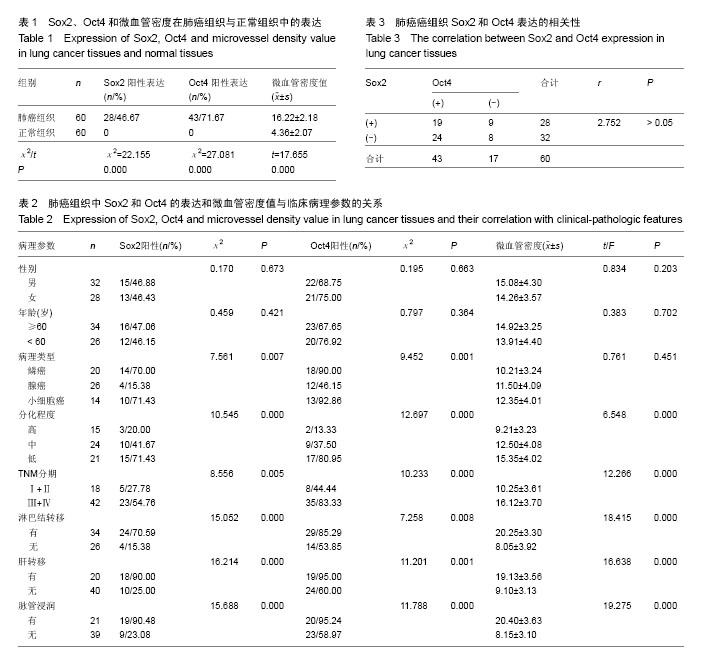
| [1] 支修益,石远凯,于金明.中国原发性肺癌诊疗规范(2015年版)[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2015,37(1):67-78.[2] 聂立功.肺癌的筛查--机遇与挑战[J].中国肺癌杂志,2015,18(12): 721-724.[3] 吉丛,喻长远,陈志华.肺癌诊治和预后判断分子标志物miRNA[J].中国肿瘤临床,2014,41(20):1333-1336.[4] 孙虎,张俊萍.晚期非小细胞肺癌靶向治疗研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2016,10(2):264-269.[5] 刘哲亮,邬娇,王林纤,等.人肺鳞癌来源肺癌干细胞原代培养:数量及功能变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(32):5172-5176.[6] Cojoc M,Mabert K,Muders MH, et al. A role for cancer stem cells in therapy resistance: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Semin Cancer Biol.2015;31:16-27.[7] Garofalo M,Croce CM.Role of microRNAs in maintaining cancer stem cells.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2015;81(21):53-61.[8] Li M, Zhang BG, Zhang ZG, et al. Stem cell-like circulating tumor cells indicate poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014(10):981261.[9] 李月雅,李凯.Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路对肿瘤干细胞作用的研究进展[J].山东医药,2016,26(9):98-100.[10] Chou MY, Hu FW, Yu CH, et al. Sox2 expression involvement in the oncogenicity and radiochemoresistance of oral cancer stem cells. Oral Oncol. 2015;51(1):31-39.[11] Wang L, Yang H, Lei Z, et al. Repression of TIF1γ by SOX2 promotes TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 2016;35(7):867-877.[12] Aksoy I, Jauch R, Chen J, et al. Oct4 switches partnering from Sox2 to Sox17 to reinterpret the enhancer code and specify endoderm. EMBO J. 2013;32(7):938-953.[13] Shin J, Kim TW, Kim H, et al. Aurkb/PP1-mediated resetting of Oct4 during the cell cycle determines the identity of embryonic stem cells. Elife. 2016;5:e10877.[14] Bou G, Liu S, Guo J, et al. Cdx2 represses Oct4 function via inducing its proteasome-dependent degradation in early porcine embryos. Dev Biol. 2016;410(1):36-44.[15] Reimer A, Vasilevich A, Hulshof F, et al. Scalable topographies to support proliferation and Oct4 expression by human induced pluripotent stem cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6: 18948.[16] Weidenr N. Current pathologic methods for measruing intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancr Res Treat.1996;36(10): 169-180.[17] 程继荣,徐虓,王淑琴,等.肺癌组织CD31、CD34及CD105标记的微血管密度的临床意义[J].中国癌症杂志,2010,20(8):638-641.[18] Jordan CT, Guzman ML, Noble M. Cancer stem cells. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(12):1253-1261.[19] Tomellini E,Touil Y,Lagadec C, et al. Nerve growth factor and proNGF simultaneously promote symmetric self-renewal, quiescence, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition to enlarge the breast cancer stem cell compartment.Stem Cells. 2015;33(2):342-353.[20] Park HJ,Oh, JS,Chang JW, et al.Proton Irradiation Sensitizes Radioresistant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells by Modulating Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-mediated DNA Repair.Anticancer Res.2016;36(1):205-212.[21] 马远,冯军,吴灵芝,等.CD133+肺癌干细胞中基质金属蛋白酶9 和缺氧诱导因子2ɑ的表达及其病理学机制[J].中华医学杂志, 2015,95(32):2607-2611.[22] Lapidot T, Sirard C, Vormoor J, et al. A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature. 1994;367(6464):645-648.[23] Al-Hajj M, Wicha MS, Benito-Hernandez A, et al. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(7):3983-3988.[24] Zhou K, Xia M, Tang B, et al. Isolation and comparison of mesenchymal stem cell?like cells derived from human gastric cancer tissues and corresponding ovarian metastases. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13(2):1788-1794.[25] Lambert AW, Wong CK, Ozturk S, et al. Tumor Cell-Derived Periostin Regulates Cytokines That Maintain Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2016;14(1):103-113.[26] Singh AK, Arya RK, Maheshwari S, et al. Tumor heterogeneity and cancer stem cell paradigm: updates in concept, controversies and clinical relevance. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(9):1991-2000.[27] Krawczyk N, Meier-Stiegen F, Banys M, et al. Expression of stem cell and epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in circulating tumor cells of breast cancer patients. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:415721.