| [1]Lekholm U. Surgical considerations and possible shortcomings of host sites. J Prosthet Dent. 1998;79(1):43-48.[2]Vidyasagar L, Salms G, Apse P, et al. Investigation of Initial Implant Stability with Different Dental Implant Designs. A Pilot Study in Pig Ribs Using Resonance Frequency Analysis. Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology. 2004; 22(18):3996-3998.[3]方开泰.正交与均匀试验设计[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2001: 85-90.[4]王晓洁, 罗教明, 杨立, 等.种植体周围骨内应力分布的三维有限元分析[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志, 2005, 21(5): 592-595.[5]谢峰, 雷小宝, 沈维蕾, 等. 基于ANSYS分析与正交试验法的压力机身轻量化设计[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2008, 20(22):6054- 6057.[6]曾祥龙. 现代口腔正畸学诊疗手册[M] .北京: 北京医科大学出版社, 2000: 65-66.[7]张君孝,乔鸣芳. 280例正畸初诊患者下颌平面角观察研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2008,22(2):161-163.[8]宿玉成. 现代口腔种植学[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社, 2004: 96.[9]Bondevik O, Espeland L, Stenvik A. Dental arch changes from 22 to 43 years of age: are they different in individuals with high versus low mandibular plane angle. Eur J Orthod. 2015; 37(4):367-372. [10]Uehara S, Maeda A, Tomonari H, et al. Relationships between the root-crown ratio and the loss of occlusal contact and high mandibular plane angle in patients with open bite. Angle Orthod. 2013;83(1):36-42. [11]Kurosawa M, Ando K, Goto S. Class II Division 1 malocclusion with a high mandibular plane angle corrected with 2-phase treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2009;135(2):241-251. [12]Griffies JM, Meyers CE. Treatment of a Class I bimaxillary protrusive malocclusion with a high mandibular plane angle: An American Board of Orthodontics case report. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000;117(1):60-67.[13]Frank CA.An American Board of Orthodontics case report: the orthodontic-surgical correction of a Class I malocclusion with high mandibular plane angle, bimaxillary protrusion, and vertical maxillary excess.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1993;104(3):285-297.[14]郭军,张锡忠,关晓航,等.两种方法远移上颌磨牙颅颌面硬软组织变化比较[J].中国美容医学,2013,22(15):1626-1628.[15]李建军,施生根. 微种植支抗关闭正畸拔牙间隙对下颌垂直向位置的影响[J].中国医药导报,2013,10(12):14-15,18.[16]曾琳,张蓓,杨狄烽,等.种植体支抗载荷部位对尖牙和磨牙应力分布的影响[J].广东牙病防治,2011,19(11):574-578.[17]宋元玲,张惠芳,任辉,等.微螺钉种植体在正畸支抗中的稳定性研究[J].中国误诊学杂志,2010,10(15):3529-3531.[18]宋元玲,张惠芳,任辉[J].微型种植体支抗稳定性的临床研究临床口腔医学杂志,2010,26(7):423-425.[19]罗宁洁,李自力,伊彪,等.口内入路髁突切除同期正颌术后颞下颌关节结构变化的影像学观察[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2016,51(6): 350-356.[20]荆璇,武秀萍.垂直骨面型对正畸诊断治疗的影响[J].中国药物与临床,2016,16(6):833-835.[21]陈向飒,肖丹娜,高辉.女性骨性Ⅱ类高角患者(牙合)平面与上下颌骨矢状向位置关系的相关性研究[J].口腔医学, 2015,35(5): 379-382.[22]陈向飒,肖丹娜,高辉.骨性Ⅱ类高角患者(牙合)平面与下颌骨位置的相关性研究[J].天津医科大学学报,2014,20(1):54-56.[23]王思.上颌前方牵引对恒牙初期不同下颌平面角Ⅲ类错(牙合)的临床疗效评价[J].黑龙江医学,2014,38(9):1058-1059.[24]罗伟民,杨玉茹.高下颌平面角和低下颌平面角女性患者牙齿移动的观察分析[J].中国美容医学,2010,19(8):1204-1206.[25]王竞鹏,柳大烈,陈兵,等.下颌角整形术安全平面的解剖学研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2010,21(3):184-186.[26]张君孝,乔鸣芳.280例正畸初诊患者下颌平面角观察研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2008,22(2):161-163.[27]王春玲,赵艳红,郭杰,等.正畸治疗骨性Ⅲ类错(牙合)对下颌平面角小的成年女性患者颞下颌关节的影响[J].中华口腔医学杂志, 2007,42(8):471-474.[28]钱文娴,秦天牧.不同下颌平面角患者对Twin-block矫治器的反应[J].口腔医学,2007,27(12):626-628.[29]石勰,张端强,许游于,等.安氏Ⅱ类Ⅰ分类病例下颌平面角与后牙倾斜度关系的研究[J].福建医药杂志,2003,25(1):50-51.[30]苏峰梅,张晓真,赵毅,等.上颌无牙颌种植固定修复中种植体位置对应力分布的影响[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志, 2016,14(2): 104-108.[31]黄美慧,姜闻博,张翕,等.牙种植体表面多孔层厚度对骨界面应力分布的影响[J].口腔材料器械杂志,2016,25(02):61-65,85.[32]杨炎忠,田小华,周延民.氧化锆角度基台及种植体周骨壁应力分布的有限元分析[J].上海口腔医学,2015,24(4):447-450.[33]邢维斌,郑淑贤,杨适宜.下颌平面角影响种植体应力分布的有限元分析[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2016,34(0): 502-505.[34]曾琳,张蓓,杨狄烽,等.种植体支抗载荷部位对尖牙和磨牙应力分布的影响[J].广东牙病防治 2011,19(11):574-578.[35]王芳,胡敏,李洪,等.种植体支抗辅助快速扩大上颌的三维有限元分析[J].吉林大学学报:医学版,2010,36(4):745-748.[36]王璐,李任,温黎明,等.正畸治疗伴上中切牙特发性牙根吸收及尖牙阻生1例[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(1):44-45,46.[37]胡玉乾,李方研,吕秀梅,等.正畸治疗中拔除第一前磨牙对下颌第三磨牙轴倾度的影响[J].中国现代医生,2016,54(30):55-58.[38]胡玉乾,孙竹萍,张鹏飞.青少年原发性关节炎患者与正畸患者的颌面形态特点的对比研究[J].中国现代医生,2016,54(28):72-75. |
.jpg)
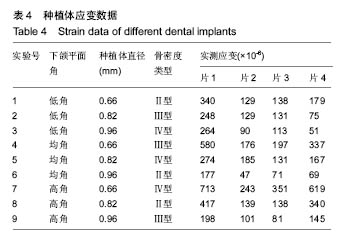

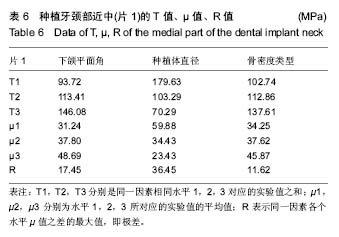
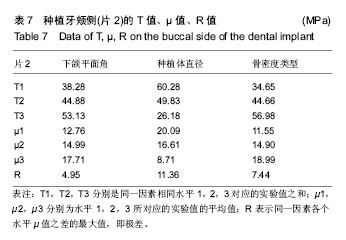
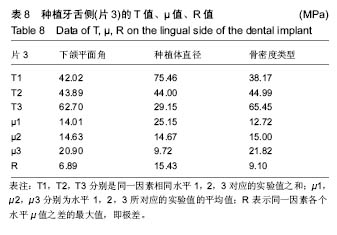
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)