Nd-Zn-Zr alloy by brushite coating. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2013;33(8): 4833-4841.[15]Gu X, Zheng Y, Cheng Y, et al. In vitro corrosion and biocompatibility of binary magnesium alloys. Biomaterials. 2009;30(4):484-498.[16]Liu N,Wang J,Wang L,et al. Electrochemical corrosion behavior of Mg–5Al–0.4Mn–xNd in NaCl solution. Corrosion Science. 2009; 51(6):1328-1333.[17]Luo TJ, Yang YS, Li YJ, et al. Influence of rare earth Y on the corrosion behavior of as-cast AZ91 alloy. Electrochimica Acta. 2009; 54(26):6433-6437.[18]Liu W, Cao F, Chang L,et al. Effect of rare earth element Ce and La on corrosion behavior of AM60 magnesium alloy. Corrosion Science. 2009; 51(6):1334-1343.[19]朱兆金. 新型医用可吸收镁合金 JDBM 的生物毒性、髓内降解及细菌学相关研究[D].苏州: 苏州大学, 2013.[20]冯晓伟,戚文军,黎小辉.生物医用挤压态Mg-Zn-Gd镁合金的组织与耐电化学腐蚀性能[J].中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2016,36(3): 267-272.[21]单玉郎,文九巴,姚怀. Gd 含量对 Mg-0.5Zn-0.4Zr-xGd生物镁合金性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报,2016,37(6):21-26.[22]冯晓伟,戚文军,黎小辉. Mg-Zn-Gd 合金的微观组织和力学性能[J]. 稀有金属, 2016,40(1):14-19.[23]程乐. Mg-Gd(Y)-Zn系多元合金相图计算和实验验证[D]. 西安:西安工业大学,2014.[24]郭连平,陈乐平,尹健,等. 锌含量对Mg-Gd-Zn 合金铸态组织和力学性能的影响[J].铸造技术,2013,34(2):129-131.[25]刘勇.自生准晶增强 Mg-Zn-Gd 基合金组织和力学行为的研究[D].上海:上海交通大学,2007.[26]Witte F, Kaese V, Haferkamp H,et al.In vivo corrosion of four magnesium alloys and the associated bone response.Biomaterials. 2005;26(17):3557-3563.[27]Witte F, Fischer J, Nellesen J, et al.In vitro and in vivo corrosion measurements of magnesium alloys.Biomaterials. 2006;27(7):1013-1018.[28]Li LC, Gao JC, Wang Y. Evaluation of cyto-toxicity and corrosion behavior of alkali-heat-treated magnesium in simulated body fluid. Surface & Coatings Technology. 2004; 185(1):92-98. |
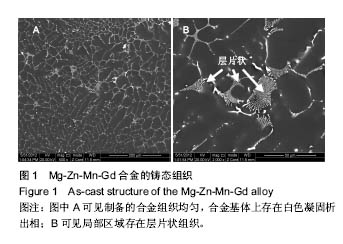
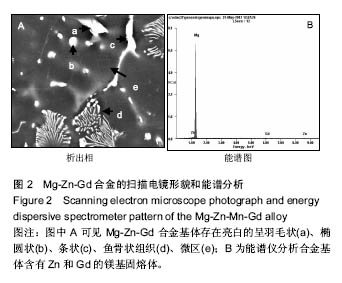
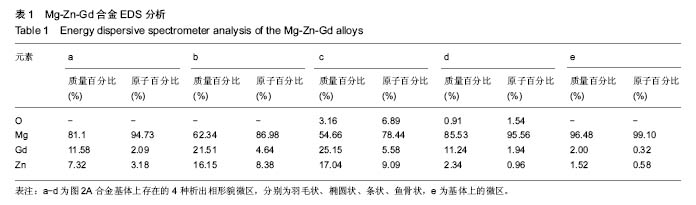
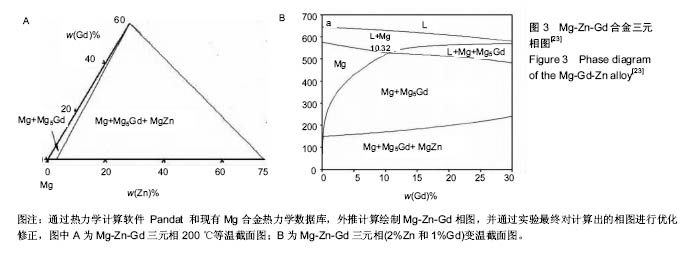
.jpg)

.jpg)