[28] Li M, Zhang B, Zhang Z, et al. Stem cell-like circulating tumor cells indicate poor prognosis in gastric cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:981261.[29] Kim CF, Jackson EL, Woolfenden AE, et al. Identification of bronchioalveolar stem cells in normal lung and lung cancer. Cell. 2005;121(6):823-835.[30] Wang X, Liu Y, Zhou K, et al.Isolation and characterization of CD105+/CD90+ subpopulation in breast caner MDA-MB-231 cell line.Int J Clin Exp Pathol.2015;8(5):5105-5112.[31] Zhao X,Ran YL,Yu L,et al.In human hepatocellular carcinoma tissue isolation and culture of tumor stem cell-like cells.Chin J Cancer Biother.2009;16(5):436-441.[32] Xie LX, Sun FF, He BF, et al. Rapamycin inhibited the function of lung CSCs via SOX2. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(4):4929-4937.[33] Bass AJ, Watanabe H, Mermel CH, et al. SOX2 is an amplified lineage-survival oncogene in lung and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Nat Genet. 2009;41(11):1238- 1242.[34] Chen S, Xu Y, Chen Y, et al. SOX2 gene regulates the transcriptional network of oncogenes and affects tumorigenesis of human lung cancer cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36326.[35] Zhang X, Yu H, Yang Y, et al. SOX2 in gastric carcinoma, but not Hath1, is related to patients' clinicopathological features and prognosis.J Gastrointest Surg. 2010;14(8):1220-1226.[36] Vural B, Chen LC, Saip P, et al. Frequency of SOX Group B (SOX1, 2, 3) and ZIC2 antibodies in Turkish patients with small cell lung carcinoma and their correlation with clinical parameters. Cancer. 2005;103(12):2575-2583.[37] Lengerke C, Fehm T, Kurth R, et al. Expression of the embryonic stem cell marker SOX2 in early-stage breast carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:42.[38] 顾晓荔.SOX2,SOX17及β-catenin在宫颈癌组织中的表达及意义[D]. 郑州:郑州大学,2012.[39] 张燕平,李宁,邓文英,等.干细胞标志物SOX-2、β-catenin表达与胃癌术后复发转移关系[J].中国癌症杂志,2014,24(9):684-689.[40] 梁洪享,钟竑,罗勇,等.肿瘤干细胞标志物CD133,CD44, SOX2,OCT4,ALDH1在非小细胞肺癌组织中的表达及临床意义[J].肿瘤防治研究,2013,40(12):1138-1142.[41] 李文鹏,罗维远,徐毅,等.下调 Oct4基因表达对 MDA-MB-231乳腺癌干细胞生物学特性的影响[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2015,37(4): 251-254.[42] Kaufhold S, Garbán H, Bonavida B. Yin Yang 1 is associated with cancer stem cell transcription factors (SOX2, OCT4, BMI1) and clinical implication. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35:84.[43] Kobayashi I, Takahashi F, Nurwidya F, et al. Oct4 plays a crucial role in the maintenance of gefitinib-resistant lung cancer stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016; 473(1):125-132.[44] Monk M, Holding C. Human embryonic genes re-expressed in cancer cells. Oncogene. 2001;20(56):8085-8091.[45] 郝美玲,李春辉.胃癌组织 Oct4表达变化及意义[J].山东医药, 2016,56(40):124-126.[46] 张超,任静文,梁迪,等.OCT4与EMT相关因子在浸润性乳腺癌组织中的表达及其临床意义[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2016, 23(4):525-530.[47] 董翠梅,涂江江,陶利英,等.非小细胞肺癌组织中OCT4和miRNA-155的表达及其与临床病理特征的关系[J].肿瘤防治研究,2013,40(8):776-779.[48] Li X, Wang J, Xu Z, et al. Expression of Sox2 and Oct4 and their clinical significance in human non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(6):7663-7675.[49] Sodja E, Rijavec M, Koren A, et al. The prognostic value of whole blood SOX2, NANOG and OCT4 mRNA expression in advanced small-cell lung cancer. Radiol Oncol. 2016;50(2): 188-196. [50] Saito S, Onuma Y, Ito Y, et al. Possible linkages between the inner and outer cellular states of human induced pluripotent stem cells. BMC Syst Biol. 2011;5 Suppl 1:S17.[51] Rizzino A, Wuebben EL. Sox2/Oct4: A delicately balanced partnership in pluripotent stem cells and embryogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1859(6):780-791.[52] Yoon HI, Park KH, Lee EJ, et al. Overexpression of SOX2 Is Associated with Better Overall Survival in Squamous Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Adjuvant Radiotherapy. Cancer Res Treat. 2016;48(2):473-482. [53] Pan X, Cang X, Dan S, et al. Site-specific Disruption of the Oct4/Sox2 Protein Interaction Reveals Coordinated Mesendodermal Differentiation and the Epithelial- Mesenchymal Transition. J Biol Chem. 2016;291(35):18353-18369. |
.jpg)
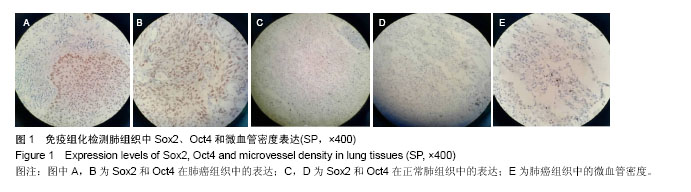
.jpg)